THE francium, symbol Fr, atomic number 87, is an element belonging to Group 1 of Periodic table, the alkali metals. However, unlike the other elements of the group, francium does not have stable isotopes, which even made its discovery difficult. In fact, francium was the last element to be discovered and isolated in natural samples.
Its great atomic instability does not allow to obtain visible and heavy samples, therefore, its physicochemical properties are extrapolated from the data of other alkali metals. It is estimated that there are only 30 grams of francium in the earth's crust, which makes it the second rarest element on the planet, behind only the astatine.
Read too: Rubidium — element used in the manufacture of special glasses and atomic clocks
francium summary
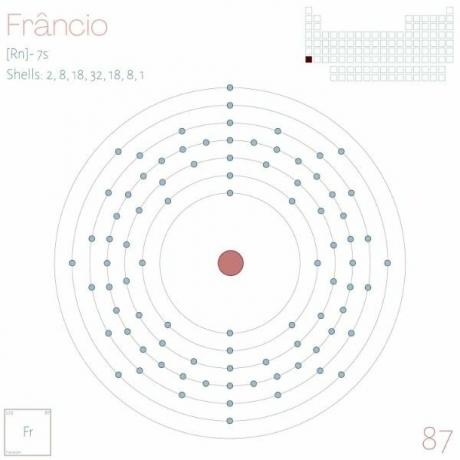
Francium is an alkali metal located in the seventh period of the Periodic Table, symbol Fr, Z = 87.
It has no stable isotopes and is the second rarest element on the planet.
Its most stable isotope has a time of half life 22 minutes.
It is the element with the greatest atomic ray of the Periodic Table, in addition to being the most electropositive.
It can be obtained only by nuclear processes, being difficult to isolate.
There are still no practical applications related to francium.
Francium Properties
Symbol: Fr.
atomic mass: 223.02 u.
Fusion point: 22°C (estimated).
Boiling point: 665 °C (estimated).
Density: 2.5 g/cm³ (estimated).
electronegativity: 0,79.
Eletronic distribution: [Rn] 7s1.
→ Video lesson on periodic and aperiodic properties of chemical elements
Francium Characteristics
the francium has several isotopes, but isotope 233 is the most stable, reaching a half-life of 22 minutes. Only isotope 212 has a similar half-life of 21 minutes, while the others don't even come close to that, and may even have half-lives on the order of seconds.

all this atomic instability hinders the determination of important physical characteristics and properties. In fact, the known properties were obtained under extreme conditions. dilution (concentration of the order of 10-15 mol/L).
As an alkali metal, its oxidation number is known to be +1. Experiments have also shown that francium is the most element electropositive of the Periodic Table. Another leading position that this element has in the table is the one with the largest diameter, with 2.7 angström (10-10 m).
Like other alkali metals, francium remains in solution while other elements precipitate in the form of hydroxides, carbonates, fluorides, sulfides, chromates, etc.
Read too: What are radioactive elements?
Obtaining francium
Francium-223, the most stable isotope of Fr, was first detected through the alpha emission of actin-227. It is also possible to produce francium (isotope 212) by bombarding gold (197Au) with oxygen-18 (18O) in a nuclear reactor.
Frantium can be obtained in a number of ways. For example, there is the possibility of precipitating it with the cesium, through salts sparingly soluble elements such as perchlorate (ClO4-), hexachloroplatinate (PtCl62-), iodate (IO4-), between others. However, separation of cesium and francium is expected to be very difficult.
Other methods developed in the 1960s and 1970s allowed the separation of francium from cesium and rubidium solutions through cation exchange resins. Frantium-223, which was discovered from the alpha emission of actinium-227, can also be separated from actinium and other breakdown products by selective precipitation techniques. There is also another technique used with relative success: the sublimation of francium chloride (FrCl) at temperatures around 300 °C.
Applications of francium
Tests with rats concluded that francium accumulates in the kidneys, liver and salivary glands. In addition, there was an attempt to apply it in nuclear medicine, in the diagnosis of cancer, but the difficulty in preparing and isolating it made the project unfeasible. This characteristic, added to its low half-life, makes francium one of the few elements no practical applications.
