You gases they are fluids which, unlike liquids, occupy all the available space of the container where they are confined. The molecules that make up the gases are free to move and interact with each other and with the walls of the container.
O perfect or ideal gas it is an idealized gas, has particular characteristics and complies with the general gas law and the Clapeyron's equation.
Characteristics of perfect gases
There is not gravitational interaction between molecules;
At collisions among the molecules are perfectly elastic, that is, there is total conservation of kinetic energy;
Molecules exhibit disorderly movement and speeds that depend directly on the gas temperature value;
The proper volume of each molecule is completely insignificant compared to the total volume of the gas.
state variables
Pressure, temperature and volume are the scalar physical quantities that characterize a gas. These quantities are called state variables and they maintain relations of proportionality.
THE boyle's law
determines that the relationship between pressure and volume of a gas is inversely proportional. The greater the pressure on the molecules, the less space they occupy.THE Gay-Lussac lawdetermines that the relationship between the volume and temperature of a gas is directly proportional. The higher the temperature of a gas, the greater the agitation of the molecules, which will tend to move apart, increasing the space occupied by them.
Charles' law determines that the relationship between pressure and temperature of a gas is directly proportional. The higher the temperature of a gas, the greater the molecular agitation. Thus, the incidence of collisions between the molecules and the walls of the container increases, making the pressure of the gas greater.
THE clapeyron equation it synthesizes the three laws presented above and determines a single relationship between the state variables.
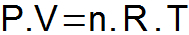
P = gas pressure (atm or N/m2);
V = gas volume (L or m3);
n = number of moles;
R = universal gas constant (0.082 atm.l/mol. K or 8.31 J/mol. K);
T = gas temperature (K).
Ideal gas in nature
Nature does not produce gases that have the characteristics of a perfect gas. The ideal gas is a theoretical and useful model for understanding the behavior of gases in face of changes in their characteristics.
By Joab Silas
Graduated in Physics
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/fisica/o-que-e-gas-perfeito.htm
