THE hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver which can have different causes, being classified as viral or non-viral hepatitis. At viral hepatitis are caused by viruses, the most common being those caused by viruses A, B and C.
In the case of non-viral hepatitis, hepatitis caused by alcohol consumption, drug use and autoimmune causes stand out. Hepatitis can be responsible for triggering symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, yellow skin and eyes, dark urine and pale stools, but some hepatitis does not cause symptoms.
Read too:Hemochromatosis — another disease that affects the liver
Topics in this article
- 1 - What is hepatitis?
- 2 - Symptoms of hepatitis
- 3 - Types of hepatitis
- 4 - Hepatitis A
- 5 - Hepatitis B
- 6 - Hepatitis C
- 7 - Hepatitis D
- 8 - Hepatitis E
- 9 - Alcoholic hepatitis
- 10 - Drug-induced hepatitis
- 11 - Autoimmune hepatitis
- 12 - Acute childhood hepatitis of unknown origin
What is hepatitis?
Hepatitis is a liver inflammation which can be mild, moderate or severe. Some types of hepatitis can lead to the development of cirrhosis and even be a risk factor for liver cancer.
Acute hepatitis: is called acute when liver inflammation occurs quickly and abruptly.
Chronic hepatitis: is called chronic when there is persistent inflammation in the liver. Hepatitis B and C often become chronic.
Do not stop now... There's more after the ad ;)
symptoms of hepatitis
Hepatitis affects a person's liver and can often cause no symptoms. When symptoms appear, these can be fever, tiredness, malaise, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dark urine, pale stools, and jaundice. This last symptom is, without a doubt, the best known of the disease and is characterized by the yellow color of the eyes and skin.
types of hepatitis
Viral hepatitis: are those triggered by infection by virus that have primary tropism for the liver. The viruses that cause viral hepatitis that are most clinically relevant are designated by the letters of the alphabet: virus hepatitis A virus (HAV), hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis C virus (HCV), hepatitis D virus (HDV) and hepatitis E virus (HEV).
Non-viral hepatitis: Not all hepatitis is caused by a virus, which is the case with hepatitis caused by the use of alcohol, medication and other chemical substances. There are also hepatitis caused by abnormalities in the Imune system, which in this case is an autoimmune disease.
Hepatitis A
THE hepatitis A, caused by HAV, is hepatitis transmitted through:
water or food contaminated with the virus;
inter-human contact, the main route of contagion being fecal-oral.
The disease can be prevented with the adoption of hygiene measures, adequacy of basic sanitation and also by vaccination. There is no specific treatment for hepatitis A.
Hepatitis B
THE Hepatitis B, caused by HBV, is transmitted through:
unprotected sex;
sharing syringes and needles;
procedures such as hemodialysis;
surgeries, dental interventions, application of piercings and other accessories without proper sterilization of the material or use of disposable material;
transfusion of blood contaminated;
vertical transmission (from mother to child);
occupational accidents with sharps.
The disease can be prevented by vaccinating against hepatitis B, controlling blood banks, not sharing sharp materials and using condoms during sexual intercourse. Hepatitis B éa serious illness and, according to the Pan American Health Organization, in the Americas, new data show that there are 10,000 new hepatitis B infections each year and 23,000 deaths.
According to the organization, only approximately 18% of people living with hepatitis B have been diagnosed. Of these, only 3% receive treatment. Hepatitis B treatment is performed according to the Clinical Protocol and Therapeutic Guidelines for Hepatitis B and Co-infections (PCDT Hepatitis B).
See too: Genital herpes — another virus transmitted through unprotected sex
Hepatitis C
THE hepatitis C, caused by HCV, can be transmitted mainly through:
sharing needles and syringes;
contaminated blood transfusion;
problems in cleaning and disinfecting instruments used in hemodialysis;
procedures in which there is contact with blood and instruments are used without proper sterilization, such as tattoos, surgeries, manicures and piercings;
transplant of contaminated organs.
Less often, the virus can be transmitted through sexual intercourse and vertical transmission..To prevent hepatitis C, it is important to control the blood and organs that will be donated and use disposable materials.
