O Phases diagram is a graph used to indicate temperature conditions and pressure needed to get a substance in a certain physical state (solid, liquid or gaseous).
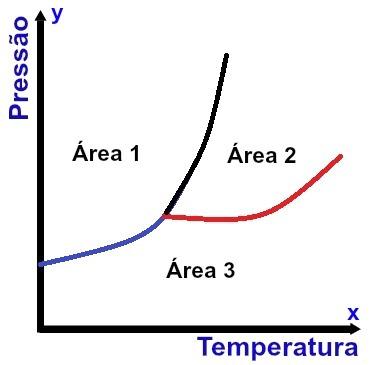
Representation of a phase diagram
The x-axis (horizontal) contains temperature values, and the y-axis (vertical) contains pressure values. In addition, there are three curves connected to a single point (called a triple point), dividing the graph into three well-defined areas, as can be seen in the diagram shown above.
In addition to indicating the conditions for the substance to be in a specific physical state, the Phases diagram indicates the conditions for any change in physical state to occur.
Changes in physical status are:
Fusion: transition from solid to liquid state;
Solidification: transition from liquid to solid state;
Vaporization: transition from liquid to gaseous state;
Condensation: transition from gas to liquid state;
Sublimation: transition from solid to gaseous state;
Resublimation: transition from gas to solid state.
a) Regions
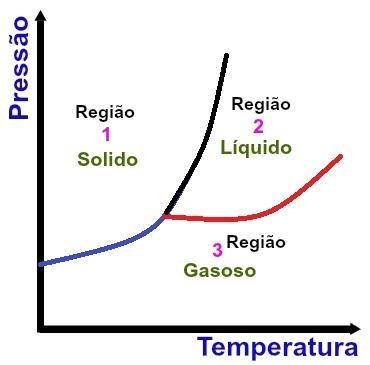
Fundamental regions of a phase diagram
Region 1
Region 1 indicates the temperature and pressure conditions under which we find the substance in the solid state.
Region 2
Region 2 indicates the temperature and pressure conditions in which we find the substance in the liquid state.
Region 3
Region 3 indicates the temperature and pressure conditions in which we find the substance in the gaseous state.
b) Curves

Curves present in a phase diagram
Curve A (purple curve)
It is the curve that divides the solid and gaseous region of the phase diagram and is commonly called the resublimation curve. Each point located on curve 1 indicates that we have a certain substance coexisting in solid and gaseous states.
In addition to indicating coexistence, curve 2 also indicates the temperature and pressure conditions for the transformation of a substance from a liquid to a gaseous state.
Curve B (black curve)
It is the curve that divides the solid and liquid region of the phase diagram and is commonly called the solidification curve. Each point located on curve 2 indicates that we have a certain substance coexisting in a solid and a gaseous state.
In addition to indicating coexistence, curve 2 also indicates the temperature and pressure conditions for the transformation of a substance that is in a liquid state to a solid state.
Curve C (red curve)
It is the curve that divides the solid and gaseous region of the phase diagram and is commonly called the condensation curve. Each point located on curve 3 indicates that we have a certain substance coexisting in a solid and a gaseous state.
In addition to indicating coexistence, curve 3 also indicates the temperature and pressure conditions for the transformation of a substance from a solid to a gaseous state and vice versa.
c) The triple point
The point where the three curves in the phase diagram meet is called the triple point. At this point, we have the temperature value and the pressure value at which we find the substance in the solid, liquid and gaseous state at the same time.

d) Physical state changes in the phase diagram
In the phase diagram below, we have 6 arrows that indicate the direction of changes in physical states of a substance.

Arrow 1: indicates the merger
Arrow 2: indicates solidification
Arrow 3: indicates vaporization
Arrow 4: indicates condensation
Arrow 5: indicates sublimation
Arrow 6: indicates resublimation
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/quimica/o-que-e-diagrama-fases.htm