However, the fact of having the largest atomic radius of the Periodic Table and having only one electron in the valence layer keeps some researchers curious about its nature. In 2002, a group of researchers in the United States managed to trap 300,000 francium atoms to find out more about the element.
Check out our podcast: Hard as a diamond: what does it mean?
history of francium
What stands out in the history of francium is the number of times people said they discovered it after Mendeleev predict the existence of this element in 1871, under the name of eka-cesium.
It has long been known that after element 83, bismuth, the Periodic Table shows only radioactive and unstable elements—with exceptions such as uranium and thorium. Even so, this has not discouraged many scientists from looking for element 87 in natural sources and, more often than not, claiming its discovery.

For example, in 1925, Russian chemist Dobroserdov observed a weak radioactivity in a sample of potassium, concluding that this would be element 87 and naming it russium, in honor of his native country. However, the best explanation for the fact was that, in fact, radioactivity from the isotope was detected. 40K, a beta emitter that makes up about 0.012% of natural potassium.
In 1926, the English chemists Druce and Loring, when analyzing spectral lines of manganese (II) sulphate, they also presumed to observe some lines relating to element 87, for which they later proposed the name of alkalinium. However, the weakness of the evidence discouraged researchers from moving forward.
Then, in 1930, Fred Allison claimed the discovery of element 87 after some experiments with samples of polucite (an ore rich in cesium) and lepidolite (an ore with lithium in its composition). Allison proposed the name virginium in honor of the US state of Virginia. However, in 1934, MacPherson demonstrated inaccuracies in Allison's discovery.
Two years later, Jean Perrin, a French physicist known to have confirmed Einstein's theory of Brownian motion, providing, thus, sufficient evidence for the existence of atoms, joined the Roman physicist Horia Hulubei in a series of experiments with rays X. They then obtained expected results for element 87, which they promptly named moldavium, in reference to the Moldova region, birthplace of Hulubei. However, again, the work was criticized in light of the interpretations.
None of the researchers could understand, but what happened is that francium has very unstable isotopes, with a very short half-life. The misfortune was such that the inexistence of element 87 was even considered.
However, in 1939, the discovery of element 87 occurred by someone who started out as a laboratory assistant to none other than Marie Curie, in Paris: The French Marguerite Perey. With good expertise in handling and purifying radioactive samples, Perey was tasked with analyzing a radioactive sample of actinium, element 89.
the scientist was the first to observe the alpha and beta emissions produced by actinium, revealing a new element with a half-life of 21 minutes. The French woman then cautiously announced her discovery and, in 1946, defended her doctoral thesis Element 87: Actinium-K.
The new element was then named francium, in honor of its native country, initially with the Fa symbol. In 1949, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (Iupac) confirmed the element with the name given by Perey, but in 1951 changed the symbol to Fr.
Solved exercises on francium
question 1
Frantium (Fr, Z = 87) is an alkali metal with a short half-life and is unstable. However, it is known to have some properties similar to other alkali metals.
Based on the above information, what is the likely compound formed between francium and bromine (Br, Z = 35)?
A) FrBr2
B) Fr2br
C) FrBr
D) FrBr3
Reply
Frantium, as an alkali metal, has NOX equal to +1. Already the bromine, a halogen, in the absence of oxygen has NOX equal to -1. Therefore, the most likely compound among them is the letter C, FrBr.
question 2
The atomic radius is an extremely important periodic property, as it not only differentiates atoms in terms of their sizes, but also helps to understand the reactivity and other properties of atoms.
Among the elements of the Periodic Table, the element that has the largest atomic radius is:
A) F
B) Cs
C) H
D) Fr
E) Og
Reply
It is known that the atomic radius is greater the greater the period of the element and the smaller the number of electrons in the valence layer. Thus, the element with the largest radius is francium, Fr, as it is in the seventh period of the Periodic Table and has only one valence electron.
By Stéfano Araújo Novais
Chemistry teacher
