floaters are an ophthalmological problem that can affect people and is characterized by the appearance of points, filaments, circles or spots that appear floating in our field of vision. Floaters generally occur due to the natural aging process of our eyes, however, they may indicate the presence of serious eye problems, such as tearing retinal.
Read too: Tips for maintaining children's eye health
Summary of floaters
Floaters is a name used to refer to an eye problem that is characterized by the appearance of spots, filaments, circles or spots in the vision.
In general, floaters are related to the natural aging process of the vitreous body.
In some cases, floaters can be related to serious eye problems such as retinal detachment.
If they are not associated with a serious eye problem, floaters have no treatment.
What are floaters?
Floaters, also called floaters, is a term used to refer to small dots, filaments, circles or spots that appear floating in ourthe field vision. These images are usually perceived when we look at a very bright object, such as a white wall or a sheet of paper. Floaters can appear in one or both eyes and move when we try to look at them.
How do floaters arise?
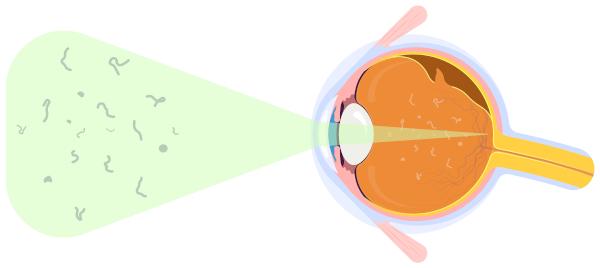
To better understand how floaters arise, we must remember the struture basic of human eye. This photosensitive structure is formed by three tunics: the outer layer, formed by the sclera and the cornea; the middle layer, formed by the choroid, ciliary body and iris; and the inner layer or retina, which ensures communication with the brain through the optic nerve.
The lens, also known as the crystalline lens, is a transparent disc that has the so-called iris, the colored part of the eye, in front of it. The iris, by changing its size, ensures the regulation of the amount of light that enters the pupil.
In the eye it is possible to observe three compartments, one located between the iris and the cornea (anterior camera); another, between the iris and the lens (posterior camera); and another, behind the lens. Behind the lens and surrounded by the retina is the so-called vitreous space, which is occupied by the so-called vitreous body, vitreous humor or vitreous. The vitreous body has the appearance of a transparent gel and stands out for being formed mainly by water and glycosaminoglycans. The vitreous body is the structure that is related to the development of floaters.
According to the Brazilian Council of Ophthalmology (CBO), the vitreous body contracts due to the natural aging process and can separate from the retina at some points. According to the council, the floaters would be “proteins or tiny particles of condensed vitreous, technically called clumps, formed when the vitreous detaches from the retina.”
Read too:Glaucoma — disease that affects the eyes and can cause irreversible blindness
Should I be concerned about floaters?
Generally speaking, floaters disappear quickly. and are not a cause for concern. In some situations, however, they may be associated with eye problems, such as retinal tear, vitreous hemorrhage and uveitis (inflammation that affects the uvea, which is made up of the iris, ciliary body and choroid).
Therefore, it is important to be aware of perceived changes in vision and to seek an ophthalmologist whenever eye symptoms arise. One warning sign is the perception that, in addition to floaters, flashes bright or dimming of vision. In this case, it is essential to seek medical help immediately.
Is there treatment for floaters?
Floaters, as pointed out earlier, are not usually related to serious eye problems,there is no treatment when they are not associated with serious problems. But when they are, for example, related to retinal tears, medical intervention is necessary. According to the CBO, when floaters are symptoms of a tear, the tear must be sealed with laser or cryotherapy. This technique prevents retinal detachment, a serious eye problem that can be responsible for causing blindness.
By Vanessa Sardinha dos Santos
Biology teacher
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/biologia/moscas-volantes.htm


