THE climate temperate is present in the temperate zones of the planet, situated between the tropics and the poles in both hemispheres. This climate type is characterized by the distinction between the four seasons, thermal amplitude annual which can be accentuated, rains well distributed during the year and mild average temperatures. He It is classified into continental temperate, oceanic temperate, Mediterranean and subtropical. The last type is present in the states of the southern region of Brazil.
Read too: The relationship between latitude and climate
temperate climate summary
Temperate climates occur between the tropics and the polar circles, therefore in the temperate zones of the planet Earth.
They are characterized by mild temperatures, annual thermal amplitude that varies from moderate to severe and rains well distributed throughout the year. In it, it is possible to identify the four seasons of the year.
Typical vegetation is temperate deciduous and temperate rainforests.
This climate is subdivided into continental temperate, oceanic temperate, Mediterranean and subtropical.
In Brazil, it is equivalent to the subtropical climate, predominant in region sul.
Characteristics of the temperate climate
the temperate climate is a type of climate characteristic of mid-latitude regions, located in the temperate zones of the planet, located between the tropics and the polar circles in both the northern and southern hemispheres. In these areas, the sun's rays reach the surface at an angle, thus conditioning a lower incidence of heat and the occurrence of milder annual temperatures than in casualties latitudes.
One of the main characteristics of temperate climates is the distinction between the four seasons of the year: summer, autumn, Winter and spring. In addition, rainfall varies from moderate to intense and occurs throughout the year, thus being well distributed. The annual and daily thermal amplitude, and consequently the average temperatures, vary according to the location (inland or coastal) and the influence of the Climatic factors.
In general, temperate climates can have relatively hot, rainy summers and cold, wet winters. low rainfall, or even mild summers and severe winters, with high rainfall throughout the year. In some areas, mainly in the continental temperate climate variation, there is in the coldest season of the year the record of frosts or even snowfall.
temperate vegetation

The temperate forest is the type of vegetation characteristic of temperate climate regions.. They are formed by a wide variety of plant species, which includes trees large, small and medium-sized, shrubs, grasses and undergrowth.
This type of vegetation is classified as deciduous forest., composed of trees that lose their leaves in one of the seasons (autumn or winter), and also as rain, which occurs in regions with an oceanic climate, where rainfall is high throughout the year and there is great availability of moisture, providing the existence of perennial plants, which do not change their structure in any period, and of large size, with tens of meters of height.
Some of plants present in temperate forests are:
Oak;
beech;
sequoia;
elm;
walnut;
Willow tree;
birch;
wild mulberry;
magnolia;
chestnut tree;
fir;
cedar;
board;
grass;
moss.
temperate climate fauna

Just like the flora, the fauna of the temperate climate is very diverse and varies significantly according to its area of occurrence. It has been in this climatic domain since great mammals even small rodents and insects.
Some of Animals present in temperate lands are:
bears (black, panda, brown);
moose;
deer;
wolves;
foxes;
coyotes;
bobcats;
wild boar;
squirrels;
rabbits;
woodpeckers;
owls.
See too: Biodiversity — the term used to indicate biological diversity
Temperate climate classifications
In temperate climates there are some subdivisions resulting from the greater or lesser interference of certain climatic factors, which conditions important regional differences.
At two main classes of temperate climates they are:
continental temperate
The temperate continental climate gets its name because takes place within the continents of temperate regions. It is characterized by slightly warmer summers than in coastal regions, with an average of 20 °C, and very cold winters, registering temperatures below 0 °C, frosts and even precipitation in the form of snow.
THE annual temperature range is very pronounced, and the difference can vary by 20 °C and 30 °C between the hottest and the coldest period. The rainfall is lower than in the continental temperate and fluctuates between 500 and 1000 mm per year. The summer months are relatively wetter than the winter months.
oceanic temperate
The temperate oceanic climate occurs in coastal areas or near the coast. This climate type is characterized by milder summers than continental temperate, with average temperatures of 18 °C and cold winters. The temperatures of the coldest months are around 7 °C, and the annual temperature range is low.
Summers concentrate less rainfall than winters, which are more humid. Annually, the accumulated rainfall can reach 1500 mm and even exceed 2000 mm in certain locations.
the climates mediterranean and subtropical are also some variations of the temperate climate. The first is predominant in cities and regions bathed by the Mediterranean Sea and resembles the oceanic temperate in terms of temperature, but annual rainfall is much lower (350 mm to 600 mm), especially in summer. The second occurs mainly in the southern hemisphere and has a high moisture content.
Temperate climate location

