The film "Oppenheimer" opens tomorrow, July 20, in theaters. The production tells the story of the physicist who invented the atomic bomb in 1945, Julius Robert Oppenheimer.
The feature film focuses on the physicist's personal life alongside his professional life. But the film especially portrays Oppenheimer's performance directing the Manhattan Project, in which he worked together with other scientists to develop the atomic bomb, during World War II.
The first atomic bomb was dropped in 1945 on the Japanese city of Hiroshima and killed more than 70,000 people. Three days later, the second bomb was dropped on the city of Nagasaki, also in Japan, and killed more than 40,000 people.
The physique is played by actor Cillian Murphy, from the series Peaky Blinders. Film critics are betting that he should win the Oscar for best actor. The director of the feature, Christopher Nolan, is also quoted to take a statuette.
Who was Oppenheimer?
Julius Robert Oppenheimer was a physicist who was born in 1904 in New York City, United States. He is known in history as "the father of the atomic bomb".
Years later, according to the biography of the scientist Oppenheimer, he even showed regret for having participated in the invention of the atomic bomb, defending the control of nuclear weapons in the world.
Studies indicate that the physicist dedicated his last years of life to reflecting on the connection between science and society. The creator of the atomic bomb had episodes of depression, even saying:
"Now I have become death, the destroyer of worlds," said Oppenheimer, the creator of the atomic bomb.
Oppenheimer died in 1967, aged 62, in Princeton, USA, from throat cancer.
What was the Manhattan project?
The Manhattan Project portrayed in the movie "Oppenheimer" was a project developed by the United States, which aimed to build the first atomic bombs in history, in the period of World War II World.
Scientists, engineers, military personnel and several other professionals were mobilized in the Manhattan Project from August 13, 1942 to August 15, 1947.
Learn more about the Manhattan Project
What is the atomic bomb?
The atomic bomb, or nuclear bomb, is an explosive weapon with a great power of destruction, due to the large amount of energy it releases. This bomb works through the nuclear reaction process of fission of atoms, which enables a large release of energy from a small amount of matter.
Do not stop now... There's more after the publicity ;)
What is the history of the atomic bomb?
The history of the atomic bomb is linked to the Second World War. With the advance of the world conflict, the Americans began a race against Nazi Germany to create the first nuclear weapon.
The Americans' project to develop more powerful weapons to cause greater impacts on adversaries was called “Manhattan Project”, which lasted from 1942 until 1945, when the first test of a nuclear fission device was carried out.
Where were the first atomic bombs dropped?
The first atomic bombs were dropped in 1945 on Japan. See below for days and locations:
-1st atomic bomb: August 6, 1945, on the city of Hiroshima
-2nd atomic bomb: August 9, 1945, in the city of Nagasaki
These bombs became known as Little boy and Fat man, because of their shapes and the explosion capacity of each one.
Read more about the bombs of Hiroshima and Nagasaki
How does an atomic bomb work?
The operation of nuclear bombs is similar, differing only by the element used in the composition. The main elements that make up the bombs are uranium-235 and plutonium-239. The nuclear bomb works on the principle of nuclear fission, which is the splitting of an unstable atom by bombarding it with particles such as a neutron. This generates a chain reaction that causes the nuclear fission of the other atoms present.
Check also: what are the types of atomic bombs?
What to study about the atomic bomb?
Studies on the atomic bomb involve several disciplines, including physics, chemistry and history. Professors explain what is important to study about the atomic bomb and what can fall into selective processes, such as entrance exams and Enem 2023.
atomic bomb in physics

Professor of Physics and general coordinator of the Course, Marcelo Fonseca, explains that the reaction of the atomic bomb is nuclear fission.
"Nuclear fission involves a nuclear splitting of atoms. Core forces are extremely powerful and when those forces are altered and disrupted, they release a lot of energy," he points out.
The nuclear fission reaction was used for atomic bombs, but it is also used in nuclear power plants. The only difference, according to the professor, is that each process involves the concentration of fuel.
"While a nuclear power plant needs a concentration of uranium 235 of around 3% to 5%, an atomic bomb needs a much higher concentration, around 90%", he details.
The professor completes the explanation about the composition of the atomic bomb: "The two main elements used in the atomic bomb are uranium and plutonium, elements with large atoms. The atomic bomb breaks these atoms, transforms them into smaller atoms and part of their mass turns into energy. However, the energy generated by nuclear fission is much more intense than the energy released in common reactions such as combustion or explosion," he says.
Radiation
The physics professor points out that another point that deserves attention is that nuclear fission, in addition to releasing a lot of energy, it also emits radiation, which contaminates the environment for a long time and takes thousands of years to completely disappear. complete.
"In studies about the atomic bomb, students who are preparing for entrance exams should pay attention to the importance of this type of nuclear reaction, its ability to production of energy and the basic principle of its operation, which is the transformation of mass into energy, which can be calculated through the famous equation of Albert Einstein, E = m. c²", emphasizes the coordinator
atomic bomb in history
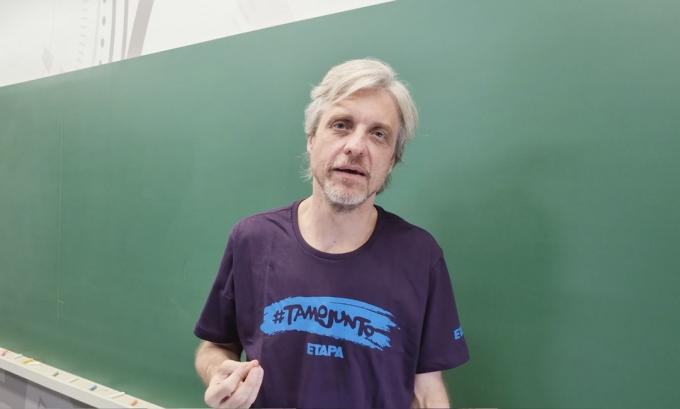

Thomas Wisiak, professor and coordinator of History at Curso Passo, comments that, with the atomic bombs used against Japan, the The United States exhibited a power of destruction unparalleled in history, increasing its negotiating power with allies at the end of the war.
The professor also recalls that, four years later, the Soviet Union carried out its first complete explosion test nuclear power, ending the monopoly of the United States and collaborating for a nuclear arms race in the plan International.
"During the Cold War, thousands of nuclear weapons were built, most of them under US and Soviet control. Since the mutual destruction of these powers was certain in the event of a nuclear confrontation, the rivalry needed to be managed to avoid direct conflict, which is at the origin of the Cold War concept" reinforces the professional.
Remember what the Cold War is
In this way, as the professor points out, nuclear weapons served as instruments of deterrence (doing what opponent giving up an attack) and persuasion (influencing the opponent's decisions) and were never used afterwards from 1945.
"It is important that the student who will take the entrance exams and Enem 2023 keep in mind a chronology and a periodization of the Nuclear Age, paying attention to changes in context. In the Cold War, initially only countries with a permanent seat on the UN Security Council had developed nuclear weapons and there was a movement to prevent this technology from spreading, resulting in the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons, of 1968, and which is still in force", reinforces the teacher.
Another important aspect related to the film "Oppenheimer", which deals with the creation of the atomic bomb, raised by the professor, is that currently the production of weapons has increased Tactical nuclear weapons that, unlike strategic ones, do not have such a great destructive power, which could lead the government of one of these countries to decide to use them, as in the case from the Russia amid war in Ukraine.
By Silvia Tancredi
Journalist