As well as the halogenation and nitration reactions presented in the texts "Organic Halogenation Reactions" and "Organic Nitration Reactions”, the sulfonation reactions are organic substitution reactions.
In these reactions, one or more hydrogen atoms attached to one of the carbon chain or aromatic ring carbons are replaced by one or more sulfonic groups (─ SO3H) of concentrated sulfuric acid (H2ONLY4).
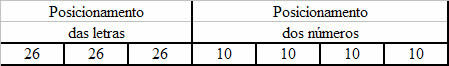
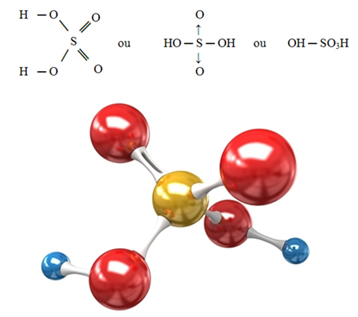
The structural formula of sulfuric acid can be represented in the following ways:
This type of reaction normally occurs in alkanes and aromatics.
In the case of alkanes, this reaction takes place hot and only those with more than 6 carbons react with the acid sulfuric acid, because if it has less carbon, the molar mass of the alkane will be low and a very violent oxidation will occur, destroying the alkane.
See some examples of monosulfonation reactions:
1st Example- Monosulfonation in an alkane (hexane):
H ONLY3H
│ │
H3C CH2 ─ CH─ CH2 CH2 CH3 + HO ─ SO3H →H2O + H3C CH2 ─ C*H─ CH2 CH2 CH3 +
ONLY3H SO3H
│ │
+ H3C─C*H─CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3 + H2C* ─ CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3
A mixture of compounds is formed.
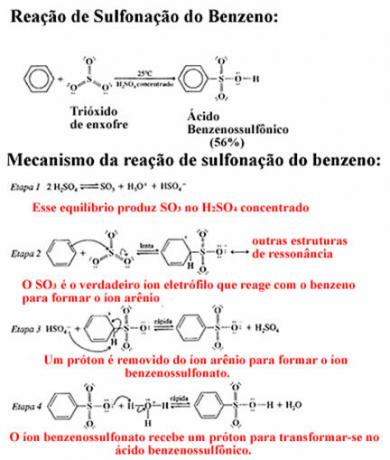
2nd Example- Benzene monosulfonation: In this case, benzene reacts with fuming sulfuric acid, that is, it contains added sulfur trioxide (SO3). If we use pure sulfuric acid, the reaction will proceed, however, very slowly.
Next we have the benzene sulphonation reaction giving rise to benzene sulphonic acid. In the mechanism of this reaction it can be seen that all steps are in chemical equilibrium and it takes place at room temperature:
In the case of other aromatics (benzene derivatives) there is also the substitution of one of the hydrogen atoms directly linked to the benzene ring. However, it is necessary to look at which functional group is already attached to the ring to determine the location of the next replacement. To understand how this is done read the texts "Steering Radicals in the Benzene Ring" and "Electronic effects of meta and ortho-to-directors radicals”.
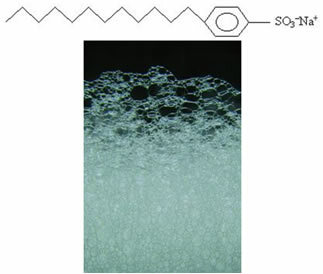
One of the applications of the compounds obtained in sulfonation reactions is that some salts such as those used in detergents are derived from these sulfonic acids. They have a long chain, and an example is p. sodium dodecylsulfonate:
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/reacoes-sulfonacao.htm