THE Communication it is associated with language and interaction, in a way that it represents the transmission of messages between a sender and a receiver.
Derived from Latin, the term communication ("communicate) means “to share, participate in something, make common”, being, therefore, an essential element of human social interaction.
The elements that make up the communication are:
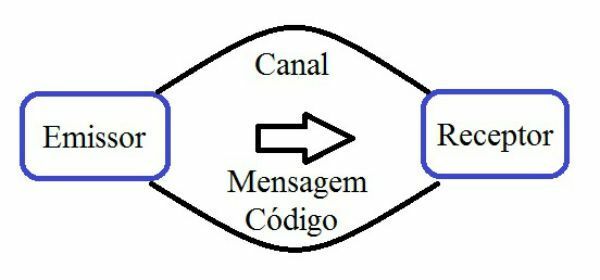
- issuer: also called speaker or speaker, the sender is the one who sends the message to one or more receivers, for example, a person, a group of individuals, a company, among others.
- receiver: called interlocutor or listener, the receiver is the one who receives the message issued by the sender.
- Message: is the object used in the communication, so that it represents the content, the set of information transmitted by the speaker.
- Code: represents the set of signs that will be used in the message.
- Communication channel: corresponds to the place (medium) where the message will be transmitted, for example, newspaper, book, magazine, television, telephone, among others.
- Context: also called referent, it is the communicative situation in which the sender and receiver are inserted.
- Noise in Communication: it occurs when the message is not correctly decoded by the caller, for example, the code used by the speaker, unknown by the caller; noise from the place; low voice; among others.
Stay tuned!!!
Communication will only take place if the receiver decodes the message transmitted by the sender.
In other words, communication takes place from the moment the interlocutor reaches the understanding of the transmitted message.
In this case, we can think of two people from different countries who do not know the language used by them (Russian and Mandarin).
Thus, the code used by them is unknown and, therefore, the message will not be intelligible to both, making the communication process impossible.
Importance of Communication
The act of communicating is essential for both humans and animals, since through communication we share information and acquire knowledge.
Note that we are social and cultural beings. That is, we live in society and create cultures which are built through the set of knowledge we acquire through language, explored in the acts of communication.
When we think of humans and animals, it is clear that something essential distinguishes us from them: verbal language.
The creation of verbal language among human beings was essential for the development of societies, as well as for the creation of cultures.
Animals, in turn, act by extinction and not by verbal messages that are transmitted during life. That's because they didn't develop a language (code) and because of that, they didn't create a culture.
Verbal and Nonverbal Language
It is important to remember that there are two basic modalities of language, that is, verbal language and non-verbal language.
The first is developed through written or oral language, while the other can occur through gestures, drawings, photographs, among others.
Media
The means of communication represent a set of vehicles intended for communication, and, therefore, approach the so-called “Channel of Communication”.
They are classified into two types: individual or mass (social communication). Both are very important for the dissemination of knowledge among human beings today, for example: television, radio, internet, cinema, telephone, among others.
Types of Communication
According to the message transmitted, the communication is classified in two ways:
- verbal communication: word usage, for example in oral or written language.
- Non verbal comunication: does not use the word, for example, body communication, gestures, signs, among others.
Language Functions
The elements present in the communication are closely related to the functions of language. They determine the objective and/or purpose of the communicative acts, being classified as:
- Referential Function: based on the “context of communication”, the referential function aims to inform, to refer to something.
- Emotive Function: related to the “message sender”, the emotive language, presented in the first person, aims to convey emotions, feelings.
- Poetic Function: associated with the “message of communication”, objective poetic language is concerned with the choice of words to convey emotions, for example, in literary language.
- phatic function: related to the “communication contact”, since the phatic function aims to establish or interrupt communication.
- Conative Function: related to the “receiver of communication”, conative language, presented in second or third person, aims above all to persuade the speaker.
- Metalinguistic Function: related to the “communication code”, since the metalinguistic function aims to explain the code (language) through itself.
