A science It is a systematic way of acquiring knowledge, based on an objective and well-defined method, known as scientific method. Science aims at the description and explanation of facts and phenomena of nature, so that it is possible to formulate theories, predictions and laws.
Validated scientific knowledge is converted into processes, products and devices that have the function of promoting technological advancement, improving the quality of life and the development of humanity.
Read too: What is ethics?
science summary
Science is a way of acquiring knowledge through a system of objective and well-defined steps.
Scientific knowledge is the product of science.
The scientific method is the system applied so that knowledge is validated scientifically.
Science aims at the description, explanation and prediction of phenomena.
It's based on experimentation, it's opinion-free, and it's verifiable.
It is not absolute truth, but fallible and capable of updating.
Concept and etymology of science

Science is a system that acquires knowledge based on a method, known as the scientific method. It is built with rational attitudes, aiming at obtaining specific knowledge, based on observation, carrying out experimental methods and developing theories and laws.
Theories are not absolute truths, on the contrary, they are constantly checked, aiming at their verification, possible updates or replacements in the face of new discoveries.
A The word “science” is derived from the Latin science, translated as “knowledge”.
Science has as its objective the description, explanation and prediction of phenomena through the application of the scientific method, which can be verified and reproduced.
What are the characteristics of science?
Factual: science develops around the occurrence of facts and phenomena.
Empirical: science uses experimentation to verify the veracity or falsity of knowledge.
Rational: science obtains its results through reason, free from researcher bias.
Systematics: science is logically built upon a system of ideas and procedures.
Verifiable: only that which can be verified or tested is part of the context of science.
Fallible: science constructs knowledge from a point of view that such knowledge is not absolute or definitive and can be updated or replaced in the face of new discoveries.
What is science for?
Science seeks to learn from nature based on observation so that it is able to control systems of in a practical way, describe and understand the phenomena, generate improvement in the quality of life and in the capacity intellectual. Based on the acquired knowledge, the science is then able to make predictions.
When science applies, through technique, the acquired knowledge, it results in a series of advances for the society, projecting new modes of production and changing the course of development of society.
Great advances provided by science over the decades were the mechanical loom, steam machines, the locomotive, medicines, vaccines, technological advances and many others.
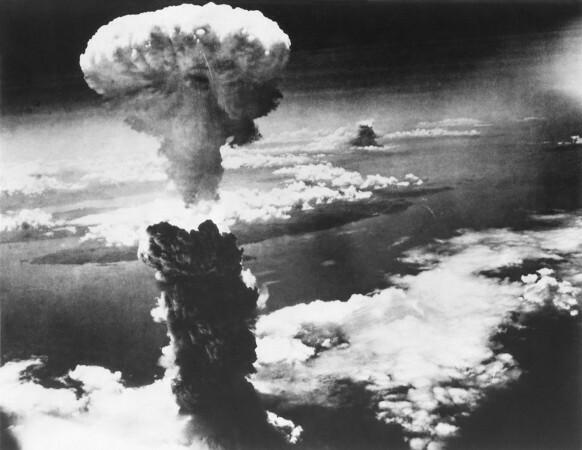
However, the scientific knowledge can even be directed to satisfy the interests of small groups. In such cases, it can become harmful. A serious example of this is the use of nuclear weapons and chemical weapons.

