Balance is a physics concept that indicates that a body remains balanced from a constant velocity, that is, when the acceleration is zero. Therefore, when there is acceleration, consequently the bodies tend to become unbalanced.
Equilibrium results from the sum of forces, whose result is equal to zero, and can be classified as static or dynamic.
static balance
When a body is in static equilibrium it means that it is at rest, which means that:
- Its vector velocity is null;
- The acceleration of the body in relation to an inert frame of reference is null;
- The sum of all forces acting on the object is equal to zero;
In the balance of forces, the sums of the vector components of the system cancel each other out and the absence of torque, capable of rotating the object, is also verified.
As an example of static equilibrium, we can mention what happens to bridges, buildings and even a person.
The center of gravity is the region where the resultant of the forces acting on the body is applied, that is, it concentrates the force of gravity acting on it. In humans, this region is located inside the belly, at the level of the navel.
dynamic balance
When a body is in dynamic equilibrium, it means that it is in uniform rectilinear motion (MRU), which means that its velocity is not zero, but always constant. In other words, it is like saying that the movement of a body is uniform and unchanging.
Cars moving at a constant speed are examples of dynamic balance.
Dynamic equilibrium is also observed in chemical reactions. When a reversible system is in equilibrium and suffers an external disturbance, the system acts to restore order, thus creating a new state of equilibrium.
The movement is dynamic because there is a movement of reactants and products, that is, the balance is reversible.
Gain more knowledge by reading an article about balance.
Balance types
There are 3 different types of balance: stable, unstable and indifferent.
stable balance: occurs when a body moves, but returns to its initial position, which is called the equilibrium position. Example: A “João Silo” doll, which after being punched, regains its balance.
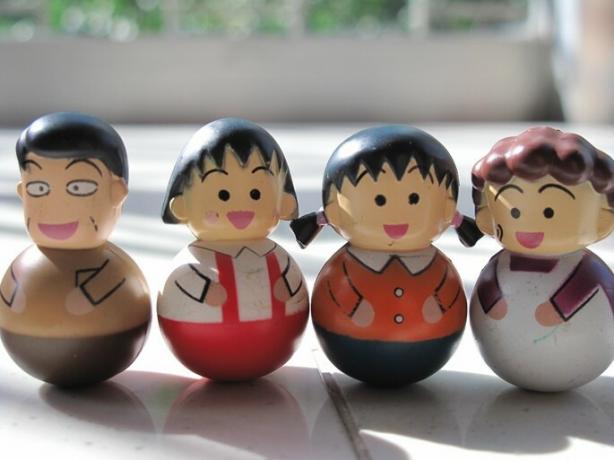

Unstable balance: occurs when a body moves and moves further and further away from its balanced position. Example: A top spinning until it loses its power and becomes unbalanced.

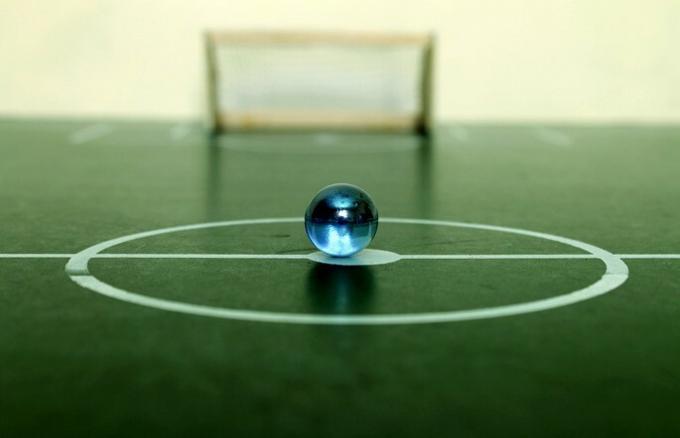
indifferent balance: Occurs when a body moves and remains balanced regardless of its position. Example: A ball rolling on a table.

Read too: Uniform rectilinear movement