solstice is a astronomy phenomenon that marks the beginning of summer or winter. It occurs twice a year and is associated with the Earth's axis of rotation, whose position is tilted at 23.5° in relation to its own axis.
 Planet Earth and solar incidence during the solstice
Planet Earth and solar incidence during the solstice
During the solstices, the Sun remains at the maximum of the equator. When the solstice occurs, sunlight reflects with greater intensity in one of the hemispheres.
As a result, the light is less intense in the other hemisphere. This phenomenon precisely marks the winter and summer seasons.
This means that the Planet's rotational and translational movements determine the distribution of sunlight between the hemispheres.
The light will fall perpendicularly on the Tropic of Capricorn (23.5° from the Equator) or on the Tropic of Cancer.
In the Arctic and Antarctic circles, the solstices have a single day of the year with 24 hours of uninterrupted light or darkness.
Due to the elliptical orbit of the Planet Earth, the dates of the solstices will vary from year to year. In general, this delay occurs from one year to another.
Learn more about Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn and the equator line.
Solstice and the Seasons of the Year
The two solstices per year, winter and summer, mark the beginning of the climatic seasons in each hemisphere. On June 21, the summer solstice occurs in the Northern Hemisphere and the winter solstice in the Southern Hemisphere.
On the contrary, December 21st marks the entry of the winter solstice in the Northern Hemisphere and the summer solstice in the Southern Hemisphere.
Summer Solstice
During this period, the Sun will be “above” in relation to its respective incidence tropics. In fact, the increase in the intensity of solar radiation across the hemispheres is called “Summer Solstice”.
See too: Summer Solstice.
Winter Solstice
It occurs when days are greater than nights. At the same time, in the opposite hemisphere, nights are longer than days, characterizing the “Winter Solstice”.
Solstice x Equinox
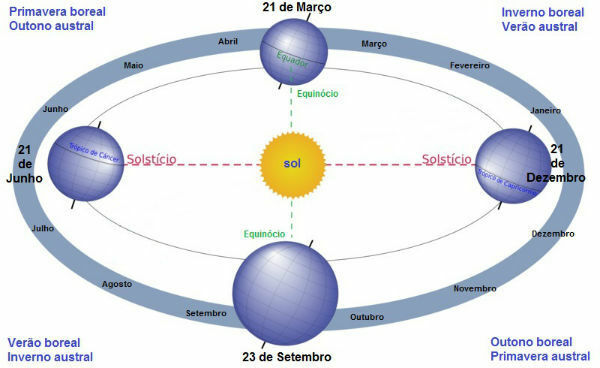 Representation of the Solstice and Equinox
Representation of the Solstice and Equinox
When sunlight falls with the same intensity on the Northern Hemisphere and on the Southern Hemisphere, the phenomenon called equinox occurs. The equinox marks the beginning of spring or autumn.
Want to know more? See:
- Equinox
- The seasons of the year
- Summer
- Winter
- Spring
- Autumn
- Autumn Equinox
Curiosities
- The word solstice is of Latin origin (Sun+sister) and means "still sun".
- On the equator, days and nights always have 12 hours during the solstices
- On the equator, the solstices are undefined (they are neither winter nor summer)
- In June, the solstice was the reason for festivities, celebrations and holidays in the Northern Hemisphere
Stay tuned!
The solstice and equinox phenomena depend on the terrestrial movements of rotation and translation.
know more aboutEarth Movements.
