O parnaiba river, also known as Velho Monge, is a 1,400-kilometer watercourse located in the Northeast region of Brazil, on the border between the states of Maranhão and Piauí. The Parnaíba is one of the most important watercourses in the Northeast region. Its waters and those of its affluents, such as the Balsas and Gurgueia rivers, serve hundreds of municipalities inserted in a hydrographic basin of 333,000 km², in which almost 4 million inhabitants live. Despite its economic, social and environmental importance, the Parnaíba River suffers from problems such as silting and pollution.
Read too: Rio Tocantins — the second longest river flowing exclusively in Brazil
Summary about the Parnaíba River
Parnaíba River is a perennial watercourse that runs along the border between the states of Maranhão and Piauí.
It is one of the most important in the Northeast region.
It has a length of 1,400 km, and the area of its watershed is 333,056 km².
It rises in Chapada das Mangabeiras and empties into the Atlantic Ocean on the coast of Piauí, in the city of Parnaíba.
It has a mouth in a delta, known as Delta do Parnaíba.
It is divided into Alto Parnaíba, Médio Parnaíba and Baixo Parnaíba.
The rivers of Balsas and Gurgueia are two of its main tributaries.
It is important for residential supply, especially in the semi-arid rural environment, for the regional economy, for transport and for the generation of electricity.
The main environmental problems of the Parnaíba River today are pollution, deforestation in the surrounding areas and the silting up of its bed.
General data of the Parnaíba River
Length of the Parnaiba River: 1,400 km.
Source of the Parnaíba River: Chapada das Mangabeiras, between the states of Maranhão, Tocantins, Piauí and Bahia.
Main tributaries of the Parnaíba river: river das Balsas, river Piauí, river Gurgueia, river Canindé, river Poti and river Longá.
Mouth of the Parnaíba River: Atlantic Ocean.
Where does the Parnaíba river flow: near Parnaíba, city in the state of Piauí.
Delta of the Parnaiba River: Delta do Parnaíba, between the states of Maranhão and Piauí.
Average flow: 2,400 m³/s.
basin area: 333,056 km².
Map of the Parnaiba river
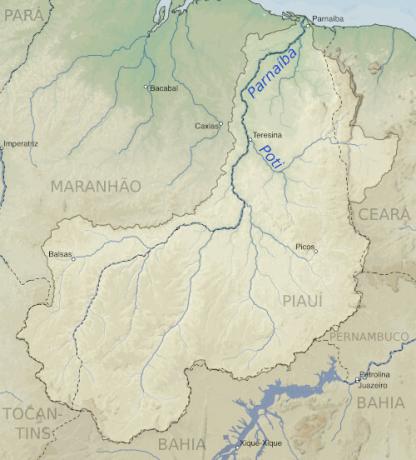
Where is the Parnaiba River?
The Parnaíba River is a Brazilian watercourse that runs exclusively through the Northeast region of the country. this river serves as a natural boundary between the states of Maranhão and Piauí, since most of its course lies on the border between these territories.
Thinking about the sub-regional division of the Northeast, the Parnaíba River is inserted in the mid-north, and the hydrographic basin formed by it also comprises the northeastern hinterland.
Characteristics of the Parnaíba River
The Parnaíba River can be described as one of the most important rivers in the Northeast region, being the second largest watercourse what walks this portion of the Brazilian territoryacross the San Francisco River. The waters of Parnaíba follow a path of approximately 1,400 km from its source, in the region of Chapada das Mangabeiras, to its mouth, located near the city of Parnaíba, on the coast of the state of Piauí.
The Parnaíba is a perennial river, which means that there is water in its bed all year round. This aspect is favored by the climate of the area where its source is located and the stretches it runs through, what is the tropical climate. As we know, this climatic occurrence is characterized by a rainy season and a dry season. The average annual rainfall in the area where Parnaíba is located is around 1,500 mm.
To the waters of the Parnaíba River bathe the Cerrado and Caatinga biomes, in addition to feeding coastal ecosystems such as mangroves, before flow into the Oatlantic ocean. Despite the steep slope that characterizes its upper course and problems such as silted up areas (presence of a large load of sediments in the river bed), the Parnaíba River presents navigable excerpts which favored the installation of the Parnaíba Waterway, which is 1,344 km long and also includes the Balsas River.
The course of the Parnaíba River is divided into three different sections:
Alto Parnaiba: It is the stretch with the steepest slope along the Parnaíba river. It is located between the springs and the dam of the Boa Esperança Hydroelectric Power Plant, with an extension of around 780 km. The altitude decreases from approximately 800 meters in Chapada das Mangabeiras to approximately 200 meters in altitude.
Middle Parnaiba: intermediate stretch that extends to the mouth of the river Poti, near the city of Teresina, capital of the state of Piauí. It has a gentler slope than the stretch above it.
Lower Parnaiba: final section of the river, which extends to the mouth in a delta that opens near the municipality of Parnaíba, in the state of Piauí. The Lower Parnaíba is characterized by the smooth relief and for comprising the widest stretches of this watercourse, reaching 600 meters in width.
