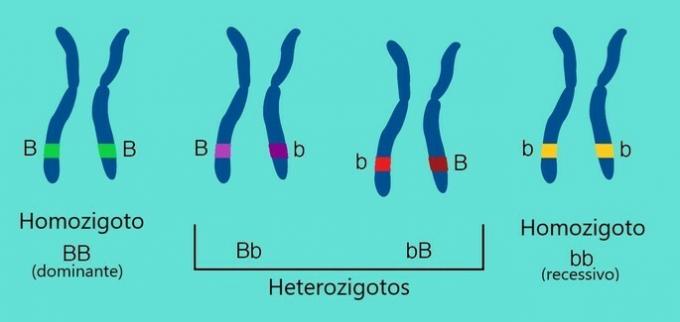
A homozygote is an individual who receives identical genes from both parents for a given trait. The heterozygote occurs when this individual receives a gene from the mother that is different from the gene inherited from the father.
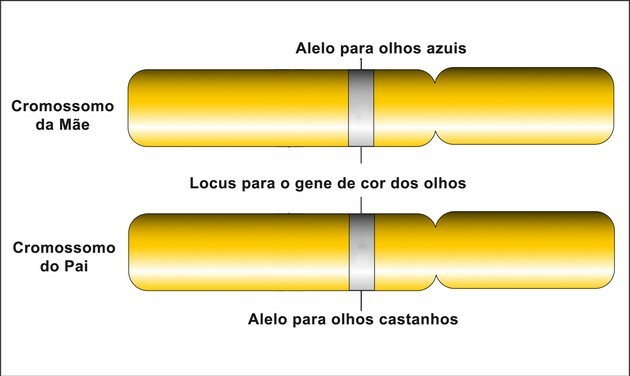
These genes occupy the same place (called a "locus") in the formation of homologous chromosomes. Its structure constitutes the DNA chain (deoxyribonucleic acid) and determines all the characteristics that the individual presents.
Thus, homozygous organisms are formed by pairs of identical alleles (AA, aa, BB, bb, VV and vv) and heterozygotes are formed by pairs of distinct alleles (Aa, Bb and Vv).
| homozygous | heterozygous | |
|---|---|---|
| Concept | Individuals formed from identical genes. | Individuals formed from different genes. |
| Etymology | Homo (from the Greek homo, "equal") and Zygote (from the Greek zygotos, "together") | straight (from the Greek straight, "different") and Zygote (from the Greek zygotos, "together") |
| Formations |
|
|
Zygosity, therefore, represents the similarity of allele genes represented by the prefix homo ("equal" in Latin) in homozygotes and the dissimilarity represented by the prefix hetero ("different" in Latin) in heterozygotes.
homozygous
The concept of homozygote represents individuals formed from identical allele genes, therefore called "pure".
The gametes produced in homozygous organisms are the same and can be represented by:
- dominant homozygotes: (AA, BB and VV) - Capital letters in dominant genes.
- recessive homozygotes: (aa, bb and vv) - Lowercase letters in recessive genes.
Thus, the characteristics donated by the mother (egg) and the father (sperm) present the same information, they are identical copies, forming a homozygous individual for that characteristic.
It is worth remembering that the characteristics of recessive genes will only be expressed in the phenotype, when they appear in homozygosis.
heterozygous
The concept of heterozygote defines individuals who have pairs of genes with alleles that are different from each other.
Thus, heterozygous gametes, unlike homozygous ones, can only manifest the characteristics present in the dominant gene.
- heterozygous: (Aa, Bb and Vv) - presence of dominant and recessive gene in the formation of heterozygous individuals.
Thus, in the union of different genes, as they are not identical copies, the characteristics of only one of the genes, the dominant one, are manifested.
See also the difference between:
- gene and allele
- dominant and recessive
- genotype and phenotype