According to data from the World Health Organization (WHO) for hepatitis C, in the region of the Americas, each year there are 67 thousand new infections and 84 thousand deaths. PAHO points out that only approximately 22% of people chronically infected with hepatitis C have been diagnosed, and only 18% of them receive treatment. Treatment follows the recommendations of the Clinical Protocol and Therapeutic Guidelines for Hepatitis C and Co-infections (PCDT Hepatitis C).
Hepatitis D
Hepatitis D, caused by the HDV virus, has the same modes of transmission as hepatitis B, and it is important to note that virus D needs virus B to cause infection in a person. Medical treatment follows the Clinical Protocol and Therapeutic Guidelines for Hepatitis B and Co-infections (PCDT Hepatitis B).
Hepatitis E
Hepatitis E, caused by HEV, has, like hepatitis A, form of fecal-oral transmission. Generally, person-to-person transmission is not common. Hygiene measures and improved sanitation are important strategies to prevent hepatitis E. According to the Department of Chronic Conditions and Sexually Transmitted Infections, Hepatitis E does not have significant prevalence data in Brazil, but it is very common in Asia and Africa.
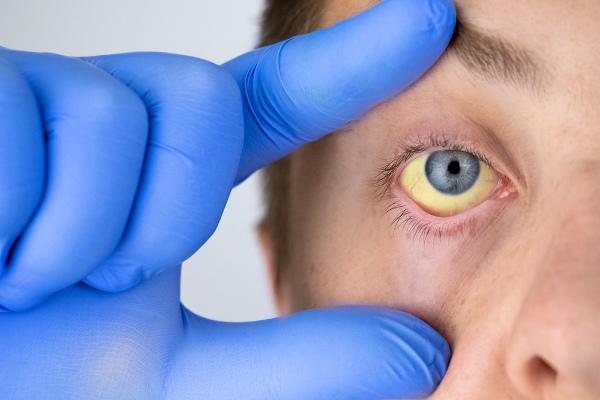
alcoholic hepatitis
Alcoholic hepatitis is a type of non-viral hepatitis triggered by alcohol consumption, and is therefore one of the complications of alcoholism. Alcoholic hepatitis is a pre-cirrhotic lesion.
drug hepatitis
Drug hepatitis, as the name suggests, is a liver damage caused by drug use. It usually manifests between one and 90 days after using the product. The clinical picture is variable and can even lead to death.
In general, the main drugs associated with this type of injury are the antibiotics, anti-inflammatories and anticonvulsants. It is worth noting that herbal medicines and the use of some medicinal plants can also damage the liver, and it is important not to use these products indiscriminately.
Know more: What are the risks of self-medication?
autoimmune hepatitis
Autoimmune hepatitis is a type of hepatitis caused by a immune system failure. In this situation, the organism itself begins to produce antibodies against the liver, triggering inflammation.
Acute childhood hepatitis of unknown origin
On April 15, 2022, the WHO issued a Global alert on cases of severe acute hepatitis no known cause in children at the United Kingdom. After this alert, cases of severe acute hepatitis of unknown cause in children were reported in several parts of the world.
Patients with this type of hepatitis ranged in age from one month to 16 years. All were tested for viruses commonly associated with the disease (HAV, HBV, HCV, HDV, and HEV) and were negative. According to the Pan American Health Organization, as of May 3, 2022, more than 200 cases had been reported in 20 countries.
For the time being, there are no concrete answers about the causes of the infection, however, it is believed that this type of hepatitis may be a consequence of adenovirus infection. Although the relationship with SARS-CoV-2 has not been ruled out, the relationship with vaccines against Covid-19 has already been disregarded. This is due to the fact that most sick children had not received the vaccine against the disease.
As with other types of hepatitis, some of the symptoms presented by patients are yellowing of the skin and eyes, fever, muscle aches, diarrhea, and vomiting. To prevent the disease, which so far is associated with adenovirus, it is important to take care of hygiene, always washing your hands and covering your mouth and nose when sneezing and coughing.
By Vanessa Sardinha dos Santos
Biology teacher

