A halide is an organic compound that has at least one halogen atom. – that is, chemical elements from family 17 or VII of the Periodic Table (F, Cl, Br, I or generically: X) – attached to a group derived from a hydrocarbon.
RX (where X = F, Cl, Br or I)
Some halides are shown below:

Iodine is the most reactive of all and fluorine the least, because the binding energy between halogen and carbon increases from the direction of iodine to fluorine.
Another point is that reactivity also increases in this sense:

This reactivity thus occurs with greater ease in tertiary carbon halides, due to the character acquired by the carbon linked to the organic halide:

Thus, the substituent group, such as the OH that will form the alcohol, is more strongly attracted to the tertiary carbon, which has a positive character (1+), and the substitution is easier.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
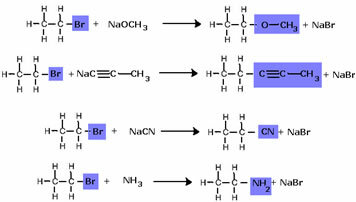
Halides can undergo reactions that allow us to obtain practically all other organic functions (alcohol, ether, alkyne, cyanide or nitrile, amine, among others). However, this is unfeasible in practice as halides are very expensive compounds.
To produce an alcohol, for example, a halide is reacted with a strong base, such as sodium hydroxide, in an aqueous medium. Let's see an example below, in which from the alkaline hydrolysis of ethyl chloride (chloroethane) ethanol will be formed:
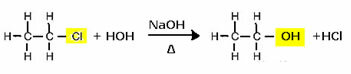
Note that the halide group was replaced by the OH, the alcohol functional group. The same scheme is followed for the formation of other groups, differentiating only the reagent:
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Brazil School Team
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FOGAÇA, Jennifer Rocha Vargas. "Organic Halide Substitution Reactions"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/reacoes-substituicao-haletos-organicos.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.



