The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for changes in the body in situations of stress or emergency. Thus, it leaves the individual in a state of alert, prepared for fight and flight reactions.
The parasympathetic nervous system has the function of making the organism return to the state of calm in which the individual was before the stressful situation.
| sympathetic nervous system | parasympathetic nervous system | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The sympathetic nervous system is the first of the two divisions of the autonomic nervous system. | The parasympathetic nervous system is the second of the two divisions of the autonomic nervous system. |
| Function | Responsible for preparing the body to respond to stress and emergency situations. | Responsible for making the body return to a stable and calm emotional state, in addition to controlling some non-conscious systems and actions, such as breathing. |
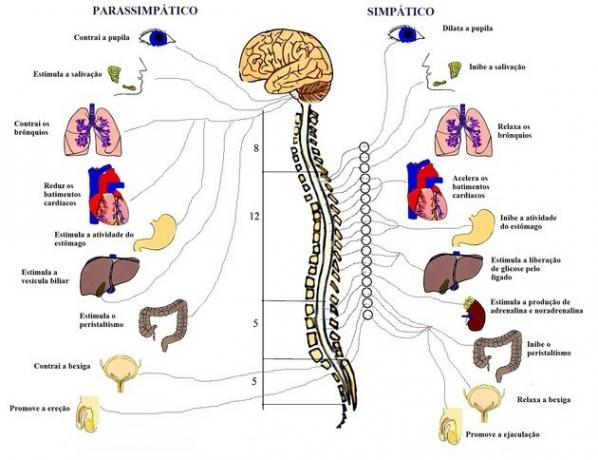
| Main activities | Increase heart rate and blood pressure, release adrenaline, contract and relax muscles, dilate bronchi, dilate pupils, increase perspiration. | Lower heart rate, lower blood pressure, lower adrenaline, lower blood sugar, control pupil size. |
Both are parts of autonomic nervous system. This is responsible for the spontaneous actions of the body, such as breathing, heartbeat, digestion, body temperature control, among many other functions, managed by the sympathetic and parasympathetic.
What is the Sympathetic Nervous System?
Also known as orthosympathetic system or thoracolumbar system, the sympathetic nervous system prepares the body to deal with stressful or emergency situations.
In this sense, when the brain perceives danger, the sympathetic nervous system comes into play.
During stress or emergency, the system will trigger a series of internal actions. Everything so that the individual responds to the situation in order to get rid of the discomfort or danger. The system will for example:
- Increase heart rate;
- Release adrenaline;
- Increase blood pressure;
- Contract and relax muscles.
There are still other physical changes at times when the sympathetic nervous system is triggered. Among them are:
- Dilation of the bronchial passages, for greater oxygen retention;
- Dilation of the pupils, to improve the sense of sight;
- Contraction of blood vessels;
- Increased contraction of the esophagus;
- Perspiration.
Other body responses are the sensation of heat and cold, as well as pain.
Example
The sympathetic nervous system is triggered in stressful or emergency situations. Thus, if a person is crossing a street and realizes that a car is moving towards him, the system is activated. This is so that the individual can deal with the possible accident.
In the case, if there is time, the body will undergo all the changes described above. And, in an impulse to save his own life, he will act to avoid being hit by the vehicle.
Saved from harm, it's time for the parasympathetic nervous system to kick in.
What is the parasympathetic nervous system?
Contrary to the sympathetic nervous system, the parasympathetic nervous system is responsible for making the body calm down after a stress or emergency situation.
Thus, it will decrease heart rate, blood pressure, adrenaline and blood sugar.
In addition to calming the body and returning it to a stable emotional state, the parasympathetic nervous system also has the function of conserving the body's energy. Along with the sympathetic system, it also controls the pupils.
See also the difference between emotion and feeling.
However, the parasympathetic nervous system is not just for calming down after a stressful situation. The system controls several areas of the human body and involuntary actions, which do not happen consciously. As:
- Cardiovascular system;
- Excretory system;
- Digestion;
- Sexual arousal;
- Breathing.
Example
Let's say that the individual realized that a car was coming towards him, and then had the sympathetic nervous system activated in order to act to save his own life, escaping the accident unharmed. That's when the parasympathetic system will kick in.
After understanding that there is no more danger, the body will trigger the parasympathetic system. This is to get the heart rate back to normal, decrease the adrenaline and return the body to the state before the stress situation.
Without the autonomic nervous system, divided into sympathetic and parasympathetic, human beings would not be able to respond to dangerous situations.
Fight-and-flight responses are essential and have helped mankind for thousands of years, since the dawn of evolution.
See also the difference between:
- systole and diastole
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells


