The nerves in the human body are structures formed by nerve fibers and connective tissue.
They are responsible for the nerve impulse transmissions (electrical impulses), known as "action potential".
Nerves are distributed throughout the human body, and start in the brain and spinal cord.
Its main function is to establish communication of Organs motor and sensing organs, all through the central nervous system.
Nerve Structure

Nerves are filamentous structures, that is, cables or bundles of nerve fibers formed by axons (motor fibers) and dendrites (sensory fibers).
Your coating is made of connective tissue, which are classified as follows:
- Epineurium: corresponds to the fibrous layer and helps to fill the spaces between the fiber bundles.
- Perineuro: corresponds to a cell sheath that covers the fiber bundles.
- endoneurium: located inside the perineurium, it is another layer of fibers.
They are considered appendages to the axons of nerve cells, which make the connections between the nervous system and the human body.
You can know more about:
- nerve tissue
- nerve cells
- Human Body
Nerve Classification
Nerves can be classified in different ways, varying according to the type of fiber that makes them up.
See the table below for these types and their characteristics.
| nerve classification | Feature |
|---|---|
| Afferent | Formed by sensory nerves, the afferent nerves send signals from the periphery of the body to the central nervous system through sensory signals (fibers). |
| Efferent | Calls of nerves (fibers) engines, the efferent nerves send signals from the central nervous system to the muscles or glands through stimulating signals. |
| Mixed | In this case, the nerves are formed by fibers sensory and fibers motor, for example, the spinal nerves. |
What are the nerves in the human body?
In the human body, the nervous system is classified into: Central Nervous System (CNS) and Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
The Central Nervous System is formed by the brain and spinal cord. The Peripheral Nervous System, on the other hand, is made up of nerves that leave the brain, called cranial nerves, and nerves originating in the spinal cord, called spinal or spinal nerves.
Thus, the nerves of the human body are part of the Peripheral Nervous System, being characterized as a communication network that runs throughout the body. Its function is to link the central nervous system with the organs.
The organs, in turn, are made up of sensory and motor pathways that are responsible for receiving and sending information based on stimuli received from the external or internal environment.
Expand your knowledge and also read about:
- Central Nervous System
- Peripheral Nervous System
- Nerve impulse transmission
Cranial Nerves
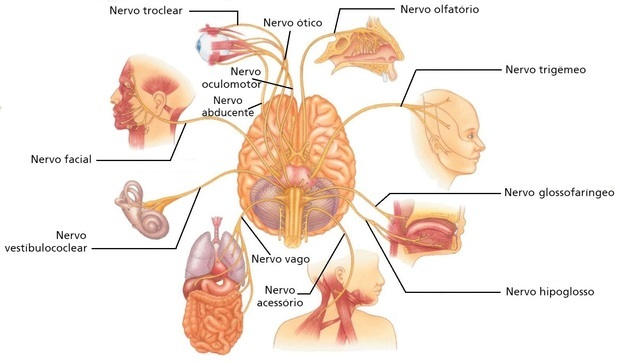
Originated in brain, the cranial nerves connect the sense organs (mouth, nose, ear and eyes) with the brain, which, in turn, innervates the head, heart and lungs.
They are made up of 12 pairs of nerves. See in the chart below how each pair of nerves works in our body.
| Nerve | Feature |
|---|---|
| olfactory nerve | With a sensitive function, it is responsible for conducting olfactory impulses. |
| optic nerve | With a sensory function, this nerve originates in the retinal region and penetrates the skull through the optical channel. |
| oculomotor nerve | Of motor function, this nerve is responsible for eye movement. |
| trochlear nerve | It has sensory and motor function and is related to eye movement and vision. |
| trigeminal nerve | The motor function of this nerve is related to chewing. The sensory function is responsible for innervating the face, part of the scalp and internal regions of the skull. |
| abducens nerve | With a motor function, this nerve is responsible for the innervation of the lateral rectus muscle of the eye. |
| facial nerve | With motor and sensory function, this nerve is related to facial expressions and muscle sensitivity. |
| vestibulocochlear nerve | With only sensory function, this nerve is related to balance and hearing. |
| glossopharyngeal nerve | This nerve is responsible for the sensitivity that involves the tongue, pharynx and eustachian tube. In addition, it acts on the pharyngeal muscles. |
| vacant nerve | Due to its motor and sensory function, this nerve is responsible for maintaining vital functions, such as regulating heart rate. |
| accessory nerve | This nerve with motor function acts on swallowing and head and neck movements. |
| hypoglossal nerve | It is a nerve that is related to the movement of the tongue. |
Spinal Nerves

Originated in spinal cord, the spinal nerves (spinal nerves) are mixed nerves that branch along the spinal cord. They are responsible for innervating part of the head, trunk and upper limbs.
They are composed of 31 pairs, being:
- 8 pairs of cervical nerves
- 12 pairs of thoracic nerves
- 5 pairs of lumbar nerves
- 5 pairs of sacral nerves
- 1 pair of coccygeal nerve
To gain more knowledge, see also:
- Neurotransmitters
- Exercises on the Nervous System