pulmonary alveoli they are structures that resemble small bags and have a very thin wall. They constitute most of the lung parenchyma and are responsible for the characteristic spongy appearance of the lung. lung. In the alveoli, the oxygen we breathe is passed to the blood, being responsible, therefore, for the gas exchanges that occur between the environment and the organism.
Read more: Respiratory system - guarantees the capture of oxygen in the air and the elimination of carbon dioxide from our body
Summary of pulmonary alveoli
They are saculiform structures.
They have thin walls, essential for gas exchange.
In these exchanges, oxygen passes into the blood and the carbon dioxide present in the blood diffuses into the alveoli.
Pulmonary emphysema is a disease in which there is destruction of the alveolar walls.
What are pulmonary alveoli?
The pulmonary alveoli are small structures that resemble tiny sacs and form most of the lung parenchyma. They are arranged in such a way that they resemble the honeycomb of a beehive. They constitute the
final portion of the bronchial tree and are the structures that give the lung its characteristic spongy appearance.What is the structure of the pulmonary alveolus?
The pulmonary alveolus, as pointed out, is a structure that resembles a small bag. Its walls are thin and formed by a single layer of epithelial tissue, which is supported by a connective tissue rich in blood capillaries.
What is the function of the pulmonary alveoli?
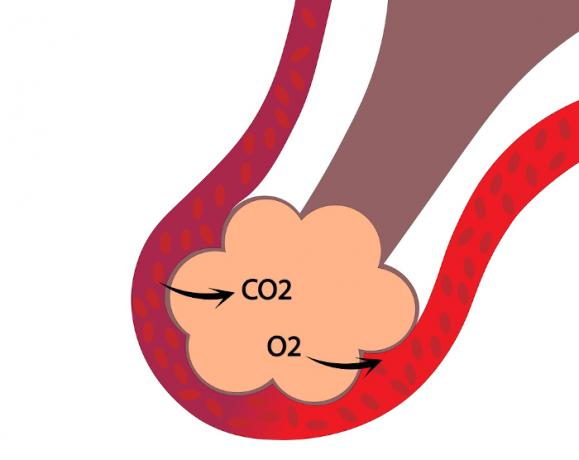
The pulmonary alveoli are regions where gas exchange takes place. When we breathe, the oxygen present in the atmosphere travels towards our lungs. Initially, the air get in our body through the nostrils, passes through the nasal cavity, passes through the pharynx, passes through the larynx, reaches the trachea, passes to the bronchi, bronchioles and finally reaches the pulmonary alveoli.
The alveoli, as mentioned, are surrounded by a large number of blood capillaries. Both pulmonary alveoli and capillaries have very thin walls, which allow the passage of oxygen and carbon dioxide. The oxygen, coming from the inspired air, will pass into the blood, and the carbon dioxide, present in the blood, will pass into the alveoli. This gas exchange process is known as hematosis.
The oxygen made available to the blood will bind to the hemoglobin of the Red Cells and will be carried, via the bloodstream, to every cell in our body. Oxygen is essential for carrying out the cellular respiration, which will ensure the production of energy for the cell. The carbon dioxide that has diffused into the alveoli, in turn, will be carried out of our body through the airways. This process of elimination of carbon dioxide to the external environment is called expiration.
Read more: Breathing movements — inspiration and expiration
What is pulmonary emphysema?
Pulmonary emphysema is a health problem that compromises the pulmonary alveoli, causing the destruction of the walls of that structure. As the alveoli are related to gas exchange, problems in these structures directly affect the body's ability to capture oxygen and release carbon dioxide.
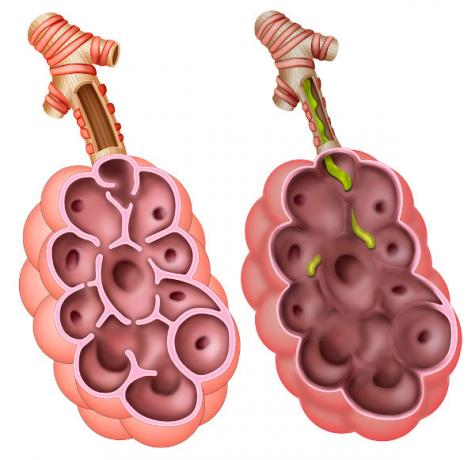
A person with emphysema develops symptoms such as difficulty breathing and chronic cough. In addition, individuals with the problem may have infections repeat breathing. It is important to note that the disease has no cure, however, there are treatments that can improve the patient's quality of life.
The main cause of pulmonary emphysema is cigarette use, therefore, it is essential that this addiction is abandoned. In addition to pulmonary emphysema, cigarette use is related to the development of cancers and contributes significantly to the development of problems such as heart attacks and strokes. In addition to being related to respiratory infections, ulcers, infertility, cataracts, osteoporosis, among other problems.