Parnaiba is the main river of the Parnaíba River Basin, or the Parnaíba Hydrographic Region, also one of the most important in the Brazilian Northeast. The area of this extensive basin is 333,056 km² and represents 3.9% of the area of Brazil.
Source of the Parnaiba River
The Parnaiba River rises at the confluence of three watercourses:
river Águas;
Curriolas River;
River Otters.
They have origin in Chapada das Mangabeiras, a relief formation located on the border between the states of Maranhão, Tocantins, Piauí and Bahia, which has an altitude of approximately 800 meters. The Parnaíba River forms in this area, more precisely in the Serra da Tabatingas. There, the Nascentes do Rio Parnaíba National Park was established, a conservation unit managed by ICMBio.
Tributaries of the Parnaíba River
The Parnaíba River and its tributaries, which influence rivers and streams, form a dense drainage network that constitutes the Parnaíba River Hydrographic Region, of great importance for the mid-north and hinterland northeastern. see below the main affluent rivers of Parnaíba:
Right bank: Gurgueia, Uruçui-Preto, Poti, Canindé, Piauí, Igaraçu, Longá.
Left margin: das Balsas, Buriti.
Mouth of the Parnaiba River
At the end of its course, the Parnaíba River branches into several channels that flow into the Atlantic Ocean, giving rise to a mouth in delta. The Delta do Parnaíba, as it is known, is located near the city of Parnaíba, on the coast of the state of Piauí, and is an important tourist spot for the region due to the dozens of river islands that form.

Upper Parnaíba River Basin
The Alto Parnaíba basin is the hydrographic region formed in the initial stretch of the Parnaíba river. It includes the sources of this watercourse and other important rivers, such as the Gurgueia and the Uruçui-Preto. Furthermore, an important extension of the biome thick it is located in the Alto Parnaíba basin, where there is intense farming activity or, more specifically, agribusiness.
That region belongs to the hydrographic basin of the Rio Parnaíba. The Parnaíba basin has an area of approximately 333,000 km², which is equivalent to 3.9% of the land in Brazil. The state of Ceará, in addition to Maranhão and Piauí, is included in this hydrographic basin. Considering its entire area, almost 280 municipalities benefit from the Parnaíba River and its tributaries in these three states.
Read too: What are the Brazilian river basins?
Importance of the Parnaíba River
The Parnaíba river basin comprises almost 280 municipalities and a population of approximately 4,000,000 inhabitants. The waters of the Parnaíba River and its tributaries are extremely important for the residential supply, especially in the rural environment of the northeastern semi-arid region.
The river is fundamental for the economic activities carried out within its watershed, especially tourism, fishing, subsistence agriculture and livestock. It should be remembered that Parnaíba lard part of the agricultural region known as Matopiba, comprising the states of Maranhão, Tocantins, Piauí and Bahia.

A power of the waters of Alto Parnaíba is used in the generation of electricity at the Boa Esperança Hydroelectric Plant, which is located in the municipality of Guadalupe (Piauí) and has been in operation since 1970. The installed capacity of this hydroelectric plant is 237,300 kW.
The navigability of extensive stretches of the Parnaíba River led to the installation of the Parnaíba Waterway. This road has 1,176 km and an average width that varies between 300 and 350 meters, which allows the passage of vessels with bulky loads. With that, the Parnaíba River also became important for the flow of agricultural production, for the transport of goods and for the transport of people.
The Parnaíba River is also of environmental importance for the Northeast. As we have seen, it is a perennial river that bathes the two main biomes present in the region (Cerrado and Caatinga), in addition to feeding the coastal system where mangroves are found, for example. Great biodiversity is also concentrated in the Parnaíba Delta, which has been transformed into an environmental protection area (APA).
Preservation of the Parnaíba River
Human intervention, marked by the intensification of agricultural activity and land use, therefore, and by projects for the construction of new hydroelectric plants, is a factor that puts the balance of the river at risk Parnaiba. At the moment, water pollution, deforestation and siltation are the main environmental problems identified on the Parnaíba River and within its watershed.
A measure that was very important for the preservation of this watercourse was the creation of the Nascentes do Rio Parnaíba National Park, which took place in 2002. The park is a conservation unit with an area of 729,774.18 hectares managed by ICMBio. In addition to protecting the headwaters of the Parnaíba, its creation favors the maintenance of part of the Cerrado's biodiversity and guarantees the protection of other springs and rivers that flow through that region.
In view of the economic importance of tourism for the municipalities of Baixo Parnaíba, mainly, the practice of ecotourism and sustainable tourism is also encouraged in the Parnaíba Delta, in order to build a harmonious relationship with the environment.
Curiosities about the Parnaíba River
The Parnaíba river is also known as Velho Monge. The nickname was given by poet Antônio Francisco da Costa e Silva (1885-1950).
There are more than 70 river islands in the Parnaíba Delta.
Most of the population of the Parnaíba river basin lives in areas closer to the coast.
75% of the area of the Parnaíba basin is in the state of Piauí. The smallest portion corresponds to Ceará.
The word “parnaíba” comes from Tupi and means “river of muddy waters”.
image credits
[1] Keenan Pepper / Wikimedia Commons
[2] Ksenia Ragozina / Shutterstock
By Paloma Guitarrara
Geography Teacher