A square is a figure with four equal sides. A square has four angles of 90 degrees (ninety degrees). As squares are closed figures, in geometry they are called polygons, and classified as quadrilaterals, figures with four sides.
Every square has four edges (sides), four vertices (where the sides meet) and four 90° interior angles.
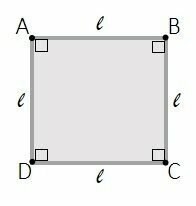
Where, l are the sides and: A, B, C and D the vertices.
Not every quadrilateral is a square. To be square, it must have four sides of the same measure, and four interior angles with 90º. The parallelogram and trapezoid are quadrilaterals, but not squares.
Squares are a category of two types of quadrilaterals: rectangles and rhombuses.
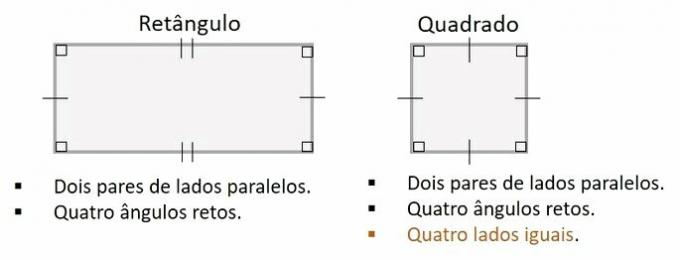
Every square is a rectangle. The definition of a rectangle is: a quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides, and the interior angles of 90º.
If the sides of the rectangle are equal in length, in this particular case, the rectangle will also be a square.
So while every square is a rectangle, not every rectangle is a square.
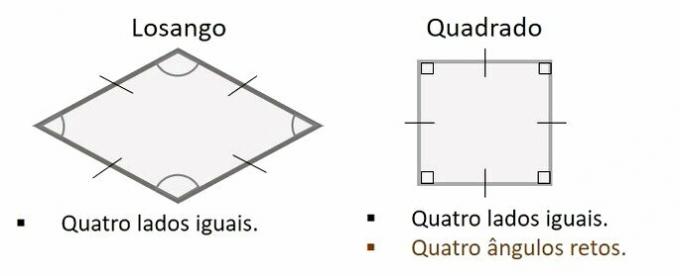
Every square is a rhombus. A rhombus is a quadrilateral with four sides of equal length. In the particular case where the rhombus has the four right angles, it is also a square.
perimeter of the square
The perimeter is the sum of the sides. Since a square has equal sides, the perimeter is:
Where L, is the measure of the side.
square area
The area of the square is the measure of its inner surface. It is calculated as the multiplication between two sides.
square diagonals
A diagonal is a line segment connecting two vertices not on the same sides. In this case, a square has two diagonals.

A diagonal divides the square into two isosceles right triangles. In this case, the measure of the diagonal of the square is also the measure of the hypotenuse of a right triangle with equal legs.
Where L is the measure of the sides of the square, applying the Pythagorean Theorem, the diagonal is calculated by:
Exercises on square
Exercises 1
Find the perimeter of a square with side 14 cm.
P = 14 + 14 + 14 + 14 = 56 cm
Exercise 2
Find the area of a square with sides of 9 cm.
Exercise 3
Find the length of the diagonal of a square with sides of 5 cm.
Factoring the 50:

The 50 can be written as:
The diagonal measures cm.
See more about:
- quadrilaterals
- Square perimeter
- Square Area
- Area and Perimeter
polygons
- quadrilaterals
- polygons
- Rectangle
- Areas of Plane Figures
- Square Area
- Plane Geometry
- parallelogram
- Polygon Area