Alcohols are compounds that have the hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to a saturated carbon in an open or closed chain.*
Thus, its official nomenclature, according to the IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry), takes into account the hydroxyl in the suffix, that is, in the termination. The rest of the chain name follows the same rules established for hydrocarbons.
Thus, we have the following nomenclature rule for alcohols:

Examples:
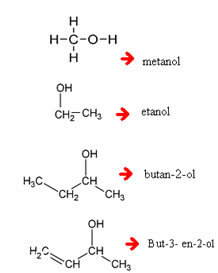
Note that, when necessary, you must enumerate which carbon the hydroxyl is coming out of.
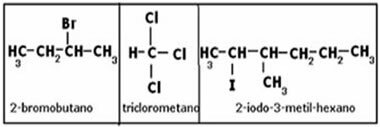
In the case below, we have a branched alcohol. Thus, it is necessary to choose the main chain, which has to be the one that contains more carbons and in which the hydroxyl is. Also, the numbering should be as close as possible to the functional group (OH). The branches are the first to be cited:

Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
These mentioned alcohols are actually monoalcohols or monools. When we have polyalcohols, that is, with more than one hydroxyl, it is necessary to put prefixes that indicate the amount, such as di, tri, etc. Note the example below:

Usual Nomenclature:
A commonly used nomenclature is:
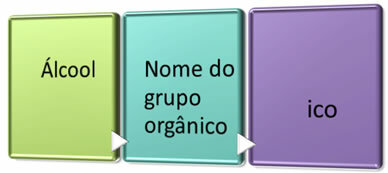
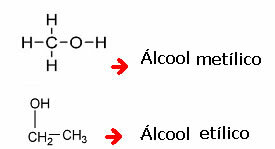
So we have:
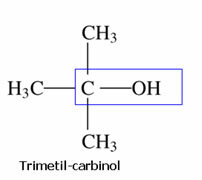
Kolbe's Nomenclature:
This nomenclature is very old and was invented by this scientist, Kolbe, who called methanol carbinol. So, just cite the rest of the molecule and add the word carbinol:
* For more information about what characterizes an alcohol, read the text "alcohols”
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Brazil School Team
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FOGAÇA, Jennifer Rocha Vargas. "Official nomenclature of alcohols"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/nomenclatura-oficial-dos-alcoois.htm. Accessed on July 27, 2021.
Chemistry

Access this link and learn about the organic function of phenols, a group of oxygenated substances, from great reactivity, whose acidity is greater than that of alcohols (compounds that also have a group hydroxyl). Its structure stands out for presenting a hydroxide group (OH) directly linked to an aromatic compound.