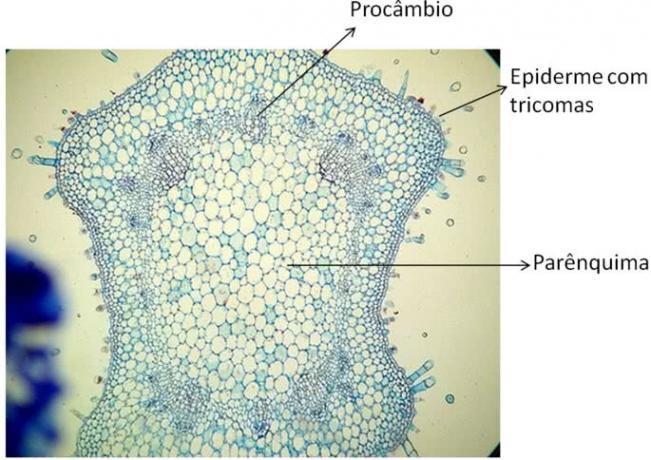
The plasma membrane is one of the parts that make up cells.
It is a thin film that lines the cell, separating the inside from the outside of the cell.
Everything that enters or leaves any cell passes through its plasma membrane. It stays around, protecting and limiting the entire cell.
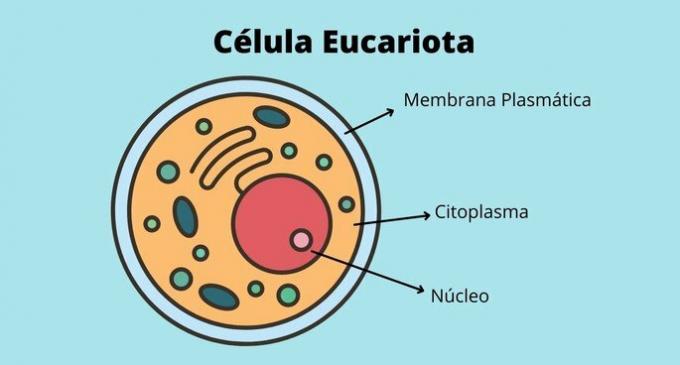
The main characteristics of the plasma membrane are that it is flexible and semi-permeable. Thus, it defines what enters and leaves the cell, isolating the external environment and the other cells.
All chemical reactions in the cell have to do with the selection carried out by the plasma membrane. The passage of substances can happen through osmosis (water) or by the active transport of membrane proteins.
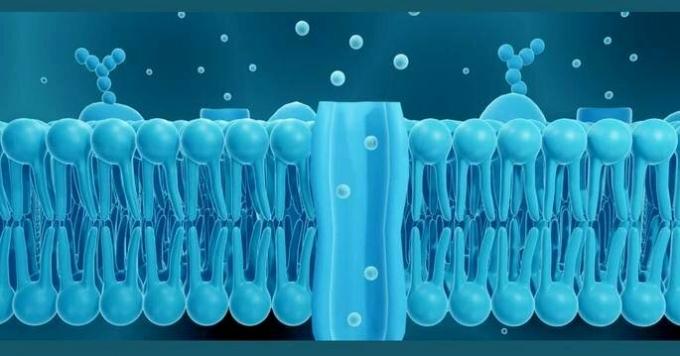
All cells and cell types that exist have a plasma membrane, from the simplest to the most complex. Some organisms also have a cell wall outside the membrane (such as plants, for example).
The function of the plasma membrane
The function of the plasma membrane is like a country border: it selects who enters the cell and who leaves.
There are elements that we need to allow in like glucose, for example. There are others that the membrane must block anyway, like viruses, for example. Just as the closed membrane ensures that the cell's organelles and substances do not come out. It keeps the environment as suitable as possible for the cell to stay alive.
The structure of the plasma membrane
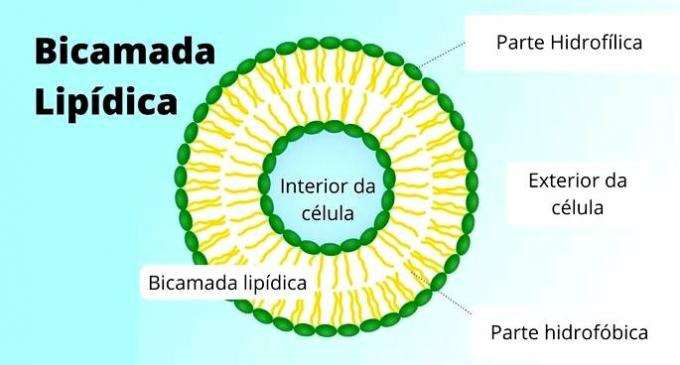
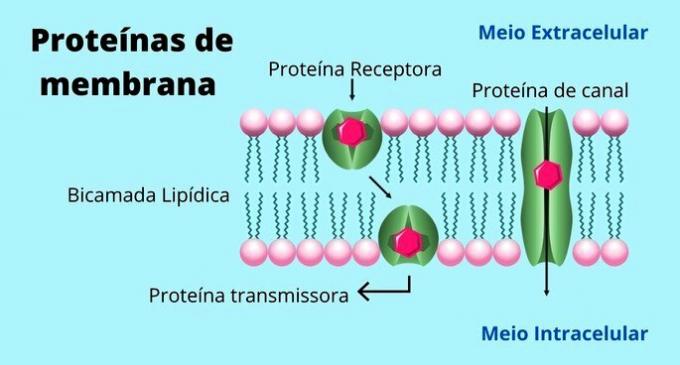
The structure of the plasma membrane is composed of an inner hydrophobic (water repelling) part and an outer hydrophilic (water-thinning) part. This makes it possible for water to exist inside and outside the cell without any liquid being able to pass freely. The name of this structure is phospholipid bilayer.
Interwoven into the phospholipid bilayer, the plasma membrane also has transport proteins. They are the passageways that allow substances to enter and leave the cells.
There are other types of membrane proteins besides transporters. These proteins and their distribution vary from one cell type to another. For example, sodium-potassium pumps in neurons; proteins secreting substances out of cells; receptor proteins that perceive the presence of substances in the external environment, among others.
Bibliographic references
Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Morgan D, Raff M, Roberts K,... & Hunt, T. (2010). Molecular biology of the cell. Artmed Publisher.