Camouflage and mimicry are skills that certain species of animals possess. Camouflage is when the animal resembles the environment that surrounds it, in order to hide from predators or used by predators to capture their prey.
Mimicry occurs when a species imitates characteristics of another to confuse its predators or prey.
| Camouflage | Mimicry | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability of an organism or object to blend in with its surroundings. | Ability to imitate characteristics and/or behavior of another species of animal. |
| types | Colors and shapes. | Bacterial, Peckhamian, Wasmannian, Müllerian mimicry. |
| Examples |
|
|
What is camouflage?
Camouflage is the ability of an organism or object to resemble the environment that surrounds them. Thus, it can occur by color or shape. It is very useful for prey to protect themselves from predators by camouflaging themselves so that they are not seen.
However, it is worth noting that the ability to camouflage itself results from natural selection. Camouflage features react directly to threats that certain organisms encounter in nature.
For example, there is no point in an animal being able to change color to blend in with the environment if its main predator is not color sensitive.

Therefore, camouflage is a reaction to help the organism protect itself and the traits of the predator are extremely important for the result.
In addition to changing colors, due to chemical effects on the skin or changing hair, there are animals that camouflage themselves to look like objects that surround them.
The best example is the stick insect, which has a woody color and a body shape that makes it look like branches of a tree.
Examples of animals that use camouflage
- stick insect: color and shape of wood to resemble a stick;
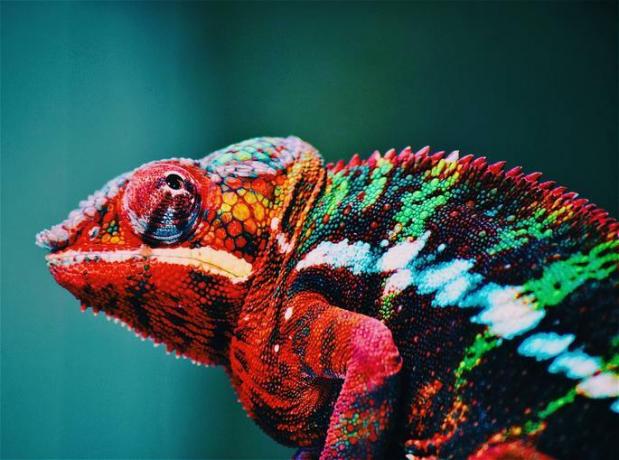
- Chameleon: changes the color of the body according to the environment in which it is found;
- Polar Bear: reflect light and appear white to blend in with snow;
- arctic fox: change of fur according to the season, being darker in summer and lighter in winter;
- Squirrel: brown hairs help it to camouflage itself in the bark of trunks;
- Octopus: changes color to blend in with its surroundings;
- sharks: some species have a gray-blue tone to go unnoticed as light reflects off the surface;
- Dolphins: Have a gray-blue tone to go unnoticed as light bounces off the surface.
What is mimicry?
Mimicry is the ability of some organisms to be confused with others of different species. Animals with the ability are called mimics.
In general, a mimic is not a creature that relies on powerful defense mechanisms. Therefore, it seeks to imitate other animals to avoid being devoured by predators.
Typically, an animal that uses mimicry has a version of colors, textures, shapes and behaviors of potentially dangerous organisms to deceive predators. This is so that it survives in nature.
One of the greatest examples of mimicry occurs in the false coral call. This snake mimics the color pattern of true coral, which is extremely venomous and can be a predator's last meal attempt.
The false coral has venom, but the lack of a loreal pit (which detects temperature variations to detect prey) prevents it from using it.
So your best survival strategy is to imitate the really dangerous snake. Thus, it avoids being devoured by predators that would not risk attacking a true coral.

types of mimicry
Batesian
It is when the mimic and the species that serves as a model share the same geographic space. Since they are in the same place, the chances of the predator attacking the dangerous animal are greater. This is because there are more specimens available, a common feature of Batesian mimicry.
Peckhamian
In this type of mimicry, the species that will imitate the other is precisely the predator. Thus, it mimics the prey's traits, in order to be able to approach and have more chances of capturing it. A true “wolf in sheep's clothing”.
Wasmannian
It is a form of mimicry between species that do not interfere with each other's way of life. That is, they do not compete with each other. Thus, they have different types of prey and do not negatively affect each other.
Müllerian
In Müllerian mimicry, both the model and imitated species have different defense mechanisms. Even so, one imitates the other and prevents the predator from attacking both species. It is a way to guarantee survival in an effective and broad way.
Examples of animals that use mimicry
- false coral: mimics true coral, which is venomous and dangerous;
- Cockroaches of the genus Prosoplecta: Filipino bugs that mimic ladybugs and toxic beetles;
- swallowtail butterfly: African insects that mimic inedible butterflies of the genera Danaus It is amauris;
- butterflies papilio laglaizei: in New Guinea, they mimic moths with their colors Alcides agathyrsus, which are toxic;
- spiders of the genus Myrmarachne: they disguise themselves as ants to capture them;
- orchids: many plants of this species imitate female insects with their flowers, in order to attract them so that it can spread pollen through their bodies and release them so that pollination can be carried out in nature.
Therefore, although many confuse camouflage and mimicry, in short, when an animal camouflages itself, it becomes confused with the environment that surrounds it.
In mimicry, a species with fewer defense mechanisms imitates another, which has more dangerous characteristics for predators. Thus, they guarantee protection and more chances of survival.
See also the difference between:
- creationism and evolutionism
- Lamarck and Darwin
- Food chain and food web
- Poisonous and venomous snakes