Oxidation is the name given to the process of loss of electrons by an atom, group or ionic species during a chemical reaction. It is identified from the increase in NOX (oxidation number) of the species or atom when comparing reactant and product.
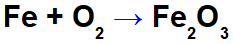
Iron oxidation equation.
In the equation above, for example, we can indicate the NOX of each of the participants:
Reagent iron (Fe): has NOX 0 as it is a simple substance;
Oxygen in reagent (O): has NOX 0 as it is a simple substance;
Oxygen in the product: it has NOX -2 because it is not linked to an alkali metal, alkaline earth or hydrogen forming peroxides or superoxides;
Iron in the product: it has NOX +3 because the sum of the NOX of iron multiplied by 2 (number of atoms) + NOX of oxygen multiplied by 3 must result in 0 as it is a compound substance:
x.2 + 3.(-2) = 0
2x - 6 = 0
2x = +6
x = + 6
2
x = +3
Comparing the NOX of the reagent iron (0) to the product (+3), we observed an increase, that is, it underwent the process of oxidation. It is worth noting that the occurrence of
oxidation it is always accompanied by the phenomenon of reduction (which means the gain of electrons), identified by the decrease in NOX, as occurs with oxygen in the example.Read too:Determination of Oxidation Number (NOX)
Examples of situations in which oxidation occurs:
1. Combustion

The combustion of a material is also indicative of oxidation.
Combustion is every chemical reaction that occurs in the presence of a fuel any and the oxidizing oxygen gas (O2), resulting in the production of heat and light. In every combustion reaction occurs oxidation.
2. Some organic reactions
In every organic reaction that takes place in the presence of the means listed below, the process of oxidation:
Potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7) or potassium permanganate (KMnO4);
Presence of strong acid or strong base;
Ozone gas (O3) in the presence of metallic zinc (Zn) and water (H2O).
3. Batteries or batteries

Batteries are devices in which oxidation always occurs.
Stacks or batteries are electrochemical devices that store chemical substances. One of these substances will undergo oxidation, and the other will undergo reduction, resulting in the production of electrical current.
4. Electrolysis
Electrolysis is a chemical process in which an aqueous solution containing a salt is subjected to an electrical current, which ends up promoting the oxidation of anions present in these materials. In all electrolysis, there is oxidation.
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/quimica/o-que-e-oxidacao.htm

