Genetics is an important branch of biology, responsible for understanding the mechanisms of heredity or biological inheritance.
Test your knowledge of the subject by solving the questions below:
question 1
(Unimep - RJ) A man has the genotype Aa Bb CC dd and his wife has the genotype aa Bb cc Dd. What is the probability of this couple having a male child and carrying the bb genes?
a) 1/4
b) 1/8
c) 1/2
d) 3/64
e) none of the above
Correct alternative: b) 1/8.
To answer this question, it is necessary to cross-reference the information provided about the father and the mother.
First, let's find out how likely the individual is to carry the bb genes.
For this, we will use the Punnett chart to find the result of the crossing.
| B | B | |
| B | BB | baby |
| B | baby | baby |
Note that of the four possible outcomes, only one of them has the bb genes. So the probability is one in four, which we can represent as 1/4.
Now, we must find out the probability of the child being male.
With the chromosomes of female XX and male XY, we will again use the Punnett framework to cross-reference the information.
| X | X | |
| X | XX | XX |
| Y | XY | XY |
Thus, of the four possibilities in the crossover, two can be male. We represent the result of interest as 2/4, which simplifying by 2 becomes 1/2.
As we saw in the statement, we need to find the probability of the child being male and carrying the bb genes, that is, the two characteristics must occur simultaneously.
According to the “and” rule we must multiply the probabilities of the two events.
Therefore, the probability of this couple having a male child carrying the bb genes is 1/8.
question 2
About gene recombination, it is correct to state that:
a) Gene recombination can be homologous or heterologous.
b) The main difference between the types of recombination is that they occur at different stages of mitosis.
c) Gene recombination is classified into homologous and non-homologous.
d) While one type of recombination allows for variability, the other type has limitations.
Correct alternative: c) Gene recombination is classified into homologous and non-homologous.
The types of gene recombination are: homologous and non-homologous.
The main difference between the types is that while homologous recombination occurs between DNA sequences that are identical or have high similarity, the non-homologous recombination occurs between sequences that are not similar.
question 3
(UERJ) It is known that the hereditary transmission of the color of flowers known as calla lily occurs through simple Mendelian inheritance, with complete dominance. In an experimental crossing of red calla lilies, a very numerous first generation - F1 - was obtained, in a ratio of 3 red offspring for each white (3:1). Analyzing the F1 genotype, the scientists found that only one in three red offspring was homozygous for this trait.
According to these data, it can be stated that the F1 genotypic production of this experimental cross was:
a) 4 Aa
b) 2 Aa: 2 Aa
c) 3 AA: 1 Aa
d) 1 AA: 2 Aa: 1 Aa
e) 1 AA: 1 Aa: 1 Aa
Correct alternative: d) 1 AA: 2 Aa: 1 aa.
According to the utterance data, color transmission occurs by complete dominance, that is, we can say that the A allele determines the red color in AA or Aa and only the individual aa has a color White.
The crossing is carried out between two red calla lilies with a proportion of 3 red descendants for each white, we can understand this information as three individuals have the dominant A and only one is recessive aa.
To have the aa homozygote, the crossing must have been carried out with a heterozygous Aa couple and one gene is inherited from the father and the other from the mother.
Let's look at this crossover with Punnett's painting.
| THE | The | |
| THE | AA | yy |
| The | yy | yy |
Thus, it can be stated that the F1 genotypic production of this experimental cross was: AA: 2 Aa: 1 aa.
question 4
(Fatec) Pairs of genes, with independent segregation, can act together to determine the same phenotypic characteristic. This phenomenon is known as:
a) gene interaction
b) epistasis
c) polygeny
d) complete dominance
Correct alternative: a) gene interaction.
Gene interaction is responsible for the emergence of a certain phenotype, that is, a characteristic visible, when two or more genes located or not on the same chromosome collaborate for a given feature.
question 5
(Mack) Achondroplasia is a type of dwarfism in which the head and trunk are normal, but arms and legs are very short. It is conditioned by a dominant gene which, in homozygosity, causes death before birth. Normal individuals are recessive and those affected are heterozygous. The probability of an achondroplastic couple having a normal female child is:
a) 1/6
b) 1/8
c) 2/5
d) 1/2
e) 1/4
Correct alternative: a) 1/6.
According to the statement, achondroplasia is conditioned by a dominant gene that, in homozygosis, causes death before birth. Knowing that normal individuals are recessive and those affected are heterozygous and taking "A" as dominant and "a" as recessive, we can deduce that:
- aa: normal individual;
- AA: individual dies;
- Aa: achondroplastic individual.
If the couple is achondroplastic then both are heterozygous. See the probability of their descendants below.
| THE | The | |
| THE | AA | yy |
| The | yy | yy |
As a lethal gene appears in probability, then this should be disregarded. Therefore, the probability of the individual being normal is 1/3.
To find out the probability of being female, we will use Punnett's chart again.
| X | X | |
| X | XX | XX |
| Y | XY | XY |
There is a 2/4 probability of being female, which we simplify to 1/2.
