You minerals are solid homogeneous substances and generally of inorganic origin, formed by one or more chemical elements, commonly found in nature. Rocks and soils are examples of materials that have minerals in their constitution.
The main characteristics of minerals are:
- Solid and crystalline structure;
- Defined chemical composition;
- Ordered atomic arrangement.
Mineralogy is the branch of science dedicated to the study of minerals. These compounds have distinct properties, which are a result of their well-defined chemical composition and structure. Examples of minerals are quartz, feldspar and calcite.
Minerals are formed in nature by crystallization, recrystallization or chemical reactions. The occurrence of these substances is influenced by the conditions of temperature, pressure and chemical environment.
Examples of minerals
Minerals can be made up of atoms of just one chemical element or of different elements. The atoms arrange themselves and form combinations with definite proportions and definite geometric shapes. Check out the main examples below.
native elements
They are minerals formed by a single chemical element in a non-ionized state. Examples are sulfur, silver, gold and carbon.
O sulfur (S) is a mineral formed by atoms joined by covalent bonds in an octahedral structure (S8). It has a yellow or greenish-yellow color and can be found in active or extinct volcanoes.

THE graphite consists of carbon atoms (C) linked in a hexagonal lattice. This natural form of crystalline carbon has a metallic luster and a gray to metallic color. It is found in metamorphic and igneous rocks.

sulfides
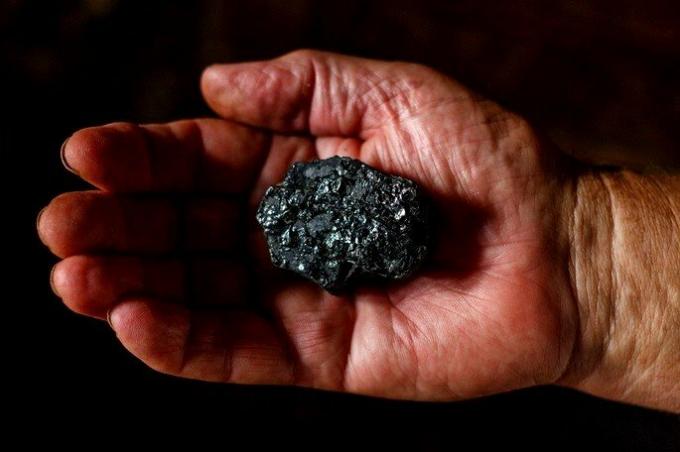
Sulfides are basically formed by the sulfide anion (S2-) and metal cations. Examples are galena and pyrite.
THE galena is a lead sulfide mineral (PbS), formed by 86.6% lead (Pb) and 13.4% sulfur (S). It has a metallic luster and a silvery appearance because of its lead gray color. It can be found in sedimentary and metamorphic rocks.
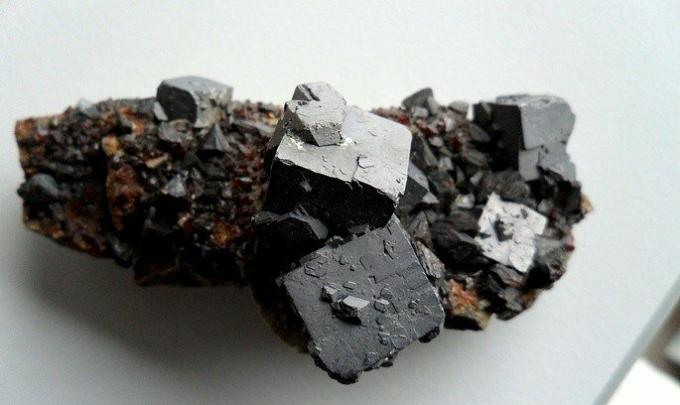

