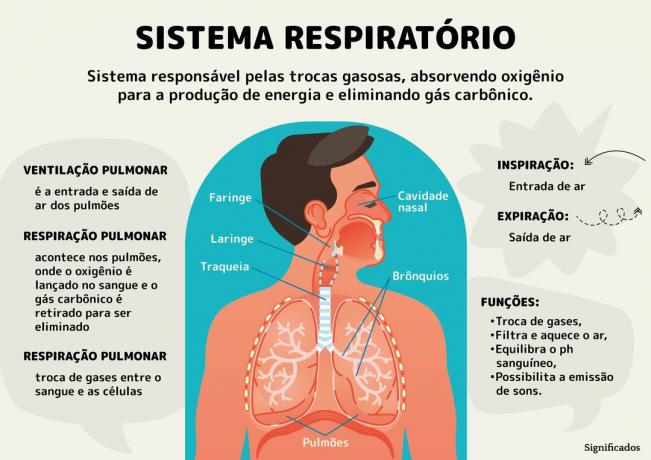
The main difference between venomous and non-venomous snakes is the presence of some mechanism to inject venom into their prey.
According to research at the University of Queensland, all snakes have venom-producing glands, even snakes that kill by constriction. However, some have them in smaller quantities, and do not have an inoculating mechanism.
In addition to this, other features can help distinguish a venomous snake from a non-venomous venomous snake.
| venomous snake | Poisonous snake | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | They are snakes that have some mechanism to inject the venom into the body of another animal. | They are snakes that produce venom but do not have an inoculating mechanism. |
| Head | It usually has a flattened, triangular and well highlighted head. It has anterior fangs. |
It has a narrow, long and slightly prominent head. It has no previous fangs. |
| loreal pit | It has. | Does not own. |
| Eyes | It has small eyes with a vertical slit pupil. | Large eyes with circular pupils. |
| Tail | It is short and sharply tapered. | It is long and gradually tapers. |
| Reaction when threatened | They attack. | Flee. |
| Movement | Slow. | Fast. |
| Behavior | It has nocturnal habits. | It has diurnal habits. |
| Examples of Brazilian snakes | Jararaca, Coral, Rattlesnake, Surucucu. | Jiboia, Sucuri. |
Although these characteristics are dominant, some species do not correspond to this pattern. An example is the coral snake, which despite being venomous, does not have a loreal pit. a mechanism that detects minute variations in the surrounding temperature in order to detect their prey.
Poison or Venom?
The venomous snake is the one that has some mechanism to inject the venom into the organism of other animals, such as the hollow teeth through which the venom passes.
Poisonous snakes, on the other hand, are those that produce toxic substances, but do not have an inoculating device, such as teeth or stingers. These animals depend on the situation to use the poison.
form of attack
When intimidated, venomous snakes prepare to attack.
They release their venom on prey through inoculation mechanisms, where they inject the toxic substance. Most venomous snakes have hollow teeth, through which the venom passes.
Non-venomous venomous snakes, on the other hand, do not have this mechanism. Generally, they kill their prey by constriction, wrapping themselves around them and crushing them.
See also the difference between:
- Camouflage and mimicry
- crocodile and alligator
- Turtle, tortoise and tortoise
- Donkey, donkey, donkey, donkey, mule and bardoto
- German and American Rottweiler