Therefore, the probability of an achondroplastic couple having a normal female child is:
question 6
Gene mutation differs from gene recombination in that
a) while the mutation corresponds to an inherited change in DNA, recombination creates new genes.
b) while the mutation corresponds to an inherited change in DNA, recombination takes place by mixing genes with beings of the same species.
c) The mutation is spontaneous and recombination is induced.
d) Mutation is a secondary source of variation, while recombination is a primary source.
Correct alternative: b) while the mutation corresponds to an inherited change in the DNA, the recombination takes place by mixing genes with beings of the same species.
Both media are responsible for genetic variability.
The mutation is a primary source for heritable variation and can occur spontaneously, such as by replication errors, or by the influence of external factors, such as UV light.
Gene recombination corresponds to a mixture of genes during sexual reproduction and, through this, is able to increase variability.
question 7
(Unifesp) Plant A and plant B, with yellow peas and of unknown genotypes, were crossed with plants C that produce green peas. The A x C cross originated 100% plants with yellow peas and the B x C cross resulted in 50% plants with yellow peas and 50% green. The genotypes of plants A, B and C are, respectively:
a) Vv, vv, VV
b) VV, vv, Vv
c) VV, Vv, vv
d) vv, vv, vv
e) vv, vv, vv
Correct alternative: c) VV, Vv, vv.
According to the statement, we have:
- Plant A: yellow peas
- Plant B: yellow peas
- Plant C: green peas
Crossings:
- H x C 100% yellow peas
- A x B 50% yellow peas and 50% green
From this, we can deduce that the dominant genotype is yellow peas, since it originated 100% in a cross and that plant A is homozygous dominant (VV). From this, we came to the conclusion that green is a recessive trait and plant C is vv.
| V | V | |
| v | Vv | Vv |
| v | Vv | Vv |
Note that the crossing of plant A (VV) with plant C (vv) formed 100% plants with yellow peas.
| V | v | |
| v | Vv | vv |
| v | Vv | vv |
Note that the result is 50% plants with yellow peas (Vv) and 50% plants with green peas (vv).
Therefore, the genotypes of plants A, B and C are, respectively: VV, Vv, vv.
question 8
Of the following alternatives which does NOT have a type of natural selection.
a) Directional selection
b) Stabilizer selection
c) Disruptive selection
d) Dimensional selection
Correct alternative: d) Dimensional selection.
Natural selection is an evolutionary mechanism based on advantageous characteristics for adaptation and survival in an environment, and it can take three forms:
- Directional selection: occurs with extreme phenotypes;
- Stabilizing selection: occurs with intermediate phenotypes;
- Disruptive selection: occurs with more than one extreme phenotype.
question 9
(UFPR) In the genealogy below, individuals marked with black have an anomaly determined by a dominant gene.
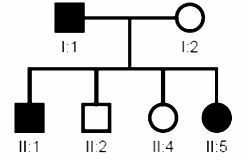
Analyzing this genealogy, it is correct to state:
a) Only individuals I: 1; II: 1 and II: 5 are heterozygotes.
b) All affected individuals are homozygous.
c) All unaffected individuals are heterozygous.
d) Only individual I: 1 is heterozygous.
e) Only individuals I: 1 and I: 2 are homozygous.
Correct alternative: a) Only individuals I: 1; II: 1 and II: 5 are heterozygotes.
As individuals marked with black have a dominant anomaly, we can deduce that those who are not marked are recessive homozygotes:
- I: 1 D_
- I: 2 dd
- II: 1 D_
- II: 2 dd
- II: 4 dd
- II: 5 D_
Since individual D_ is able to produce children without the anomaly, then he is heterozygous (Dd). Watch:
| D | d | |
| d | dd | dd |
| d | dd | dd |
Analyzing the data, we came to the conclusion that only individuals I: 1; II: 1 and II: 5 are heterozygotes.
question 10
(UFC) Gregor Mendel, considered the father or founder of classical genetics, carried out experiments with pea-producing plants. To demonstrate his hypotheses, Mendel used this type of vegetable because:
a) the androco and the gynoecium are present in the same flower, which facilitates the occurrence of self-fertilization.
b) the seed has only two cotyledons, which absorb food reserves for embryo nutrition and pea development.
c) the anatomical characteristics of its flowers facilitate cross-fertilization and thus enable the observation of pure genetic characteristics.
d) the pollen grains are transferred to the stigma of the same strobile, since the modified leaves are located very close to each other.
e) the number of descendants per generation is small and the generations are long, which facilitates the observation of flower and seed characteristics.
Correct alternative: a) the androco and the gynoecium are present in the same flower, which facilitates the occurrence of self-fertilization.
The flower of a plant is considered its reproductive structure. The set of stamens in a flower is also called the male structure, whereas the set of carpels corresponds to the female part of the flower.
The occurrence of androco and gynoecium in the same flower facilitates self-fertilization.
question 11
(UFRN) In peas, yellow is dominant over green. From the crossing of heterozygotes, 720 offspring were born. Check the option whose number corresponds to the number of yellow descendants.
a) 360
b) 540
c) 180
d) 720
Correct alternative: b) 540.
