In biology, the kingdom is a type of organization used to group individuals according to the similarity between structural, anatomical and genetic characteristics.
You five biological kingdoms they are:
- Animal Kingdom, Animalia or Metazoa
- Vegetal Kingdom, Plantae or Metaphyta
- Protist or Proctist Kingdom
- Kingdom Fungi
- Kingdom Monera
The first organization of living beings into kingdoms was created by Aristotle, dividing them into animals and plants, which was confirmed by Carl von Linnée according to the analysis of characteristics.
In 1866, the German biologist Ernst Haeckel was responsible for the creation of the Protista kingdom and in 1956 Herbert Copeland organized the Monera kingdom. Finally, in 1969, biologist R.H. Whittaker also proposed the inclusion of the fungal kingdom, totaling five kingdoms.

Characteristics
Living beings have characteristics that together differentiate them from non-living beings. By organizing organisms according to similarities we can group them into realms and thus distinguish them from one another.
The main features are:
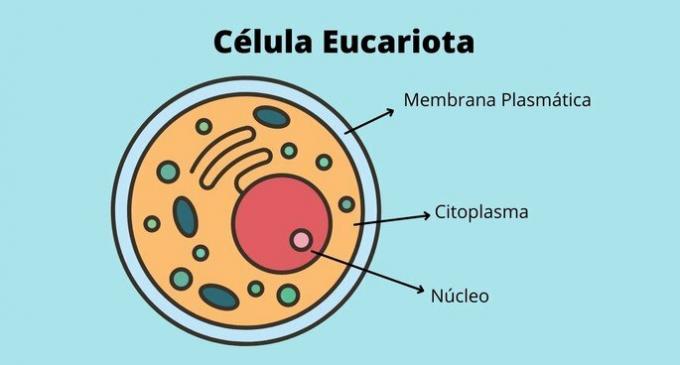
O cell type divides living beings that have eukaryotic cells, with a well-defined cell nucleus, and prokaryotic cells, where the genetic material is dispersed in the cytoplasm.
THE cell organization distinguishes beings in unicellular, formed by a single cell, and multicellular, when they are constituted by countless of them.
THE nutrition differentiates autotrophic beings, capable of producing their own food, from heterotrophs that feed on other beings.
THE reproduction of living beings can occur sexually, by the union of two members of a species, or generate descendants by asexual reproduction, where a single organism is capable of generating others.
THE breathing it is essential and can be aerobic for beings that need oxygen to survive or anaerobic for those that do not need this element.
Learn more about the characteristics of living beings.
Animal Kingdom
O animal Kingdom it is a realm that presents beings that are quite distinct in anatomy and physiology, but that have the following characteristics:
- Nutrition: they are heterotrophs
- Cell type: have eukaryotic cells
- Cell organization: they are multicellular beings
- Reproduction: most reproduce by sexual reproduction
- Breathing: perform aerobic breathing
Examples of beings from the animal kingdom
Animals are classified as vertebrates, from the Phylum of Cordados, due to the presence of a vertebral column. The classes with examples of animals are:
- Fish: shark, sardine and seahorse
- Amphibians: frog, salamander and blind snake
- Reptiles: snake, alligator and lizard
- Birds: ostrich, peacock and hen
- Mammals: cat, monkey and bat
There are also invertebrate animals, which are characterized by the absence of a dorsal column and there are several phyla that fit this classification. Some examples of animals are: squid, slugs and earthworms.
In a food chain, animals, which are heterotrophic by ingestion, are inserted as consumers, being able to feed on autotrophs or other animals.
plant kingdom
O plant kingdom presents living beings with the following characteristics:
- Nutrition: they are photosynthetic autotrophs
- Cell Type: Eukaryotes
- Cell organization: multicellular
- Reproduction: sexual or asexual, depending on the plant
- Breathing: aerobic
Although plants and animals have the same cell type, plant cells have different structures, such as vacuoles, chloroplasts and cellulose in the cell wall.
Examples of beings from the vegetable kingdom
Taking into account the sap-conducting vessels, plants are classified as vascular, when they have the structure, and avascular, if they don't.
Examples of vascular plants are:
- Pteridophytes: fern, mackerel and maidenhair fern
- Gymnosperms: pine, araucaria and cedars
- Angiosperms: orange, mango and coconut trees
Avascular plants are bryophytes, such as mosses, which are small and grow in humid places and do not receive direct sunlight.
There are also parasitic plants that have different nutrition from others, as they need other plants to survive and therefore are heterotrophic.
Kingdom Fungi
O fungi kingdom presents macroscopic and microscopic living beings with the following characteristics:
- Nutrition: they are heterotrophs
- Cell Type: Eukaryotes
- Cell organization: single or multicellular
- Reproduction: sexual or asexual
- Breathing: aerobic or facultative anaerobic (in low oxygen environments)
Examples of beings from the fungi kingdom
Many macroscopic fungi are used in food, such as champignon mushrooms, and in food production, such as yeasts used in the fermentation of beverages and breads.
