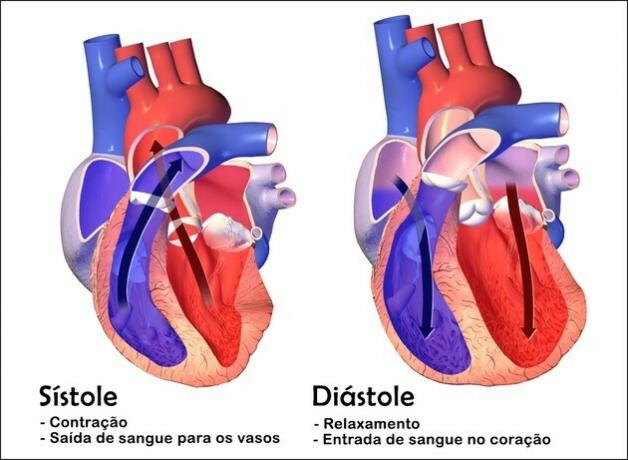
Systole and diastole are two stages of the cardiac cycle. Systole is the contraction phase of the heart, where blood is pumped into the blood vessels, while diastole is the relaxation phase, causing blood to enter the heart.
In a normal adult, the average systolic pressure is 120 millimeters of mercury (mmHg), while the diastolic is 80 mmHg.
| Systole | Diastole | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Systole is the phase of the cardiac cycle in which the heart is contracting. |
Diastole is the phase of the cardiac cycle in which the heart is relaxed. |
| Function | In the systole stage, the heart contracts, pumping blood from the heart into the aorta and pulmonary artery. | In the diastole stage, the heart relaxes, allowing the heart chambers to fill with blood, which comes from the pulmonary veins and vena cavae. |
| Blood pressure | High. | Low. |
| average pressure | The recommended systolic pressure for a normal adult is 120 mmHg. For a child it is 100 mmHg (6 to 9 years old) | The recommended diastolic pressure for a normal adult is 80 mmHg. For children it is 65 mmHg. |
| Blood vessels | Contracted. | Relaxed. |
| blood pressure reading | The largest number is the systolic pressure. | The lower number is the diastolic pressure. |
| phases | Atrial systole and ventricular systole. |
Atrial diastole and ventricular diastole. |
Diastolic pressure occurs at the beginning of the cardiac cycle. It is the minimum pressure in the arteries when the heart's pumping chambers fill with blood. At the end of the cardiac cycle, systolic pressure occurs when the ventricles contract.
blood pressure reading
The blood pressure reading is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and is given in two numbers.
The largest number is the systolic blood pressure reading, which represents the maximum pressure exerted when the heart contracts. The lowest number is the diastolic blood pressure reading, which represents the minimum pressure in the arteries when the heart is at rest.
So, if the doctor says that your pressure is 12 by 8, it means that in systole it is 120 mmHg and in diastole it is 80 mmHg.
Regarding heartbeats, which can be heard with a stethoscope, the first beat marks the beginning of systole, and the second is the beginning of diastole.
Normal and abnormal ranges of systolic and diastolic pressure
In children, the systolic measurement varies from 95 to 100 and in adults it varies from 90 to 120 mmHg. The diastolic measurement is around 65 mmHg in children, and in adults it ranges from 60 to 80 mmHg.
In cases of abnormality, the following numbers are identified in adults:
- Hypotension if the systolic reading is < 90 mmHg and the diastolic reading is < 60 mmHg;
- Prehypertension if the systolic reading is 121 to 139 mmHg and the diastolic reading is 81 to 89 mmHg;
- Stage 1 hypertension if the systolic reading is 140 to 159 mmHg and the diastolic reading is 90 to 99 mmHg;
- Stage 2 hypertension if the systolic reading is 160 mmHg and the diastolic reading is 100 mmHg.
See also the difference between:
- Sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system
- Incidence and prevalence