The cell wall, cellulosic wall or cellulosic skeletal membrane, is a tough, flexible cellulose structure that delimits cell organelles in a plant cell.
Remember that plant cells form the tissues of plants. In turn, animal cells lack cell walls, chloroplasts and vacuoles.
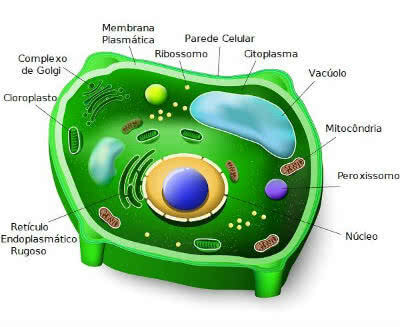 Plant cell and its organelles
Plant cell and its organelles
Roles
The main functions of the cell wall are to provide support, resistance and protection against external pathogens. Therefore, it collaborates with the absorption, transport and secretion of substances.
In addition, the cell wall works as a filter for plant cells, as it allows the exchange of substances between other neighboring cells.
It also protects against excessive water ingress, thus preventing osmotic lysis, that is, cell rupture. Another important function is that the cell wall shapes the various plant cells.
Read more about Osmosis.
Structure
The cell wall is a very resistant structure composed of polysaccharide microfibrils called cellulose.
It involves the plasma membrane and in its structure it has pores that act as filters in relation to the external environment.
 Cell wall structure scheme
Cell wall structure scheme
Classification
The cell wall can be primary and secondary:
- Primary Cell Wall: are basically formed of cellulose, hemicellulose and pectins. Although thin, it is resistant and flexible, thus allowing cell growth. It has a high water content, around 70%. In the primary walls, hydrogen bonds provide greater elasticity to the structure.
- Secondary Cell Wall: are basically made up of cellulose and hemicellulose. Not all plant organisms have this type of structure. It is thicker than the primary, in addition to being quite resistant since it is made up of lignin. It has a lower water content than the primary, that is, 20%. Secondary walls limit space and provide greater rigidity.
In addition to the primary and secondary wall, the medium lamella it is a thin layer outside the walls that has the function of connecting the cell with others that are nearby.
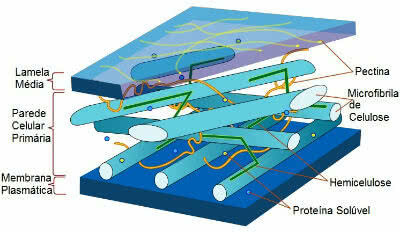 Schematic of the structure of the primary cell wall and the middle lamella
Schematic of the structure of the primary cell wall and the middle lamella
Types
The cell wall is present in plants, algae, fungi and some bacteria. Thus, they differ somewhat in their structure and composition.
- Plant Cell Wall: formed by cellulose microfibrils, the cell wall of plants generally has a primary and a secondary wall.
- Algae Cell Wall: formed by different types of cellulose as the walls of glycoproteins and polysaccharides.
- Fungi Cell Wall: formed by chitin, and in some cases, by cellulose, the cell wall of fungi protects these organizers against invaders.
- Bacterial Cell Wall: formed by peptidoglycan (sugars linked to amino acids), the bacterial cell wall is classified as Gram Positive and Gram Negative.
Learn more about the topic by reading the articles:
- plant cell
- animal cell
- Cell Organelles