Kp is the acronym used to determine the constant of an equilibrium in terms of partial pressures. This constant works with the values of the gaseous participants of an equilibrium in the atm unit, for example.

Equation representing a chemical reaction with gaseous components
In this equation, all participants are gaseous, so when a participating gas has a partial pressure in the mixture, it is represented by the abbreviation pX.
When setting up the chemical equilibrium equation (in terms of concentration), the products must be placed in the numerator and the reactants are placed in the denominator:
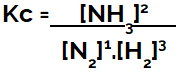
Kc expression of ammonia formation equilibrium
the expression of equilibrium constant in terms of pressure (Kp) follows the pattern of Kc, that is, the partial pressures of the reagents are positioned in the denominator and the partial pressures of the products in the numerator:
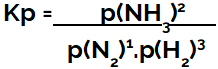
Kp expression of ammonia formation equilibrium
Observation: If the reaction equation of the chemical balance do not present any gaseous participant, it will not automatically present Kp.
Example: (PUC-MG) For the reaction: 2 CO(g) + O2(g)? 2 CO2(g), the partial pressures of CO(g) it's the2(g) at equilibrium they are, respectively, 0.2 atm and 0.4 atm. The total system pressure is 1.4 atm. The value of Kp for the reaction is:
a) 56.2
b) 40.0
c) 35.6
d) 28.4
e) 25.6
The data provided by the exercise are:
Carbon monoxide partial pressure (pCO) = 0.2 atm;
Partial pressure of carbon monoxide (pO2) = 0.4 atm;
Total pressure =1.4 atm;
To determine the Kp of this system, we must perform the following steps:
1st Step: Determine the partial pressure of carbon monoxide (pCO2).
For this, just remember that the total pressure (pt) is the sum of all partial pressures:
pt = pCO + pCO2 + pO2
1.4 = 0.2 + p (CO2) + 0,4
1.4 - 0.2 - 0.4 = pCO2
pCO2 = 0.8 atm
2nd Step: Determine the Kp of the exercise.
For this, just use the values in the expression of the equilibrium constant Kp:
Kp = (pCO2)2
(pCO)2.(dust2)1
Kp = (0,8)2
(0,2)2.(0,4)1
Kp = 0,64
0,04.0,4
Kp = 0,64
0,016
Kp = 40 atm-1
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/quimica/o-que-e-kp.htm
