O ABO system they are classifications of human blood into the four existing types: A, B, AB and O.
while the Rh factor is a group of antigens that determines whether the blood is Rh positive or negative.
Blood inheritance, that is, a person's blood type, is genetically determined, being a case of multiple alleles, by genes ITHE , IB Hey.
How were the ABO and Rh Systems discovered?

The ABO system was discovered in the early 20th century by Austrian biologist Karl Landsteiner (1868-1943) and his team of scientists.
They found some differences in the blood of individuals, which certainly clarified the death of many people after blood transfusions.
The discovery of the ABO System was an important milestone in the history of medicine. Because of this study, the physician and biologist Karl Landsteiner won, in 1930, the “Nobel Prize in Physiology”.
According to scientists, the property of incompatibility of blood types was confirmed from the immunological reaction between substances present in blood plasma and red blood cells.
Thus, the blood that suffered agglutination from certain antigens present in the membranes of red blood cells, became known as agglutinogens (A and B). While agglutinating substances, antibodies, found in blood plasma, were called agglutinins (anti-A and anti-B).
In addition to unraveling the blood typology, Karl Landsteiner (1868-1943) discovered the Rh Factor (antibodies), derived from the name of the “monkey of the genus Reshus”. This animal was used as a guinea pig in investigations for the advancement of the ABO system.
Research indicates that certain blood types lack the Rh factor. This happens because the individuals who presented Rh antibody agglutinated red cells were classified as Rh positive (Rh+). On the other hand, the red cells of those that did not agglutinate were called Rh negative (Rh-).
Learn more about issues related to this topic:
- antigens
- Antibodies
- ABO system
- Rh factor
Blood Types
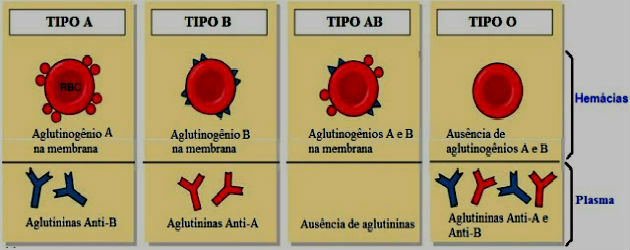
Blood groups, according to the ABO system, are classified into: A, B, AB and O.
The types are differentiated by the presence or absence of agglutinins, in the blood plasma, and of agglutinogens, in the membrane of the Red Cells.
- Type A: Type A blood has anti-B agglutinin (antibodies) in plasma. Thus, individuals with this blood type can receive types A and O, however, they do not receive type B or type AB.
- Type B: Type B blood has anti-A agglutinin (antibodies) in plasma. Thus, individuals with this blood type can receive blood types B and O, but cannot receive blood types A and AB.
- Type AB: Type AB blood is the “Universal Receiver”, so AB has no agglutinins in plasma and can receive any type of blood. In other words, AB blood has both the A and B antigens, however, no antibodies.
- Type O: Type O blood is the “Universal Donor”, since they have both types of agglutinins (antibodies) in plasma, anti-A and anti-B, and do not have agglutinogens (antigens) of types A and B. Despite being universal donors, that is, they can donate their blood to any blood group, these individuals only receive type O blood.
Check out the table below indicating the existing relationships in blood donation:
|
blood group |
Agglutinogens in Red Blood Cells |
Plasma agglutinins |
receive from |
donate to |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| THE | THE | anti-B | A and O | A and AB |
| B | B | anti-A | B and O | B and AB |
| AB | AB | - | A, B, AB and O | AB |
| O | - | anti-A and anti-B | O | A, B, AB and O |
Also read about:
- Blood
- Circulatory system
- Blood vessels
What happens if a person receives a different blood type than yours?
In that case, there may be a mismatch between blood types. The red blood cells received will clump together, to the point of forming larger, more compact clumps, preventing blood circulation.
Fetal Erythroblastosis
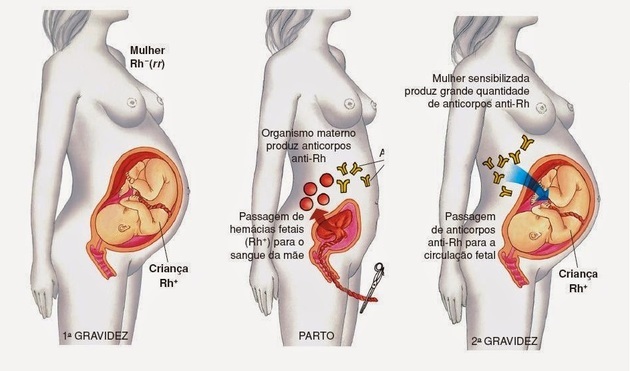
Newborn hemolytic disease or fetal erythroblastosis occurs when blood from an Rh+ fetus is agglutinated by antibodies in the mother's Rh- blood, in a process called hemolysis.
Thus, the child is born with a profound anemia (jaundice), due to the high destruction of red blood cells.
Thus, it is clear that the ABO system and the Rh factor play a very important role in human biology.
To identify whether a person is Rh positive or negative, the blood is mixed with Rh antibodies, and if the red cells clump together, that person has Rh+ blood. On the other hand, if they don't coalesce, that person has Rh- blood.