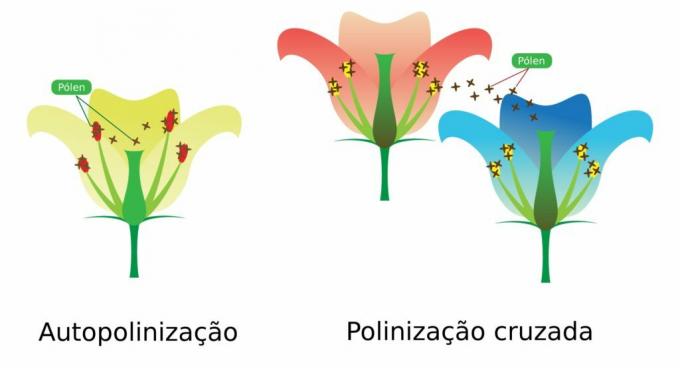
What is pollination? A pollination is the sexual reproduction of seed plants.
It is through this process that the male gamete (present in the pollen grain) reaches the stigma from a flower of the same species, which may be the same flower that produced the pollen grain (self-pollination) or another flower, to only then find the female gamete.
see more
Biology teacher fired after class on XX and XY chromosomes;…
Cannabidiol found in common plant in Brazil brings new perspective…
For the pollination process to occur, plants need aids biotic, that is, of other living beings or even of abiotic factors, that is, environmental factors such as water and wind.
You must have noticed the variety of plants that exist, especially when it comes to the angiosperms, the plants that have flowers. This happens because there are several types of pollination and each one needs the plant to adapt for it to occur.
Types of pollination and theadaptations to attract the pollinator
- anemophily: through the wind
These plants have anthers with elongated and flexible filaments, which oscillate with the wind. The stigmas are large and feathery to facilitate the reception of pollen grains that are produced in large quantities.
- hydrophilicity: through the water
It is usually associated with aquatic plants, pollination can take place on the surface or underwater.
- Artificial: with human intervention
This type of pollination does not require many plant specializations.
- entomophilia: by insects
In general, plants with this type of pollination have blue or yellow pigmented petals, which is the color spectrum that insects see. They also produce aromatic substances because insects are animals with a well-developed sense of smell. It is one of the most common types among Angiosperms.
- melitophilia which is pollination by bees and wasps, is a type of entomophily.
The number of food plants pollinated by bees is very high, so if bees were extinct, it would cause food shortages and, consequently, hunger across the planet.
- Cantharophilia: aid of beetles, is also a type of entomophilia.
Plants pollinated by beetles do not invest in colorful flowers, they always have unattractive colors because these animals do not have well-developed eyesight. However, beetles have a very good smell and, therefore, the flowers have a very strong odor, similar to that of food in the process of fermentation.
- Phalenophilia: by moths and butterflies, it is also a type of entomophilia.
The nectar in these plants is only available to animals with long mouthparts, such as moths and butterflies. In general, they are paler in color than those pollinated by moths, due to the nocturnal habits of these animals.
- ornithophilia: through birds
Plants pollinated by birds generally have no odor, but are quite colorful and have a lot of nectar to attract these animals.
- Chiropterophilia: by bats
As bats are nocturnal, these plants are not very colorful, but they produce a lot of nectar and a strong odor.
See too:
- What are the parts of plants?
- Reproduction of plants – See how this process occurs in nature