the temperate climate is characteristic of the temperate zones of the planet. It occurs in regions located between the Arctic Circle (66°N) and the Tropic of Cancer (23°27'N) and between the Tropic of Capricorn (23°27'S) and the Antarctic Circle (66°S).. Therefore, the presence of this type of climate is observed in the following territories:
Europe;
North America;
Countries and regions in southern South America;
extreme north and south of Africa;
east and southwest of Australia and in New Zealand;
Northwest, west and eastern part of Asia.
Know more: Difference between weather and climate — understand these concepts
temperate climate in Brazil
In Brazil, the temperate climate is identified as being the subtropical climate. It occurs in the areas below the Tropic of Capricorn, comprising the southern end of the state of São Paulo, most of the Paraná and the states of Santa Catarina and Rio Grande do Sul.
The Brazilian subtropical climate is characterized by distinction between the four seasons and well-distributed rainfall throughout the year. The annual thermal amplitude is high, with the occurrence of hot summers, which can reach maximums of 30 °C, and cold winters, which mark temperatures below 18 °C. In some areas, thermometers record negative lows.
In addition to the rains, the coldest months of the temperate climate are marked by the occurrence of frost and precipitation in the form of snow in certain cities. predominantly, The vegetation is formed by the pampas or grasslands and the araucaria forest.
Exercises solved on temperate climate
question 1
(Unesp) Analyze the climograms of figures A and B.
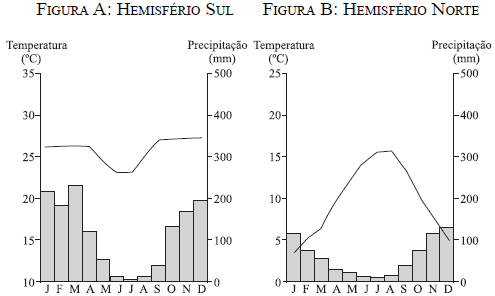
(J. THE. Ayoade, 2003)
Tick the alternative that presents the correct sequence of the two weather types represented.
a) Tropical climate and oceanic or maritime temperate climate.
b) Tropical climate and continental temperate climate.
c) Subtropical climate and temperate oceanic or maritime climate.
d) Subtropical climate and continental temperate climate.
e) Mediterranean semi-humid climate and oceanic or maritime temperate climate.
Resolution:
Alternative A
First of all, remember that the solid line indicates the temperature, read on the vertical axis on the left, and the columns represent the monthly volume of rainfall, arranged on the axis on the right. Climagram A presents humid and hot summers and mild and dry winters, thus characterizing a tropical weather. The climogram B indicates a high thermal amplitude, with cold and humid winters and hot and relatively dry summers, as in oceanic temperate climates.
question 2
(Unicamp) The map below highlights the area of occurrence of the Pampas, in Brazil. In addition to presenting soils susceptible to erosion, the Pampas are characterized by:
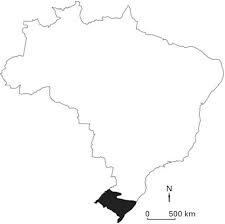
a) by arboreal vegetation, in an area with a temperate climate, subject to gullying processes resulting from the elimination of vegetation cover.
b) by arboreal vegetation, in an area with a subtropical climate, subject to sandization processes resulting from the elimination of vegetation cover.
c) by grass vegetation, in an area with a subtropical climate, subject to sandization processes resulting from the elimination of vegetation cover.
d) by grass vegetation, in an area with a temperate climate, subject to gullying processes resulting from the elimination of vegetation cover.
Resolution:
Alternative C
The vegetation of the Pampas is formed predominantly by grasses and occurs under the subtropical climate. Due to the intensive use of soils in these areas, which is mainly due to the advance of agricultural activities, they have become more susceptible to the process of sandization. This is a recurring environmental problem in the Pampas biome, which has shallow sandy soils.
Thus, with the removal of vegetation cover for the constitution of pastures and monocultures (only of soy and eucalyptus, for example), the soil is unprotected and more prone to degradation by the action of erosive agents, such as winds and rain, resulting in the appearance of deposits or patches of sand.
The gully consists of erosion caused by rainwater in deforested areas, giving rise to gullies, large holes in the ground that, due to their depth, can reach the water table water table. Although this phenomenon also occurs in the Pampas, sandization is more common because of the natural predisposition of the soil in this region.
By Paloma Guitarrara
Geography teacher
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/geografia/clima-temperado.htm