O bismuth It is a metal belonging to group 15 of Periodic table which has the symbol Bi and atomic number 83. It has a silvery white color, with a pink tinge on its surface. It's a brittle metal, and despite being a heavy metal, it's not toxic at all.
Bismuth is used in metallic alloys, as well as in the cosmetics and medicine industries. It is well known for its diamagnetic property and is one of the few materials that expand when solidified (like water). It is found in the form of sulphides or oxides but also in the form of elementary crystals, which form small layers of oxides on the surface and reflect iridescent tones.
Read too: Scandium — a metal capable of making good metal alloys
bismuth summary
- Bismuth is a metal belonging to group 15 of the Periodic Table.
- Chemically it is more similar to arsenic and antimony than to nitrogen and phosphorus.
- It is a metal that expands when solidified, in addition to being diamagnetic.
- Despite being a heavy metal, it is not toxic, like the other elements in this group.
- It can be used in metallic alloys, as well as cosmetics and medicines.
- It is found in the form of oxides, sulfides, but also in elemental form, with colorful and quite striking crystals.
- Its discovery took place in 1753, when Claude François Geoffrey distinguished it from lead and tin.
bismuth properties
- Symbol: Bi
- Atomic mass: 208,98040(1)
- Atomic number: 83
- Boiling point: 1564°C
- Fusion point: 271.4°C
- Density: 9.79 g. L-1 (20°C)
- Electronic configuration: [Xe]4f145d106s26p3
- chemical series: group 15, heavy metals
characteristics of bismuth
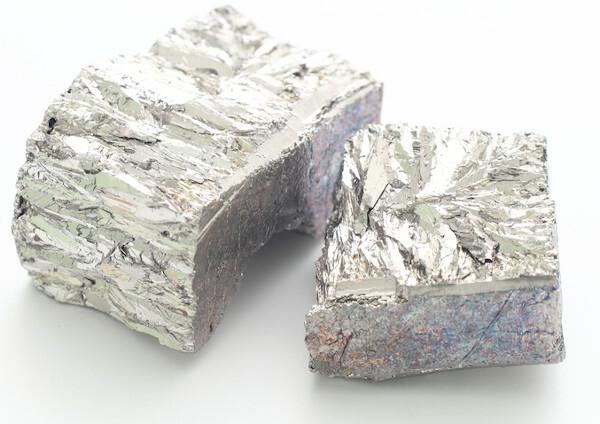

Bismuth, atomic number 83 on the Periodic Table, is the chemical element with the highest metallic character of group 15. In its pure form, it is brittle and, although its appearance is typical of a metal (it has a luster and silvery white color), it is the pink and red colors that make us realize that it is bismuth pure.
the isotope 209Bi is the only one of this element found in nature., and is often regarded as the heaviest stable isotope of all elements. However, it is known that it is actually slightly radioactive. the time of half life of this isotope is very long, in the range of 1.9 x 1019 years. For comparison, the estimated age of the Universe is 1.4 x 1010 years.
Bi's chemistry is closer to arsenic It is antimony than from nitrogen It is phosphor. For example, like As and Sb, bismuth can undergo combustion when heated with air, producing a blue flame and yellow fumes due to the oxide formed, as well as react with halogens.
4 Bi (s) + 3 O2 (g) → 2 Bi2O3 (s)
Bismuth resists the attack of alkaline substances and non-oxidizing acids, even strong ones (as is the case with HCl), but it can react with HNO3 concentrated to form Bi (NO3)3 and also with H2ONLY4 concentrated to form Bi2(ONLY4)3.
It's a metal with low thermal conductivity, being only greater than the Mercury. also presents great electrical resistance and is recognized as one of the most diagnostic materials available (is repelled by magnetic fields). Bismuth is one of the few substances besides water that expands when it solidifies. The increase in volume is around 3.32%.
What is bismuth used for?
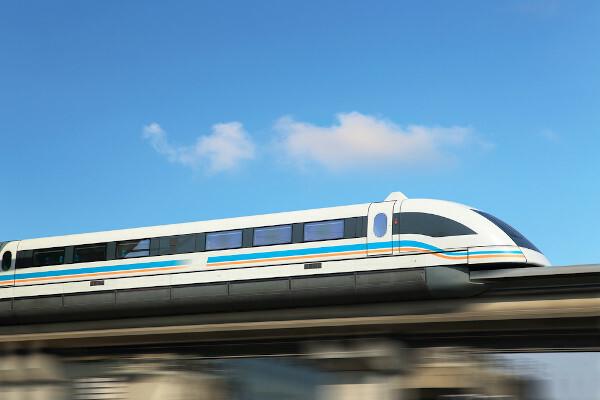
The fact that bismuth expands as it solidifies puts it in the composition of low melting point alloys, which need to expand to fill molds. With other metals, such as tin, cadmium and so on, bismuth is also used in shape of alloys in safety devices, such as flame detectors. Its diamagnetic property places it in the manufacture of magnetic lift trains (Maglevs), which can exceed 400 km/h.

