We say that a compound has mixed functions when it has more than one function in its structure. The nomenclature of compounds with mixed functions is always done considering only one of the functions as the main one, whose prefix will be the only one to be part of the name of the substance. The other functions will be indicated by specific prefixes.
The order of priority to consider a function as the main one is indicated in the table below:

Thus, the carboxylic acid is considered the main functional group in a mixed chain compound. In its absence, the aldehyde is the main one and so on.
Let's look at some examples to better clarify how this nomenclature is put into practice:

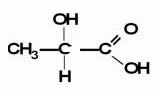
Note that the two functions present in this compound are: carboxylic acid and alcohol. As the carboxylic acid is first in order of priority, it will be the main one, so we have to write the word at the beginning. "acid" and the suffix that will appear will be the "Hi co". The OH group, that is, of alcohol, will be identified by the prefix
"hydroxy". It is also necessary to number which carbon this last functional group is coming out of. Carboxylic acid always comes at the end of the carbon chain, so it is not necessary to indicate its position.Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
The remainder of the chain corresponds to 3 carbons (prop), linked with only single links (an).
Thus, we have that the official name of this compound is given by:
2-hydroxy-propanoic acid
This compound is better known as lactic acid, as it is present in milk and in muscles as well.
 br
br
│
H3C CH ─ CH2 ─ NH2
In this case, the amine is the main group, as this group comes before the organic halides, of which the bromine group is a part. So the suffix will be "the mine" and the prefix will be "bromine". In this case, it is necessary to locate the position of the two functional groups:
2-bromopropan-1-amine
 NH2
NH2
│
H2C ─ C═O
│
oh
The main function is acid, so its suffix is oic; and the secondary function is the amine, which will be indicated by the prefix amino:
Aminoethanoic acid or aminoacetic acid
This last structure corresponds to the glycine, a constituent amino acid of proteins.
Some common names were mentioned, because normally the compounds with mixed functions have a very complex nomenclature to memorize. Thus, until now, many usual nomenclatures are adopted.
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FOGAÇA, Jennifer Rocha Vargas. "Nomenclature of compounds with mixed functions"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/nomenclatura-compostos-com-funcoes-mistas.htm. Accessed on July 27, 2021.



