Prokaryotic cells are distinguished from eukaryotes by their structure. While eukaryotic cells have complex structures, formed by inner membranes, cytoskeleton and a nucleus, prokaryotic cells do not contain a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles.
Prokaryotic cells were the only form of life on Earth for millions of years, until more complex eukaryotic cells arose through the process of evolution.
| prokaryotes | eukaryotes | |
|---|---|---|
| What is it | Prokaryotic cells are the most primitive cells. They have a less complex structure, without a nucleus, and the genetic material is dispersed in the cytoplasm. | They are believed to have evolved from prokaryotes. Eukaryotic cells are larger than prokaryotic cells, and demonstrate better structural organization and functional efficiency. |
| Core | They do not have a defined core. | Contains core. |
| Type | Usually unicellular. | Multicellular. |
| cell wall | The cell wall, if present, contains peptidoglycan. | The cell wall, when present, contains cellulose. |
| Meaning | From Greek, "before the nucleus" (pro = before, primitive and karyon = nucleus). | From Greek, "true nucleus" (eu = true and karyon = nucleus). |
| DNA | The DNA is generally circular, and has no association with histone proteins. | DNA is commonly linear, is within the nucleus, and is associated with histones. |
| Transcription | Transcription takes place in the cytoplasm. | Transcription takes place inside the nucleus. |
| Examples | Unicellular beings, such as some bacteria, blue algae, blue algae and mycoplasmas. |
Animals, plants, fungi and protists. |
| Size | 1 to 5 µm in diameter. | 10 to 100 µm in diameter. |
Definition of eukaryotes and prokaryotes
Prokaryotic, or prokaryotic, cells are organisms without a cell nucleus or any other membrane-bound organelle. Their genetic material is dispersed in the cytoplasm, and most prokaryotes are unicellular, although some prokaryotes are multicellular.
Eukaryotic cells, or eukaryotes, are organized into complex structures by internal membranes and a cytoskeleton. The most characteristic structure of the membrane is the nucleus.
What are prokaryotic cells?

Prokaryotic cells are less complex than eukaryotic cells. They have no true nucleus, as the DNA is not contained within a membrane or separated from the rest of the cell, but is dispersed throughout a region of the cytoplasm called the nucleoid.
The following structures and organelles can be found in prokaryotic cells:
- Capsule: additional outer covering that protects the cell, prevents dehydration and favors adhesion to surfaces;
- cell wall: external covering that protects the bacterial cell and gives it its shape;
- Cytoplasm: is a gel-like substance. Its role is to give structure and maintain the shape of the cell;
- Plasmid: are double DNA molecules that store genetic material;
- Cell Membrane: it is responsible for enveloping the cell's cytoplasm and regulating the flow of substances in and out of it;
- flagellum and cilium: they help in the locomotion of the cell;
- ribosome: are cellular structures responsible for the production of proteins;
- nucleoid: area of the cytoplasm that contains the DNA molecule.
Also know the difference between DNA and RNA.
What are eukaryotic cells?
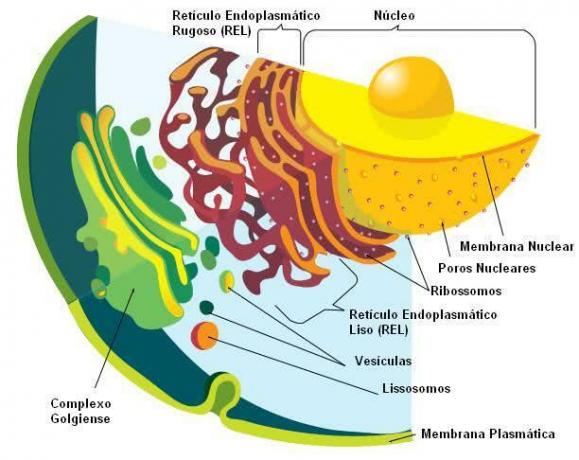
- Core: is the largest and most visible organelle in a eukaryotic cell. It contains the cell's DNA;
- Endoplasmic Reticulum: its function is to produce and send proteins and lipids;
- Golgi complex: is responsible for modifying cellular molecules and sending materials out of the cell. It is also the only organelle that can generate lysosomes;
- lysosomes: play an important role in cellular digestion;
- peroxisomes: are structures that have enzymes that transform hydrogen atoms into oxygen;
- Nucleoli: they are located inside the nucleus, where the synthesis of ribosomes takes place;
- mitochondria: responsible for releasing energy from glucose molecules and fatty acids;
- Vacuoles: structures that store substances related to digestion or cellular nutrition;
- plastids: present only in plant eukaryotic cells. Responsible for photosynthesis and storage of substances. They are of three types: chloroplasts, chromoplasts and leucoplasts.
See also the difference between:
- Animal cell and plant cell
- Simple and easy distribution
- Viruses, bacteria and fungi