Bismuth, due to its similar density, is used as a substituent of lead, since it is extremely toxic and suffers from several environmental regulations. An example where this substitution occurs is in sport hunting events.
Bismuth is not a dangerous element for human health and, therefore, has been explored in cosmetics and pharmaceuticals industry. BiOCl (bismuth oxychloride) is used as a pigment to impart a silvery sheen to some personal care products. Monobasic bismuth salicylate, marketed under the name Peptobismol, is a well-known antacid in order to treat some discomforts and infections in the intestinal tract and stomachsuch as heartburn, nausea and diarrhea.

Where is bismuth found?
On average, there is 0.1-0.2 ppm of bismuth in Earth's crust, an amount close to silver. The main bismuth ores are bismuthinite (Bi2S3) and the bismite (Bi2O3).
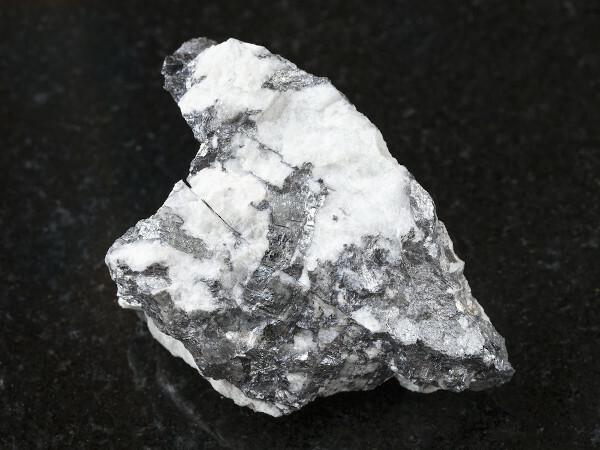

the bismuth can also occur in its elemental form — in the form of crystals with oxide layers of different widths that reflect colors in an iridescent tone.

See too: Nickel — a metal often used to make stainless steel
Obtaining bismuth
Like other minor metals, bismuth is obtained as a by-product of the process of obtaining more common metals, in case, copper and lead. The main bismuth producers are: China, Laos, South Korea, Mexico, Kazakhstan and Japan.
Currently, the main production processes are Betts and Kroll-Betterton. The first is an electrolytic method, which starts with a lead bar, which contains copper, antimony, arsenic, selenium, tellurium, silver, gold and bismuth. While lead is obtained from the cathode of the electrolytic cell, the impurities (in which bismuth is) are retained in the form of a very dark slurry, whose bismuth content can reach about 20% in pasta.
The Kroll-Betterton process differs from the previous one in that it selectively removes bismuth from a lead mixture. In that case, calcium It is magnesium are added to the formation of CaMg2Bi2, calcium dimagnesium bismuth. From there, bismuth can be recovered by using chlorine or lead chloride, producing a metallic alloy of lead and bismuth, whose Bi content is in the range of 7% by mass.
the bismuth can be refined using chlorine, reaching a purity of 99.99%.
Precautions with bismuth
Although bismuth occupies a heavy metal position on the Periodic Table, next to elements such as antimony and lead, the metal and its compounds are harmless to our health. To be clear, some bismuth compounds are less toxic than table salt.
history of bismuth
the bismuth has been known to mankind for a long time, as is the case of the Inca society, which, in the 16th century, used bismuth mixed with tin to produce bismuth bronze.
However, it was constantly confused with lead and tin. Until, in 1753, the Frenchman Claude François Geoffrey demonstrated that it was an element distinct from lead and tin. Its name derives from the German word wismuth, which means “white mass”.
By Stefano Araujo Novais
Chemistry teacher