scientific method
The scientific method is the method by which science is put into practice. It is the set of procedures that have the function of validating a study as scientific, extracting from it laws, postulates or scientific theories.
It is through the application of the scientific method during research that the knowledge derived from it is considered valid and reliable.
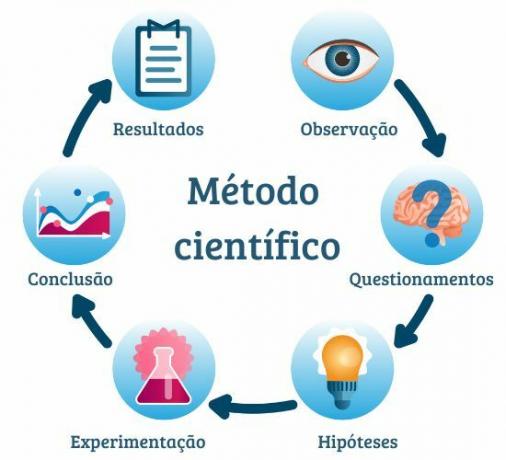
The scientific method is divided into steps:
observation of a phenomenon;
formulation of questions;
construction of hypotheses;
experimentation;
analysis or testing of hypotheses;
conclusion.
→ Video lecture on science and the scientific method
science vs common sense
O common sense It is a form of knowledge acquired spontaneously in everyday life. and through experimentation, called popular knowledge. It is knowledge generated by intuition, accidentally or just by causal observation. Still, it can be achieved through a deliberate effort to solve a problem.
Knowledge derived from common sense is not classified as correct or incorrect, but limited, since they are not obtained through systematic and efficient methods, based on the simple opinion. Thus, deep and complex knowledge cannot be reached by common sense.
O common sense differs from science, not because of its veracity or the nature of the study, but rather because of the way it was constructed.
Science is based on the application of methods (such as the scientific method) and has the following characteristics: rationality and the personal non-interference of the researcher, and, therefore, scientific knowledge is reliable.
Meanwhile, common sense — due to the absence of methods — is not scientifically tested and validated, being susceptible to interference, irrationality, and, therefore, it is not considered knowledge reliable.
Check it out on our podcast:science vs common sense
technology and science
A technology is a product of science, a practical application of scientific knowledge that spans several areas.
Technology employs the scientific knowledge acquired in the act of “doing science” to produce results and solve everyday problems. Technology products do not only involve devices, equipment or tangible goods, but extend to methods, techniques and “knowing how to do” something.
A Science and technology are fundamental for the development of humanity, the economic growth of nations, the reformulation and expansion of the labor market and the democratization of opportunities, the clearest example of which being the Internet.

importance of science
Science is so tightly intertwined with the modern world that it's hard to pinpoint its importance.
The science contributes to the increase of Life expectancy, provides equipment, medicines and devices for maintaining health. Allows for increased food production and expands food supply. Due to science, today there are several ways to obtain energy, through fuels, the sun, the water or the winds. Science offers solutions for a more practical, safe and comfortable everyday life.
Current environmental issues such as pollution It is global warming, can be associated with advances in science, such as the creation of automobiles, machines and synthetic chemical substances. However, the continuous scientific advance is one of the ways to overcome such problems, through the development of new techniques, materials and habits that are less harmful to the planet and more sustainable.
Read too:Scientific discoveries that happened by accident
branches of science
Even if science has a classification, it is important to make clear that science is unique and that such classifications only have the function of systematizing the objects of study, but that they continue to depend on each other.
There are several points of view to determine the branches of science. One considers the objects of study and assumes science organized into formal and factual sciences.
To the formal sciences embrace the study of ideas, processes of logic and mathematics. This includes studies on computational science, information theory, statistics, among others.
To the factual sciences they are further divided into natural sciences and social sciences. The natural sciences are concerned with the study of nature and its phenomena, including Biology, Physical, Chemical, Geography, Astronomy etc. The social sciences focus on the study of human behavior, including psychology, History, Anthropology, Political Science, among others.
history of science
The need to develop an understanding of how nature works and to find solutions to everyday problems goes back to the Antique.
You ancient myths were one of the first forms that human beings created to interpret facts and transformations of nature, transmitting them through narratives based on fantasies and supernatural aspects.
In the sixth century a. c., the first Greek philosophers began to develop more rational observations and reflective about nature, seeking to understand, in fact, the existing logic. Aristotle he was one of the first scholars to propose ways of classifying animals and plants, drafting a first form of scientific method.

Science has had periods of slow development in history, mainly due to religious issues and the predominance of aspects of faith.
Later, during the Rebirth, in the 16th and 17th centuries, modern science began to take shape with the contributions of Francis Bacon, Galileo Galilei, Rene Descartes and Nicolaus Copernicus, who began to develop cause-and-effect reasoning.
During this period, science began to be seen as a useful tool for solving humanity's problems and a form of technological propulsion.
Over the years, scientific formalism has been developed, and knowledge becomes universal, and then scientific laws and theories are enunciated, some of which are still in force today.
The scientific method, as it is known today, was being built in parallel with science and is currently a fundamental tool for scientific validation, for technology and for the development of the world modern.
By Ana Luiza Lorenzen Lima
Chemistry teacher
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/quimica/o-que-e-ciencia.htm

