The pH corresponds to the hydrogenic potential of a solution. It is determined by the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) and serves to measure the degree of acidity, neutrality or alkalinity of a given solution.
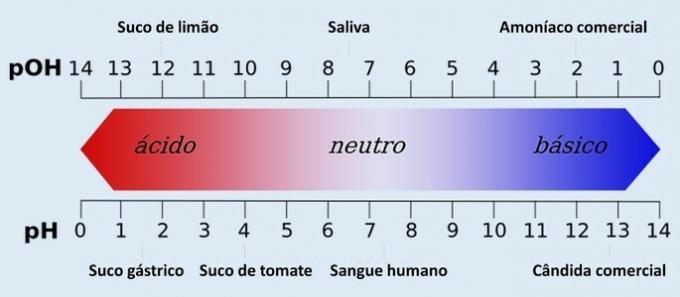
In addition to pH, there is also another quantity that determines the acidity and basicity of an aqueous system: the pOH (hydroxylionic potential). This scale has the same function as pH, although it is less used.
pH scale
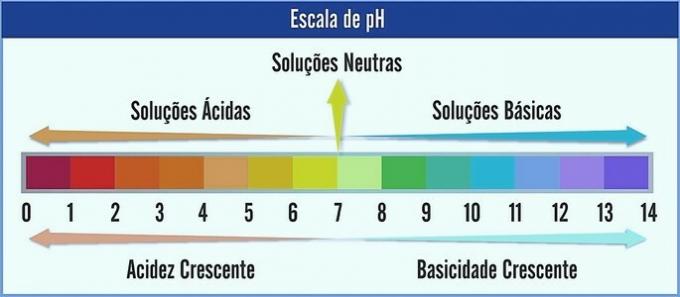
The pH is represented on a scale ranging from 0 to 14. It measures the acidity and basicity of a solution.
Therefore, pH 7 represents a neutral solution (eg pure water). Those before it are considered acidic solutions (acidic pH), and those after 7 are the basic solutions (alkaline pH).
With this observation made, the acid character is increasing from right to left. The basic character, from left to right. Note that the lower the pH value, the more acidic the solution will be.
Learn more at:
- Buffer solution
- Titration
- Neutralization reaction
Examples
Acid Solutions
| Solution | pH |
|---|---|
| Gastric juice | 2,0 |
| Lemon juice | 2,2 |
| Vinegar | 3,0 |
| Coffee | 5,0 |
| Cow milk | 6,4 |
Basic Solutions
| Solution | pH |
|---|---|
| human blood | 7,35 |
| Sea water | 7,4 |
| Sodium bicarbonate | 8,4 |
| Milk of magnesia | 10,5 |
| Bleach | 12,5 |
How to calculate pH?
In 1909, the Danish chemist Soren Sörensen (1868-1939) proposed that the acidity of solutions, measured in terms of the concentrations of H ions+, had its values transformed using logarithms to facilitate understanding.
At a temperature of 25 °C the ionic product of water is equal to 10–14 mol2/L2.
Applying the cologarithm in the expression, we have to:
Through this expression, we can obtain the corresponding value from one scale to another through subtraction.
How to measure pH?
Controlling pH is important not only for scientific purposes, but also in everyday life.
The pool pH needs to be checked, as well as the aquarium pH and even the soil pH to allow for certain types of crops.
Below are the main ways to measure pH.
acid-base indicator
So-called acid-base indicators are used to measure the pH of a solution. They are substances that change color indicating the character of the solution. The most used indicators are: litmus and phenolphthalein.

Pedometer
In addition to indicators, the pH of a solution can be measured using an instrument called a peagometer. This electronic device measures the electrical conductivity of the solution and converts it to the scale of pH values.

Entrance Exam Exercises with Feedback
1. (Enem/2014) A researcher realizes that the label of one of the glasses in which he keeps a concentrate of digestive enzymes is illegible. He doesn't know what enzyme the glass contains, but he suspects it is a gastric protease, which works in the stomach by digesting protein.
Knowing that digestion in the stomach is acidic and the intestine is basic, he assembles five test tubes with food different, add the enzyme concentrate to solutions with a determined pH and wait to see if the enzyme acts in any their.
The test tube in which the enzyme must act to indicate that the researcher's hypothesis is correct is the one that contains:
a) potato cube in solution with pH = 9
b) piece of meat in solution with pH = 5
c) boiled egg white in solution with pH = 9
d) portion of noodles in solution with pH = 5
e) butter ball in solution with pH = 9
Correct alternative: b) piece of meat in solution with pH = 5.
Protease is an enzyme that digests proteins and because it is gastric it acts in the stomach, whose pH is acidic.
Analyzing the alternatives, we have to:
a) WRONG. Potatoes are high in carbohydrates and the pH of the concentrate is basic.
b) CORRECT. Meat contains proteins and enzymes can act on it, and the pH of the concentrate is acidic, like the stomach.
c) WRONG. Concentrate pH is basic.
d) WRONG. Pasta is rich in carbohydrates.
e) WRONG. Concentrate pH is basic.
2. (Udesc/2009) "Acid rain" is a term that refers to precipitation from the atmosphere of rain with greater than normal amounts of nitric and sulfuric acids.
Precursors to acid rain come both from natural sources, such as volcanoes and decaying vegetation, and from processes industrial emissions, mainly sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides from burning fuels fossils.
The pH of rainwater considered normal is 5.5 (due to the presence of carbonic acid from the solubilization of carbon dioxide). A chemist monitoring a highly industrialized region noted that the pH of rainwater was 4.5.
Considering that acidity is related to the concentration of H3O+, it is correct to say that water with pH 4.5 was:
a) twice as basic as normal.
b) twice as acidic as normal.
c) ten times more basic than normal.
d) ten times more acidic than normal.
e) one hundred times more acidic than normal.
Correct alternative: d) ten times more acidic than normal.
According to the expressions pH = - log [H+] and [H+] = 10-pH, We have to:
pH = 5.5
[H+] = 10-5,5
pH = 4.5
[H+] = 10-4,5
The difference between the values is: 10- 5,5 - ( - 4,5) = 10 -1
As the pH scale is a logarithmic scale, changing one unit equals a 10 times more acidic solution.
3. (UFMG/2009) Consider a certain amount of water and lemon juice, mixed, contained in a glass. Review these three statements regarding this system:
I. The system is acidic.
II. The system pH is greater than 7.
III. In the system, the concentration of H ions+ is bigger than the OH–.
Based on this analysis, it is CORRECT to state that:
a) only statements I and II are correct.
b) only statements I and III are correct.
c) only statements II and III are correct.
d) all three statements are correct.
Correct alternative: b) only statements I and III are correct.
I. CORRECT Lemon contains citric acid, which in solution releases H ions+ and so the system is acidic.
II. WRONG. The pH is less than 7, characterizing an acidic system: the closer to 0 the solution pH, the more acidic it is.
III. CORRECT The acidic pH is a result of the high concentration of H ions+ in solution, since pH = - log [H+].
For more questions, with commented resolution, be sure to check:Exercises on pH and pOH.


