The hydration of alkynes is a reaction of addition of water molecules in an acidic medium in the presence of the catalyst HgSO4.
These reactions are important because through them it is possible to obtain aldehydes and ketones.
Aldehyde compounds are organic compounds that have a carbonyl group attached to a hydrogen. Ketones, on the other hand, have a carbonyl group between two carbons, as shown by their functional groups below:
Aldehydes: Ketones:
OO
║║
H ─ Ç ─ C ─ Ç ─C
If the alkyne that undergoes the hydration reaction is ethane, we will have the formation of the aldehyde ethanal. Initially, an intermediate compound is formed that has the generic name of enol.
This enol is a very unstable compound that undergoes molecular rearrangement because of the high electronegativity of oxygen causes the attraction of electrons from the double bond of carbon, which is a weak and easy bond. move. In this way, the enol and the aldehyde will coexist in dynamic equilibrium. This phenomenon is a case of aldoenolic tautomeria:
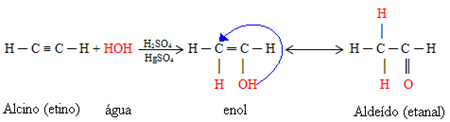
However, if any other alkyne with three carbons or more is used, the corresponding ketones will be formed. This is because this reaction follows the Markovnikov's Rule, which says the hydrogen in water will add to the triple bond carbon that has the most hydrogens bonded to it, while the OH in water will bond to the triple bond minus carbon hydrogenated.

Propanone is acetone, used to remove nail polish.
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/hidratacao-alcinos.htm

