E-mail or Electronic Message is an epistolary textual genre in the electronic medium that is currently being explored.
From English, the term “e-mail” corresponds to the abbreviation of “electronicmail”.
Email Characteristics
The e-mail replaces, in part, the old letters sent by the post office. Even though it has proliferated in a very remarkable way, cards are still part of today's world.
However, the importance of e-mail as a support and modern communication vehicle is indisputable.
In order for the emails to be sent, people create it on a specific page called the "provider". That is, companies dedicated to these services, for example, yahoo, hotmail, globomail, gmail, msn, among others.
To access the email page, the person must create a password ("password” in English) which will be identified whenever you want to enter the page and check your e-mail inbox. This security system prevents the invasion of privacy.
The structure of the email address is defined by [email protected]
where the term “com” indicates the commercial word and the “br” refers to the country's abbreviation, in this case Brazil. The @ symbol (at sign) is essential for an email address to be identified by the computer system.Commonly, above the space destined to the message appears the recipient “To” (“to”), which can be for one or for several people.
In the line below, the subject (“subject” in English) of the e-mail appears. For it to be sent there is a box below with the word “send” (or “send” if it is in English).
In addition, there are two optional fill-in fields below “To”. They are observed by the abbreviations “Cc” (with copy) and Bcc (with blind copy). In the first case, another email address(es) can be entered where the people who receive it can see who it was sent to.
In turn, the “Bcc” field indicates that the message will be sent with a copy to other e-mails. However, the recipients cannot see the other recipients (senders).
Automatically, the date and time are sent with the message. Thus, the user does not need to fill in these fields or even indicate them above, as in cards.
Everything is recorded on the system and further separated by folders, for example, emails received (incoming), sent, important, drafts and trash. The user himself can create folders and organize the information in the way he prefers.
With the email address, you can send a message and even attached files (photos, documents, images, videos, etc.) in real time, free of charge and efficiently.
Although it is widely used in the personal scope, e-mails are widely used by companies, institutions, associations, among others.
Depending on the proximity between the sender (sender) and the receiver (recipient), the language used can be formal or informal.
Like letters, the e-mail may have a postscript (PS acronym) at the end of the message body that indicates information or observations that the sender would like to add. Generally, emails are short and objective texts and besides following a similar structure to the letter, they can be compared to notes.
Learn more about At sign (@): meaning and symbol
Email structure and examples
The production structure of e-mails is similar to that of letters, namely:
Subject matter
Represents the email theme completed in the dialog box that appears above the message body.
It is called a subject ("subject"), for example:
Exam Note, Curriculum Lattes, Job Vacancy, etc.
Vocative
In the body of the message, the name of the receiver is placed, that is, to whom the message is being intended, for example:
“Dear Senhor Rodrigues”, in a more formal language; or simply the name of the friend “Carol” in a more colloquial or informal language, which may appear in an abbreviated way.
Text
In the text body (or message body) are placed the information that the sender wants to express according to the message subject.
As an example, let's suggest a message with the theme "Job Vacancy":
“I hereby affirm my interest in the Marketing position offered by the Risus Company. To do so, I send my resume attached for analysis.
Thank you in advance for your attention and I look forward to hearing from you!" (formal language).
Or an informal e-mail with the subject “Feast ruffles”:
“I want to know how the party ended. Tell me all the details, pleaserrr!!! Send news when you can.
P.S.: Do you have the geography exam commented on? I need to deliver the exercise next week.
Help me please!!!"
farewell
Indicates the end of the message with farewell expressions such as:
- "Sincerely"' or "Greetings" (formal language);
- "big kisses" or "with affection" (informal language)
Signature
At the end of the message, the sender signs his name. Depending on the message content, the language should be more formal, where the sender signs his full name; or informal, with abbreviations, names in the diminutive, surname, etc.
Fun Facts: Did You Know?
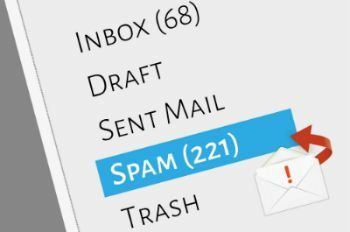
In E-mail, Spam is a folder that usually stores the received advertising messages.
The term is an acronym that can mean “mass mailing and posting” (in English “sending and Posting Advertisement in mass) or “annoying, useless and stupid messages” (in English “Stupid Pointless Annoying Messages”).
Some of them are disguised messages that contain viruses or unwanted content.
Read too:
- Genres Textual
- Textual Genre Blog