Other examples of fungi are:
- Yeasts: multicellular fungi with hyphae
- Molds: fungi that arise in organic matter
- Lichens: species that arise from the association of fungi with other organisms, such as algae and cyanobacteria.
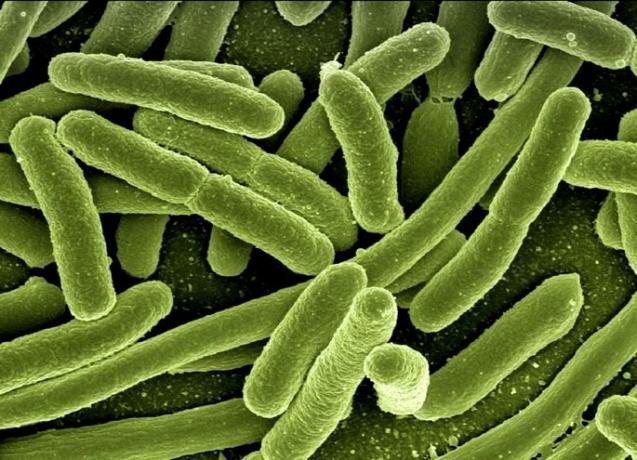
Kingdom Monera
O monera kingdom presents living beings with the following characteristics:
- Nutrition: autotrophs or heterotrophs
- Cell Type: Prokaryotes
- Cell organization: unicellular
- Reproduction: sexual or asexual
- Breathing: aerobic or facultative anaerobic (with or without oxygen)
Examples of beings from the Monera Kingdom
The Monera kingdom is made up of simple microscopic beings. There are thousands of bacteria, which live in the most diverse environments. These beings are grouped according to their structure into cocci, bacilli, spirils and vibrios.
Cyanobacteria are also part of this kingdom and are photosynthetic. Blue or cyanophyceous algae live in isolation or form colonies.
Protist Kingdom
O protist kingdom presents living beings with the following characteristics:
- Nutrition: autotrophs or heterotrophs
- Cell Type: Eukaryotes
- Cell organization: single or multicellular
- Reproduction: sexual or asexual
- Breathing: most perform aerobic breathing
Examples of beings from the protist realm
Examples of protozoa, classified according to locomotion, are:
- Sarcodines: amoebas
- cilia: paramecium
- Flagellates: Trypanosoma cruzi
- Sporozoa: malaria-causing plasmodia
Algae, on the other hand, are photosynthetic autotrophic organisms and because they have a simpler structure, they were included in this group. By type of pigment, algae are classified as green, red, brown or gold.
current ranking
The classification into realms is the most comprehensive for classifying living beings. To distinguish species, within a kingdom there are other categories that group organisms, the so-called taxonomic categories:
Kingdom → Phylum → Class → Family → Gender → Species
There are also studies that indicate the existence of at least one more kingdom, proposed by Carl Woese, in 1977, in addition to the 5 previously mentioned. According to the researcher, the Monera Kingdom should be extinct and the beings divided between the Bacteria and Archea kingdoms.
Although organisms from the Bacteria and Archea realms are prokaryotic and unicellular, beings from the Archea realm have characteristics closer to those of eukaryotic beings.
Learn more about classification of living beings
Exercises on realms of living things
question 1
Of the realms of living beings, the only one that DOES NOT contain eukaryotic organisms is:
a) Kingdom of Monera
b) Protist Kingdom
c) Kingdom Fungi
d) Metaphyte Kingdom
Correct alternative: a) Kingdom Monera.
This kingdom is formed by prokaryotic and unicellular microscopic organisms: bacteria and cyanobacteria (blue or cyanophyceous algae).
question 2
The realm that presents beings that constitute the base of the food chain as it is formed by autotrophic organisms is:
a) Protist Kingdom
b) Animal Kingdom
c) Kingdom Fungi
d) Plant Kingdom
Correct alternative: d) Plant Kingdom.
Plants are at the base of the food chain because they are capable of producing their own food. Because they produce organic matter, these beings feed heterotrophs and without plants there would be no life on Earth.
question 3
Animals and plants are grouped into different kingdoms. Although they are made up of eukaryotic cells, some of the characteristics that distinguish these types of living beings are, EXCEPT
a) Size and shape
b) Cell wall
c) Cell organelles
d) Cell complexity
Correct alternative: d) Cellular complexity.
The eukaryotic cell is the most complex cell type that exists, as it has an individualized nucleus delimited by a membrane. However, the differences between animal and plant cells are:
Size and shape: the animal cell is irregular in shape, while the plant cell has a fixed shape.
Cell wall: is present only in plant cells and is formed by cellulose.
Cellular organelles: vacuoles, glyoxisomes and plastids are components present only in plant cells.
question 4
Define what realm is and identify the five existing realms to classify living beings.
Answer suggestion:
Reino is a classification used in Biology to group living beings according to structural, anatomical and genetic characteristics.
The five biological kingdoms group living beings into:
animalia kingdom
Kingdom Plante
Kingdom Fungi
Kingdom Monera
Protist Kingdom
Gain more knowledge with the contents:
- What are living beings?
- living beings and non-living beings
- Exercises on classification of living beings