Xylem and Phloem are plant tissues responsible for conducting the sap through the stem. The main difference between these conducting vessels is that the xylem transports water (crude sap) and the phloem conducts organic substances (elaborated sap).
Xylem
The xylem or wood, conducts the raw sap (water and minerals), in addition to reserve substances. It is primarily responsible for conducting water in vascular plants.
The main cells that make up the xylem are the tracheids and vessel elements. Also called tracheal elements, they are elongated cells with secondary walls that die when they become mature.
You vessel elements have perforations in their walls, especially at the ends. They are joined through these holes into long, continuous columns called vessels.
At tracheids they do not have perforations, but pits, which are thinner regions, without a secondary wall.
Due to their structure, vessel elements are more efficient as the flow of water through the perforations is easier. However, in tracheids, the passage of water through the membrane prevents bubbles from circulating through the plant. Therefore, it is safer for the plant.
In the xylem there are also cells of the parenchyma, which store several substances, sclereids and fibers.
Primary and Secondary Xylem
O primary xylem is formed from the prochange (primary meristem) during the period of primary growth, ie when the plant grows in length.
Cells are elongated, with dense cytoplasm and well-defined nucleus. They have a primary wall, which is a cellulosic layer that is deposited outside the cell wall during growth.
The primary xylem can be of two types: protoxylem (graduates first) and metaxylem (differentiates later).
O secondary xylem originates from vascular exchange. This occurs when the plant has secondary growth, that is, when it grows laterally, increasing its thickness.
| XYLEM | PHLOEM | |
|---|---|---|
| OCCUPATION | Conducts raw sap (water and minerals) |
Conducts elaborated sap (organic compounds) |
|
MAIN TYPES CELL PHONES |
Tracheal elements are elongated cells that die in maturity. They can be of two types:tracheids and Vessel Elements |
The screened elements are living cells in maturity. They have pores at the ends of the walls. There are two types: Screened Cells and Screened Tube Elements |
|
GROWTH PRIMARY |
Primary Xylem - originates from the Procambio. It can be of two types: protoxylem and metaxylem |
Primary Phloem: originates from the Procambio. It can be of two types: protophloem and metaphloem. |
|
GROWTH SECONDARY |
Secondary Xylem - is formed from the Vascular Exchange |
Secondary Phloem: Drift of the Vascular Exchange |
Phloem
the phloem or release conducts the elaborate sap, that is, the organic compounds produced in the leaf through photosynthesis. So it is the main nutrient-conducting tissue in vascular plants.
The most important cells of the phloem are the crimped elements, which are so named because of the pores that cluster especially at their ends.
Through these pores, neighboring elements connect through their protoplasts. The crimped elements can be of two types: screened cells or screened tube elements.
In sieve cells the pores are narrower and more uniform than in sieve tube elements. In the latter, the larger pores are located in a region of the wall called screened plate.
Primary and Secondary Phloem
O primary phloem just as the primary xylem is formed from the prochange (primary meristem) in the primary growth of the plant.
It is differentiated in protophloem (graduates first) and metaphloem (differentiates later).
O secondary phloem drift from vascular exchange, in secondary growth.
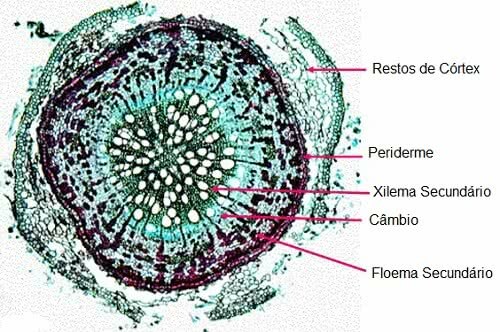
Root cutting of a plant of the genus Salix. Note that there was secondary growth, since there is secondary xylem and phloem
See too:
- meristem
- plant histology
- Stalk
- Plant Parts