If the yellow color is dominant, then at least one of the genes is dominant (AA or Aa). In relation to green, we can say that it is recessive (aa).
Crossing heterozygotes can be done like this:
| THE | The | |
| THE | AA | yy |
| The | yy | yy |
Note that the dominant gene (A) appears in 3 of the possibilities, so the probability of the yellow color is 3/4.
If the total descendants is 720, by performing a simple rule of three, we find out how many yellow descendants they had.
So there are 540 yellow descendants.
question 12
(Enem) The pedigree shows the incidence of a genetic anomaly in a family group.
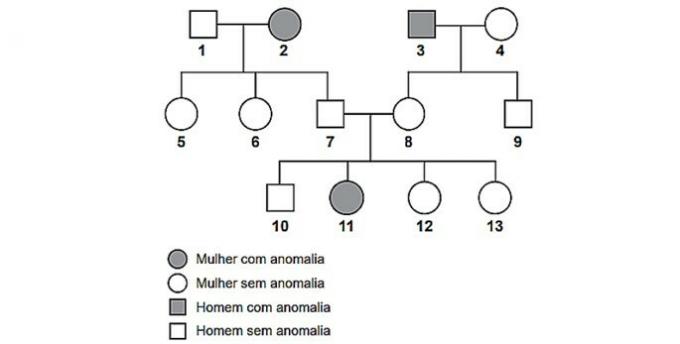
The individual represented by the number 10, concerned with transmitting the allele for the genetic anomaly to their children, calculates that the probability of him carrying this allele is:
a) 0%
b) 25%
c) 50%
d) 67%
e) 75%
Correct alternative: d) 67%.
If we look at the couple (7 and 8) we will see that they are the same and that they only produced a different child (11). Therefore, it can be deduced that the couple is equal, heterozygous, and a child is recessive.
| THE | The | |
| THE | AA | yy |
| The | yy | yy |
Excluding the possibility that he does not have the anomaly (aa), then the probability of having the allele (Aa) is 2/3.
question 13
(PUC - RIO) A recessive genetic characteristic present on the Y chromosome is:
a) it can be inherited from the father or mother by male and female descendants.
b) can only be inherited from the father by his male descendants.
c) can only be inherited from the father by his female descendants.
d) can only be inherited from the mother by her male descendants.
e) can only be inherited from the mother by her female descendants.
Correct alternative: b) can only be inherited from the father by his male descendants.
As women have two XX chromosomes, then inheritance can only be inherited from the father and male descendants, since only men have the Y chromosome, that is, it is XY.
question 14
(UFF) The pedigree below shows the occurrence of a certain anomaly in a family.
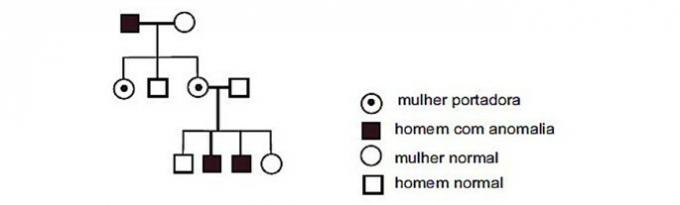
The condition shown in the pedigree is inherited as a characteristic:
a) autosomal dominant.
b) autosomal recessive.
c) Y-linked recessive.
d) X-linked recessive.
e) X-linked dominant.
Correct alternative: d) X-linked recessive.
As a woman has XX chromosomes and a man has XY chromosomes, the anomaly is probably related to an X chromosome in the woman.
This type of case is what happens in color blindness, as the anomaly is associated with a recessive gene (Xd). Watch.
| XD | Y | |
| XD | XDXD | XDY |
| Xd | XDXd | XdY |
Note that the mother carries the gene but does not have the anomaly. We can say then that your genotype is XDXd.
Their male offspring then have the disease, as it is linked to the mother's X chromosome and lack the dominant allele that would be able to impede the gene's expression. So they are XdY.
question 15
(Enem) In an experiment, a set of plants was prepared by cloning technique from an original plant that had green leaves. This set was divided into two groups, which were treated identically, with the exception of the lighting conditions, with one group exposed to natural sunlight cycles and the other kept in the dark. After a few days, it was observed that the group exposed to light had green leaves like the original plant and the group cultivated in the dark had yellowish leaves.
At the end of the experiment, the two groups of plants presented:
a) genotypes and identical phenotypes.
b) the identical genotypes and the different phenotypes.
c) differences in genotypes and phenotypes.
d) the same phenotype and only two different genotypes.
e) the same phenotype and wide variety of genotypes.
Correct alternative: b) identical genotypes and different phenotypes.
While genotypes are associated with genetic constitution, phenotypes are related to external, morphological and physiological characteristics.
As a difference in color was observed for plants exposed or not to light, then they have different phenotypes.
The genotypes are identical, as they are clones.
Want to learn more about Genetics? Read too:
- Introduction to Genetics
- Mendel's Laws
- Phenotype and Genotype

