The cytoplasm of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells is filled with a viscous and semi-transparent matrix, the hyaloplasm or cytosol.
In the hyloplasm are molecules and cell organelles.
The set formed by the hyaloplasm and cell organelles constitutes the cell's cytoplasm.
The cytosol is in continuous movement, driven by the rhythmic contraction of certain strands of proteins present in the cytoplasm.
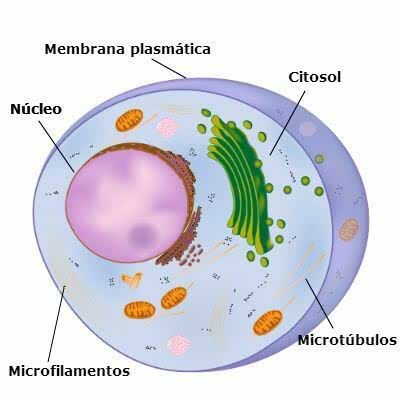 The cytosol or hyaloplasm fills the cytoplasmic space
The cytosol or hyaloplasm fills the cytoplasmic space
Structure and Composition
In eukaryotic cells, the hyloplasma occupies 50-80% of the total cell volume.
It consists of 70-80% water. The other elements found are ions, amino acids and carbohydrates.
Depending on the amount of water, hyloplasma can be found in two states:
- Sun state: it has a fluid consistency;
- Gel state: has a viscous consistency.
The outermost region of the cytoplasm tends to be more viscous and is called ectoplasm or cytogel.
While the inner region tends to be more fluid and is called endoplasm or cytosol.
Roles
- Regulates intracellular pH;
- It is the space where vital chemical reactions for the cell take place, such as anaerobic glycolysis and protein synthesis;
- Contributes to cell movement through cyclosis. THE cyclosis it is a cytoplasmic current oriented in a certain direction, capable of dislocating cell organelles;
- It stores reserve substances from animal cells, such as fats and glycogen.
Want to learn more? Also read about the cells.