The natural aspects of the Midwest region are greatly influenced by the location of this region, in the central zone of Brazil and in a tropical strip continental, given that this region is positioned above the Tropic of Capricorn, which cuts a strip in the extreme south of Mato Grosso do South.
To characterize the physical aspects of the Midwest, we will highlight, respectively, the relief, climate, vegetation and hydrography of this important Brazilian region.
O relief The Midwest is divided into three main areas or sub-regions: the central plateau, the southern plateau and the wetland plain, as shown in the following map:
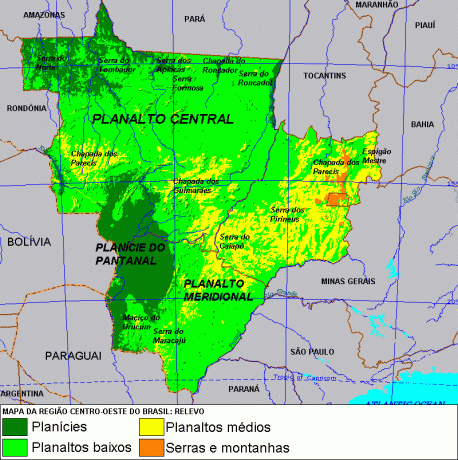
Map of the spatial distribution of the relief of the Brazilian Midwest *
The central plateau, as shown in the map above, is located in most of the Midwest, but it also extends to other regions, mainly to the state of Minas Gerais. This type of relief has altitudes ranging from 600m to 1000m on average, with a predominance of crystalline rocks and some sedimentary ones, in addition to oxisols. There are a reasonable amount of mountain ranges and some chapadas, such as Chapada dos Veadeiros, declared a World Heritage Site.
The southern plateau, in turn, is nothing more than an extension south of the central plateau, characterized by presenting a less rugged relief and with more fertile soils than those in most parts of the Cerrado. In some regions, there is the presence of the so-called “purple earth”, which arose from the sedimentation of basalt, a rock of volcanic origin that originated in the region in a remote geological past, when there were now extinct volcanisms.
The Pantanal Plain, which basically occupies the west of Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso do Sul, is considered to be the largest floodplain in the world. In times of rain and flooding rivers, most areas of the site flood, creating the characteristic environment of the region. The great lakes are mainly supplied by the Paraguay River.

Brazilian wetlands floodplain
O climate from the Central-West Region is characterized by the predominance of the tropical humid type in most of this region, occupying a large extension of Goiás and Mato Grosso. In this climate, there are two well-defined seasons throughout the year: a dry winter and a very hot, rainy summer. Temperatures reach an average of 22°C, with very variable minimums and maximums of more than 40°C. Due to the dry weather for most of the year, the temperature range is accentuated, that is, during the day there is a big difference between the lowest and highest temperature.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
In the north of Mato Grosso, however, there is a humid equatorial climate, largely due to the influence of the Amazon biome, which is typical of the North region and extends to this region of the Midwest. The precipitation index in this area is more accentuated, with a more humid environment, hot most of the year and with low thermal amplitudes.
THE vegetation The most abundant part of the Midwest, at least in its original aspect, is the Cerrado, a type of savanna in South America. This biome, initially, was the second largest in the Brazilian territory, only behind the Forest Amazon, but currently much of its area has been devastated, leaving less than 20% of its vegetation original.
Although the Cerrado is known for its trees with twisted trunks and branches, with spaced vegetation (image below), its landscape is quite diverse, with areas of dirty and clean countryside with few trees, to denser areas, as in the case of the thickets. A typical and well-known tree in this biome is the Pequizeiro, whose fruit is Pequi, a food widely consumed in the region.

Typical landscape of the Brazilian Cerrado **
Another important natural domain in the Midwest is the Amazon Forest, north of Mato Grosso, in the same occupation range as the humid equatorial climate. In this area, there are many conserved reserves, but also many disputes in one of the agricultural frontier strips of Brazil involving Indians, squatters and land grabbers.
In addition, the Pantanal, whose flood area has already been mentioned, is also an important natural area in this region, with a great diversity in fauna and flora, constituting one of the most important natural domains of the humanity.
THE hydrography The Center-West region is quite rich, with the presence of a considerable amount of large rivers, highlighting the Tocantins, Araguaia, Paraná, among countless others. The three hydrographic basins are: the Amazon, in Mato Grosso, with an emphasis on the Xingu River; Tocantins-Araguaia, dominated by the two aforementioned rivers; and the Platinum basin, with the presence of the Paraguay and Paraná rivers.

Aerial image of the Araguaia River drainage
_________________________
* Image credits: Deyvid Setti / Wikimedia Commons
** Image credits: Hedgehog Rapper / Wikimedia Commons
By Rodolfo Alves Pena
Master in Geography

