O Extractivism it consists in the activity of extracting the natural resources that the Earth offers through manual or machine harvesting.
It is the oldest economic activity of the human being, when he was nomadic, being practiced until today.
Extractivism can be used for subsistence such as gathering fruit, wood, fishing and hunting, ores that will be transformed into metals for the manufacture of utensils.
In this way, extractivism was an activity that was deeply integrated with ancient peoples and nature.
However, it is now practiced on an industrial scale, as it is the raw material that will feed factories around the world in order to produce consumer goods.
Extractivism can then be an extremely harmful activity to the environment. Developing countries are the ones that most practice this type of activity, unlike developed countries that are more industrialized.
Types of Extractivism
There are three types of extractivism: vegetal, mineral and animal.
Vegetal Extraction
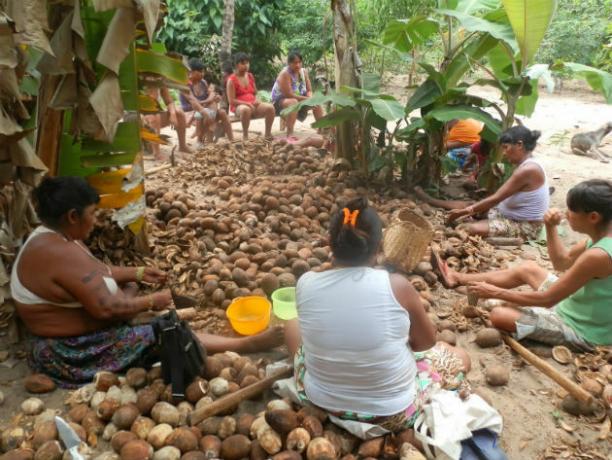

Plant extraction consists of collecting fruits, wood and roots from nature. It is also possible to remove resins and latex from certain tree species that will be transformed into wax and rubber, respectively.
It is necessary not to confuse the agriculture with plant extractivism. This is practiced on plant species that grow spontaneously in nature and have not been cultivated by humans.
Mineral Extractivism

Mineral extraction is the economic activity that extracts ores from the soil, rivers and seas. The most important are iron, petroleum, manganese, bauxite, nickel, in addition to silver and gold.
Currently, ore extraction is highly mechanized and its exploration leaves deep marks in the region where it takes place. Often, the natural landscape is no longer restored, which has drastic consequences for the population and for nature.
Animal Extractivism

Animal extraction is summed up in hunting and fishing. For economic reasons, hunting wild animals is prohibited in several countries.
In Brazil, hunting is only allowed for traditional communities such as indigenous peoples and regions where it is considered the only way to obtain animal protein.
However, fishing is still widely practiced, especially in countries where fish are the staple of food, such as Japan, Norway, Sweden, Finland, etc.
Extractivism in Brazil
Extractive activity is extremely important for the Brazilian economy, as iron ore and oil are one of the country's major export products.
Extractivism is also vital for communities in the Amazon and the Northeast, as they depend directly on plant extraction for survival.
Read more:- Economy of Brazil
- Livestock
- Emerging Countries
- Sectors of Economy