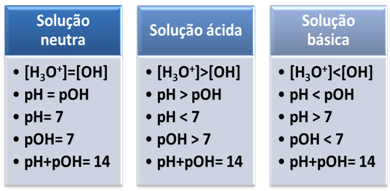
- Neutral medium:
A medium is considered neutral if it has the same concentration, in mol/L, of the hydronium ions (H3O+) and hydroxide (OH-).
An example of a neutral medium that even serves as a standard for other solutions is pure, distilled water at a temperature of 25ºC. At this temperature, it has exactly 1. 10-7 mol/L of both ions. Hence, your ionic product (Kw) is equal to 10-14 (mol/L)2:
Kw = [H3O+]. [oh-]
Kw = (1. 10-7 mol/L). (1. 10-7 mol/L) = 10-14 (mol/L)2
The pH and pOH are given below:
pH= - log [H3O+] pOH= -log[OH-]
pH= - log 1. 10-7 pOH= - log 1. 10-7
pH = 7pOH = 7
This shows us that, in a neutral solution, the pH is equal to pOH.
- Acid medium:
In an acidic medium, the concentration of H ions3O+ is larger than that of OH ions-.
Such a solution can be achieved by adding a small part of the H ions3O+, for example, by means of an acid.
According to Le Chatelier's principle, when a disturbance is caused to a system in equilibrium, it tends to readjust itself in order to reduce the effects of this force. This means that if an acid is added to water, the H ions
3O+ they will be in excess and the balance will shift in the reverse reaction direction, to the left. So these excess ions will react with the OH ions-. Thus, the concentration of OH ions- will decrease and the solution will become acidic.Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)

The ionic product (Kw) is always equal to 10-14, but the concentration of H ions3O+ is greater than the concentration of OH ions-1. Therefore, the pH is greater than the pOH in an acidic medium, but its sum always equals 14.
Also, the greater the concentration of H ions3O+, the greater the pH value. At room temperature (25°C), pH < 7 and pOH > 7.

- Basic means:
In the basic medium, the concentration of OH ions- is larger than that of H ions3O+.
If we add a base to water, it means we are adding OH ions.- and, as explained in the previous item, by Le Chatelier's principle, the equilibrium of the reaction of self-ionization of water will move in the opposite direction, with excess ions reacting with H ions3O+, decreasing your concentration and making the solution basic.
In that case, the pOH will be greater than the pH. At room temperature (25°C), pH > 7 and pOH < 7.

Briefly:
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FOGAÇA, Jennifer Rocha Vargas. "Neutral, acidic and basic media"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/meios-neutro-acido-basico.htm. Accessed on July 27, 2021.


