According to the principles of light propagation, we saw that the first of these principles says that in a homogeneous, isotropic and transparent medium, light propagates in a straight line. The other two principles are: principle of independence of rays it's the reversibility principle.
In order to prove that the principle of straight light propagation is valid, we have the orifice darkroom, which is basically made up of a box with opaque and black walls internally, completely closed, with the exception of a small hole made in one of the walls, through which the light penetrates.
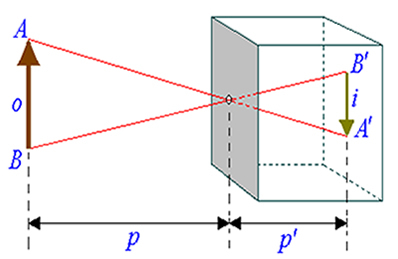
Let's see the diagram in the figure below, in it we have an AB object, luminous or illuminated, which is placed in front of the wall that has the hole. The light rays that depart from the object and pass through the hole project, on the wall opposite the hole, a figure A’B’, similar to the object, but inverted. This figure is called Image of object AB.
The fact that the image is similar in shape to the object and is inverted highlights the straight propagation of light.
The image projected on the chamber wall can be seen by an outside observer if this wall is, for example, made of tracing paper. The image can be registered internally, by placing a film or photographic paper in the region where it is formed. For this reason, the orifice darkroom is sometimes called a rudimentary camera.
Historically, we can say that the capture and registration of images was possible after the creation of the hole darkroom.
It turns out that in current cameras, as well as in our eyes, the images that are formed have the same characteristics as those obtained with the dark chamber: All are upside down and have right and left sides inverted when viewed from behind the bulkhead.
According to the figure above, the triangles ABO and A’B’O’ are similar, we can relate the heights AB and A’B’ of the object and the image at distances p (from the object to the camera) and p’ (from the image to the wall with hole). So we have:

Let's see an example of the application of the mathematical concepts contained in the object and image relationship formed in a darkroom.
On a very sunny day, a man and a pole project, on the ground, shadows equal in length to 2 meters and 4.8 meters, respectively. Determine the height of the pole in meters, knowing that the height of the man is 1.6 meters. Consider the pole and man standing on the horizontal ground.
Resolution: From the equation above, which relates similarity of triangles, we have:
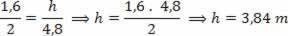
By Domitiano Marques
Graduated in Physics
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/fisica/camara-escura-orificio.htm