THE pyrite is an iron disulfide mineral (FeS2), formed by 53.4% sulfur (S) and 46.6% iron (Fe). Because of its appearance, with its metallic luster and yellow-brass color, it is known as fools gold. It is commonly found in sedimentary rocks, but can be part of igneous rocks and metamorphic deposits.
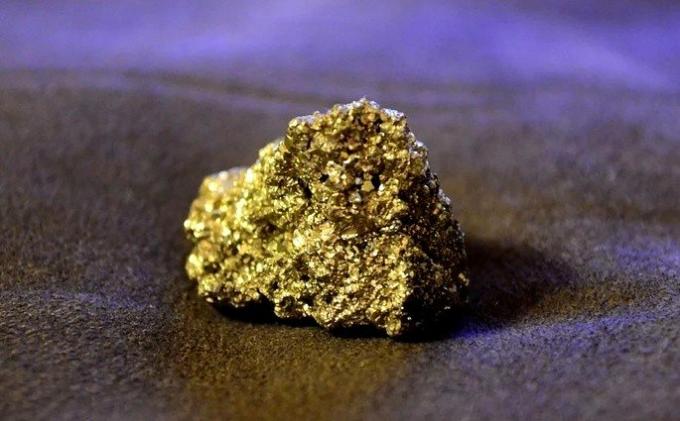

sulfates
Sulfates are basically formed by the sulfate anion () and metal cations. Examples are barite and anhydrite.
THE barite is a barium sulfate mineral (BaSO4), formed by 34.4% sulfur trioxide (SO3) and 65.7% lead oxide (PbO). Its appearance is of a vitreous luster and a whitish color. It is found in sedimentary rocks and limestone veins.

THE anhydrite is a calcium sulfate mineral (CaSO4), formed by calcium (Ca) and sulfate. Its appearance is a clear mass, ranging from white to gray, similar to plaster. It is found in hydrothermal veins and lining salt formations.

silicates
They are minerals that have chemical species formed by the elements oxygen (O) and silicon (Si), such as SiO2 and SiO5, combined with other chemical elements. Examples are quartz and kyanite.
O quartz, formed by silicon dioxide (SiO2), is one of the most known and used minerals. This material has a whitish color and a vitreous luster, but due to the presence of impurities, it can also present other colors.

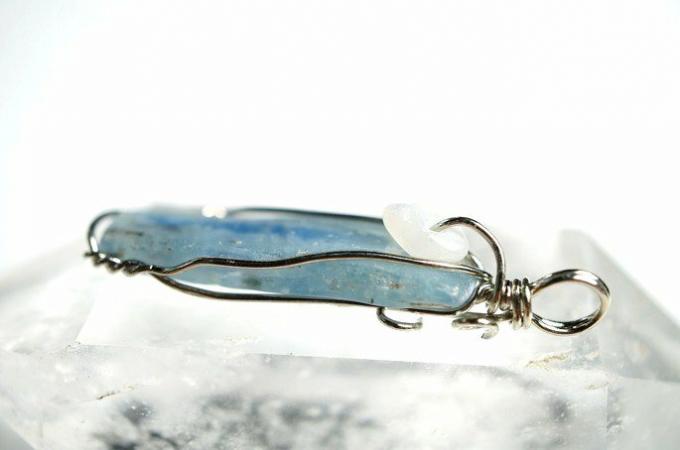
THE kyanite (Al2SiO5), formed by 62.92% of aluminum oxide Al2O3 and 37.08% silicon dioxide (SiO2), is extracted from aluminous rocks and used in the manufacture of refractory porcelain. This mineral has a transparent appearance and different colors, such as blue, gray and green.

Learn more about the metals.
Classification of minerals
In terms of composition, minerals are classified as metallic and non-metallic. Metallic minerals contain metals such as iron, magnesium and aluminum in their composition, and therefore are good conductors of electricity and heat.
Non-metallic minerals have only non-metallic chemical elements in their composition. For example, diamond is made up of the chemical element carbon.
The aggregate of one more minerals form the rocks. These minerals are classified into:
- essential mineral: is usually found in greater quantity and characterizes the type of rock.
- accessory mineral: characterize special crystallization conditions.
- secondary mineral: they are united to the rocks after being formed.
Strategic minerals are those used in industries and economically exploited as raw material for the production of consumer goods.
Learn more about Mineral Kingdom and about the Types of Rocks.
Minerals in food
Foods are classified according to their origin as plant, animal and mineral. The best known minerals are in the form of salts. You mineral salts important for the functioning of our organism are:
- Calcium
- Iron
- Magnesium
- Phosphor
- Potassium
- Sodium
- Zinc
- Manganese
Also read about foods of mineral origin.