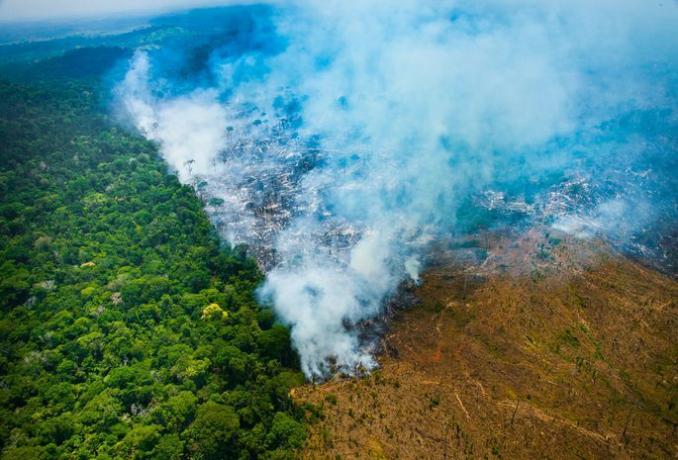
Extinct animals are those that have disappeared from nature and captivity. Human action is the main responsible for the disappearance of species.
The determination to include an animal on the extinction list can take years and several researches are carried out. This only happens when no record of the live animal is identified, even with intensive searches in different periods.
Therefore, there are several classifications, such as animals that are extinct in nature, but which still exist in captivity and regionally extinct animals, those that no longer exist only in a given local. In addition, there are a large number of species that are critically endangered.
Brazil presents a list with 8 extinct species, according to ordinances published by the Ministry of the Environment, in 2014:
1. Nosemouse

The noronha rat (Noronhomys vespuccii) is a mammal that existed in the Fernando de Noronha archipelago and disappeared during the time of the first settlers. Its existence was only known through the study of fossils.
One of the explanations for the disappearance of the noronha rat was the introduction of another species of rat (rattus rattus), native to Asia, brought by the colonizers in their boats. This mouse also brought some diseases to our country, such as bubonic plague.
2. Cabure-de-Pernambuco

The caburé-de-pernambuco (Glaucidium Mooreorum) is a species of owl that inhabited the Atlantic Forest, in the state of Pernambuco.
This species was described in 2002 and since then there have been no other records of its presence in forests. The reason for the disappearance of the caburé-de-pernambuco is the destruction of its habitat, as a result of deforestation.
3. Northeast screamer

The Northeast Screamer (Cichlocolaptes mazarbarnetti) is a bird that inhabited the Atlantic Forest, between the states of Pernambuco and Alagoas.
The name of the species is due to the fact that the bird makes sounds similar to screams when capturing its prey. The species was last seen in 2005, and in 2014 it was scientifically described based on stuffed individuals collected in the 1980s.
4. Northeast leaf cleaner
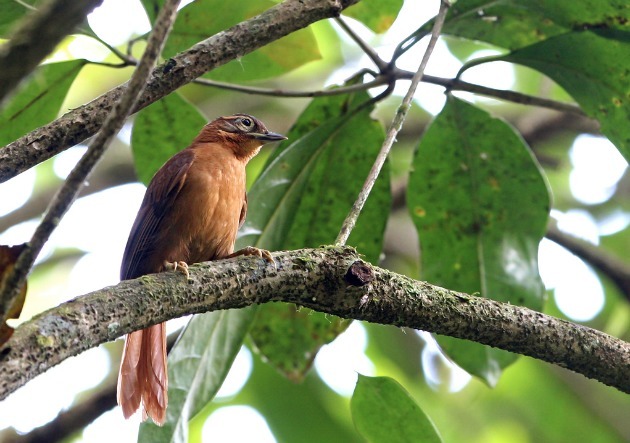

The Northeastern Leaf Cleaner (Philydor novaesi) is an endemic bird of the Atlantic Forest, in the states of Alagoas and Pernambuco. The bird was last viewed in 2011.
The fragmentation and destruction of forests were the main responsible for the extinction of the northeastern clearleaf.
5. Green fimbria tree frog

The green fimbria tree frog (Phrynomedusa fimbriata) occurred in the Serra de Paranapiacaba, in the municipality of Santo André, in São Paulo.
It was last seen in 1923, due to lack of information about the species, researchers have not yet come to a conclusion as to what may have caused its disappearance.
6. Eskimo curlew
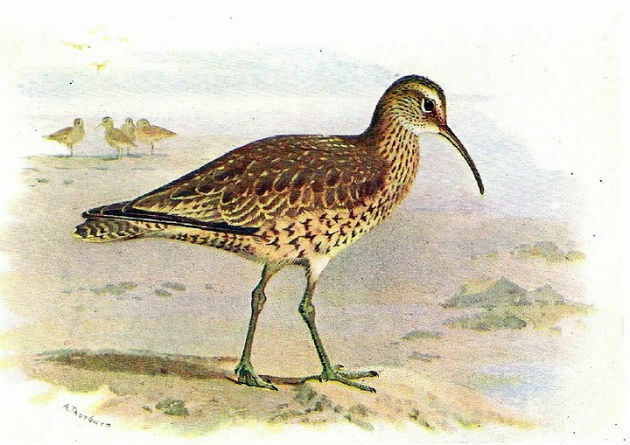
The Eskimo Curlew (Numenius borealis) is an extinct species in Brazilian territory, where it was a common visitor during its migration from Canada to South America.
In Brazil, the species has not been seen since 1930 and is believed to be really extinct throughout the world.
Indiscriminate hunting and the destruction of forests are the main reasons for the extinction of the Eskimo curlew.
7. little hyacinth macaw
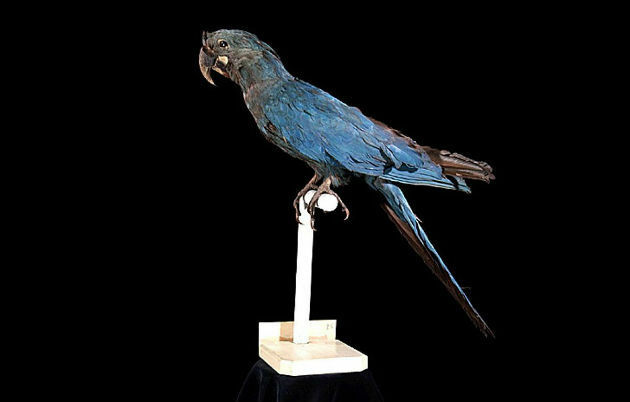

The little hyacinth macaw (Anodorhynchus glaucus) is an extinct bird in Brazilian territory and in captivity. In Brazil, the last visualization of the species took place more than 80 years ago.
Naturally, the species was not common in its range, which encompassed northern Argentina, southern Paraguay, northeastern Uruguay and southern Brazil. Thus, it became more vulnerable to extinction due to illegal hunting and destruction of its habitat.
8. big red breast

The big red breast (sturnella defilippii) is a bird that is endangered in Brazilian territory. In Brazil, the species was last seen in the 70s.
However, it has been seen more recently in Uruguay, Paraguay and Argentina, where populations are small and critically threatened.



