Zooplankton corresponds to the group of organisms that live floating in marine and freshwater environments. It is one of the components of plankton.
The term derives from the Greek zoon (animal) and planktos (the drift), that is, it means "drifting animals".
Remember, plankton encompass the microorganisms that are part of aquatic ecosystems. It can be of the zooplankton and phytoplankton types.
Learn more about Plankton.
Characteristics and Species of Zooplankton
Zooplankton are made up of a great diversity of organisms. Among them are protozoa, worms, crustaceans and insect larvae.
Insect larvae, despite constituting zooplankton, are rarely found.
There are some differences between the marine zooplankton it's the freshwater zooplankton. In the marine environment a greater number of beings from the invertebrate phylum is found. Freshwater zooplankton are characterized by lower species diversity.
Zooplankton, in general, feed on phytoplankton and bacteria. They are considered the primary consumers of aquatic environments. In turn, they serve as food for other organisms, such as fish.
Due to the diversity of species that compose it, zooplankton has several characteristics.
Protozoa
You protozoa they are simple, single-celled beings. The main groups of protozoa found in plankton belong to the phyla Ciliophora and Sarcomastigophora.
Most are free-living and include ciliates, flagellates and sarcodines.
The diet is varied and can be bacteriophage (they feed on bacteria), detritivores (they feed on organic matter), herbivores, carnivores and even cannibals.
Protozoa have an important ecological role in the recycling of organic matter, by transforming it into smaller particles and allowing them to be consumed by other zooplankton beings (rotifers and microcrustaceans).
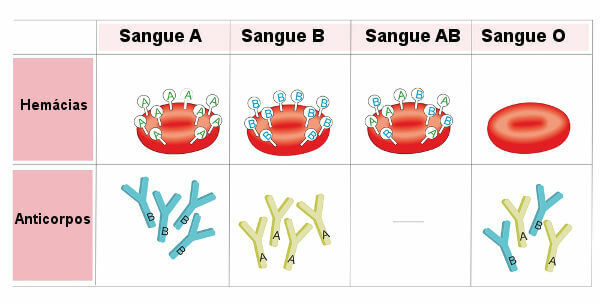
Rotifers
The rotifers are microscopic beings, with different sizes and body shapes. For a long time they were classified in the same group as roundworms (worms). Currently, they fall within the Rotifera phylum.
rotifer
As for food, rotifers can be omnivores, herbivores and carnivores.
In freshwater environments, rotifers tend to have the highest number of species compared to other zooplankton components.
In ecological terms, rotifers serve as a basis for feeding larval fish.
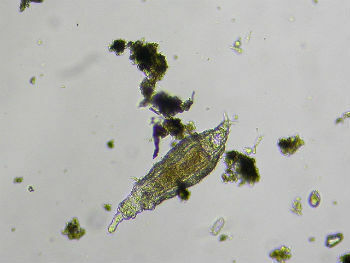
Crustaceans
The crustaceans present in zooplankton belong to the groups of copepods and cladocerans. Because they are small, they can be called microcrustaceans.
Copepods have 12,000 species and are the most diverse group of crustaceans. They are found in fresh and salt water environment.
Copepods can be herbivores, omnivores, carnivores or detritivores.
Copepoda
Cladocerans are generally freshwater. They feed on organic matter, phytoplankton and bacteria.
Phytoplankton
Unlike zooplankton, the phytoplankton comprises the set of photosynthetic and unicellular microscopic algae that inhabit aquatic ecosystems. We can say that it is the plant part of plankton. While zooplankton is the animal part.
The most abundant and representative groups of phytoplankton are the algae of the dinoflagellate and diatom group.