THE plasma membrane it is a structure formed by two layers of phospholipids present in all existing cells. Through this bilayer, proteins are inserted and some function as true pores in the membrane and others act as receptors. Thanks to these characteristics, the membrane has the ability to select what enters and what leaves the cell, thus ensuring the maintenance of the intracellular environment.
Substances enter and leave the cell in different ways and transport across the membrane can be classified into two groups: passive and active.
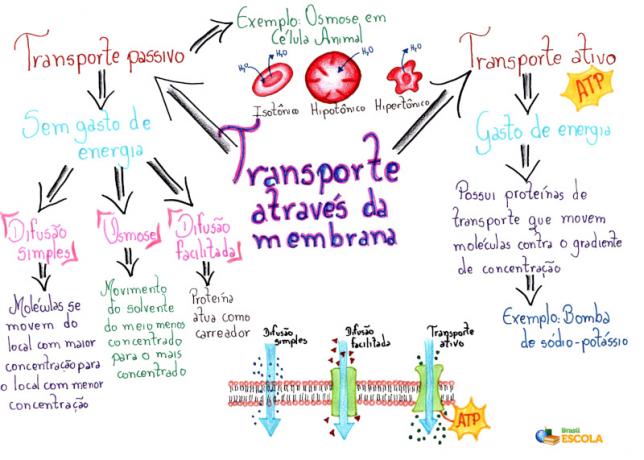
Passive transport: is one in which there is no energy wasted during the process.
Active transport: is the one in which energy is spent during the process.
→ Mind Map: Transport Across the Membrane
*To download the mind map in PDF, Click here!
→ passive transport
We can classify passive transport into three types: diffusion simple, easy diffusion and osmosis.
-
simple broadcast
In simple diffusion, molecules and ions are transported naturally from the place where they are in greater concentration to the place where they are present in less quantity
. In this case, we say that there is a movement of substances in the direction of the concentration gradient. Oxygen and carbon dioxide cross the plasma membrane in this way. -
Osmosis
Osmosis is nothing more than a special type of broadcast. In this type of transport, the solute does not move, but the solvent, which, in this case, is water. It takes place between two aqueous media that are separated by a semi-permeable membrane. Water diffuses from the least concentrated medium to the most concentrated medium until equilibrium is reached. Water can also cross the membrane through the presence of channels called aquaporins.
Osmosis can be observed in the region of root hairs, which have a higher concentration of solutes than soil water. This difference in concentration causes the water enters the inside of the roots and be taken later to the rest of the plant.
-
Diffusion facilitated
Facilitated diffusion is one in which there is a membrane protein that acts as a carrier. This transport takes place in favor of the concentration gradient, but impermeable substances are involved, hence the need for binding to a carrier protein. These proteins present a binding site so that the solute can be transported. After binding, they undergo a modification that causes the solute to be carried around. It is also worth noting that facilitated diffusion can occur through unspecific transporters.
→ Active transport
Active transport takes place with the expenditure of energy and, just as in facilitated diffusion, it takes place with the help of carrier proteins, which are called pumps. Unlike diffusion, however, transport occurs against the concentration gradient. The best known example of active transport is the sodium and potassium pump.
By Ma. Vanessa dos Santos
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/biologia/transporte-ativo-passivo.htm
