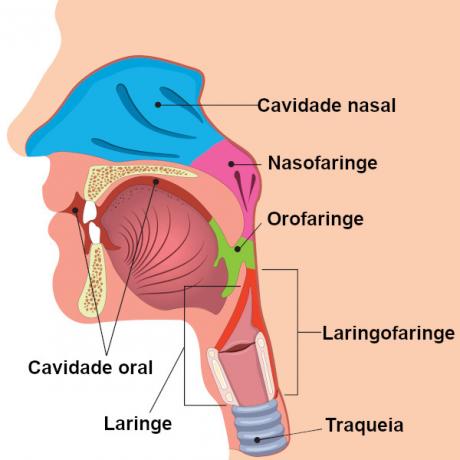
THE pharynx is a structure that is so much part of the digestive system how much of the respiratory system, being a place where food and air pass. This organ allows, for example, that we are able to breathe even when our nasal cavities are obstructed. The pharynx has three regions: nasal, oral and laryngeal.
Know more: Organs of the human body - what they are and their functions
Pharyngeal characteristics
The pharynx is approximately 12.5 cm long, is a tubular musculomembranous organ, and has three distinct regions: nasal, oral and laryngeal. The nasal region is called nasopharynx, while the oral is called oropharynx, and the laryngeal region is known as laryngopharynx.
pharyngeal regions
The first region of the pharynx is the nasopharynx, located just behind the nose. It has four openings, two of them for the Eustachian tubes and two for the nose region. The opening to the Eustachian tubes ensures communication between the nasopharynx and the tympanic cavity, ensuring that pressures are equalized in the regions. A problem with this communication is that it also allows infections that reach the pharynx to affect the ear region.
THE oropharynx arises after the nasopharynx and is situated just behind the mouth. The nasopharynx and oropharynx are incompletely separated by the soft palate. Moving the soft palate during swallowing prevents the food from going to the nasal region of the pharynx. The pharynx communicates with the mouth through an opening that is named isthmus of the fauces.
Finally, we have the laryngopharynx, located under the hyoid bone and behind the larynx. The pharyngeal larynx opens in the larynx and esophagus.
Tonsils
Astonsilas are important structures found in the pharyngeal region. They are formed by fabric lymphaticand are related to the defense of our body, acting in the production of lymphocytes, which are important to ensure protection against antigens which may be present in air and food.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
The palatine tonsils are found in number of two and are present on the lateral wall of the oropharynx. Also called tonsils, these tonsils are larger in children than in adults, and the involution of the structure is observed after the period of puberty. A common problem that affects the palatine tonsils is the tonsillitis, an inflammation of this region, which can be triggered by different agents, such as virus and bacteria.
Inflammation can cause sore throat, ear pain, fever, headache, pus formation in the tonsils and bad breath. Treatment includes painkillers, anti-inflammatories and antibiotics, the latter being the drug used when the infection it's bacterial. Many people perform surgeries to remove the tonsils, but the removal of the structure is only indicated in specific cases, such as cases of recurrent tonsillitis.
THE pharyngeal tonsil it is a unique structure that is located at the bottom of the posterior wall of the nasopharynx, with a location close to the choanas (openings that communicate the nasal cavity with the pharynx). When the pharyngeal tonsil is enlarged, it can obstruct this communication in a situation known as an adenoid. It is noteworthy that some authors use the term adenoid as a synonym for pharyngeal tonsil.
Finally, we have the lingual tonsils, which are located at the base of the tongue. They differ because they are found in greater numbers than other tonsils and because they have a small diameter.
Read more: Gastritis - stomach muscle infection
Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis is a inflammation that affects the pharynx, which can be caused, for example, by viruses or bacteria, with viruses being the main causes. In pharyngitis, the region becomes quite red, and the patient may experience symptoms such as sore throat, dry throat, difficulty in swallowing food, fever, and general malaise.
O diagnosis it is basically clinical, with the observation of the area by the doctor. Throat secretions may be collected to identify the cause of pharyngitis. The treatment varies according to the causative agent, being administered, for example, antibiotics in cases of bacterial infections. In pharyngitis, the use of anti-inflammatory and analgesics may also be recommended.
By Vanessa Sardinha dos Santos
Biology teacher
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SANTOS, Vanessa Sardinha dos. "Pharynx"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/biologia/faringe.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.