THE gametogenesis it is the process of formation of gametes, with the genetic characteristics that will be transmitted to the descendants of a species.
In human gametogenesis, for example, the male gamete is called sperm and its development occurs through the spermatogenesis. The female gamete, on the other hand, is called an egg and the emergence occurs through the oogenesis (or ovulogenesis).
What is gametogenesis?
Gametogenesis is the process of production of gametes, which will give rise to living beings. The formation of gametes is part of sexual reproduction and after this process fertilization occurs, which corresponds to the union of gametes.
Gametogenesis involves two types of cell division: mitosis, which increases the number of mother cells, and meiosis, which produces daughter cells with half the chromosomes of the parent cells.
The specialized organs of the reproductive system where gamete formation occurs are the sexual glands, called the gonads: the ovaries, which form the eggs inside, and the testes, which originate sperm in the tubules. seminifers.
In biology, the formation of gametes is studied in Embryology. This process is important, as it is part of the species' ability to continue.
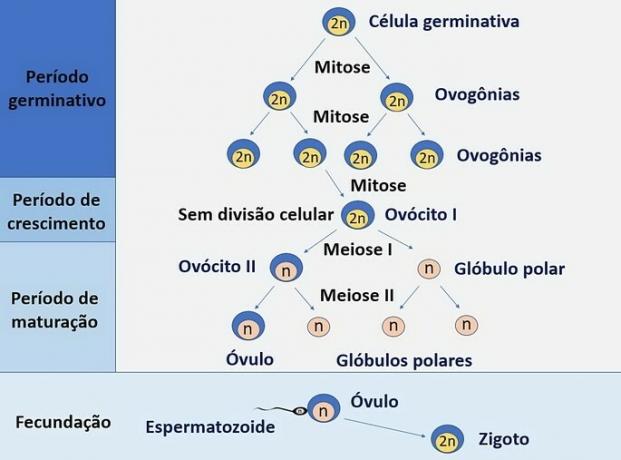
Oogenesis: female gametogenesis
Oogenesis is the process of development and maturation of female germ cells, called eggs. Unlike spermatogenesis, oogenesis is only complete if there is fertilization.
The sperm is responsible for starting the fertilization process, ending meiosis and the egg is formed.
Stages of oogenesis
- multiplication phase
- Growth stage
- maturation phase
At multiplication phase the germ cells, located in Graff's ovarian follicles, undergo mitosis and multiply, forming oogonias that will also undergo successive mitotic divisions.
At growth stage the oogonia increase in size and go through the meiosis process, which occurs until prophase I, for the formation of oocytes I.
THE maturation stage it is marked by the end of meiosis in oocyte I and will give rise to two cells: an oocyte II, released at ovulation, and a polar globule.
With the fertilization the sperm initiates the process of meiosis II, by entering oocyte II, and produces an egg, a cell larger than the sperm and without mobility. With the fusion of the genetic material of the egg and the sperm, the zygote is produced.
The development of the zygote is marked by a process of cell multiplication and reproduction of embryonic cells.
Therefore, oogenesis, together with the fertilization process, causes an egg and three polar bodies to emerge from each oogonia. Remember that the egg is functional and in some cases the polar globules do not form or soon degenerate.
Also read about mitosis and meiosis.
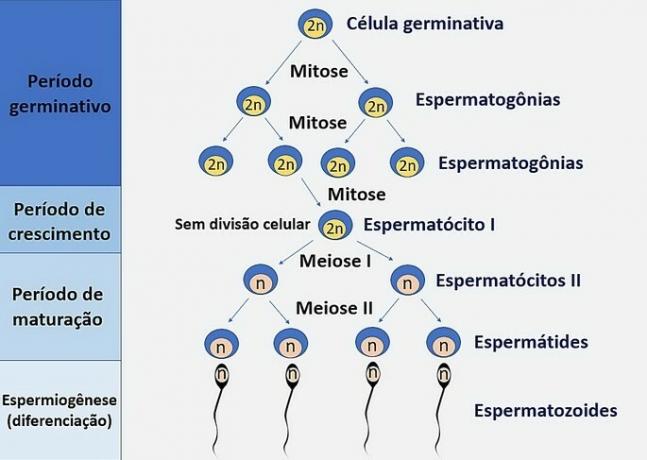
Spermatogenesis: male gametogenesis
THE spermatogenesis it is the process of development and maturation of sperm. The beginning of this process occurs at puberty, between 10 and 16 years of age, and continues throughout life.
In men, sperm are produced in the testes, specifically in the seminiferous tubes, with approximately 200 million sperm a day.
Stages of spermatogenesis
- multiplication phase
- Growth stage
- maturation phase
- spermiogenesis
Spermatogenesis starts with the multiplication phase, where germ cells give rise to spermatogonia, diploid cells located in the seminiferous tubules, which multiply through mitosis. Each diploid cell (2n) produces two cells with the same number of chromosomes.
THE growth stage it is marked by an increase in cell volume and the occurrence of a second mitosis, producing the primary spermatocytes (I spermatocytes), which are also diploid (2n) cells.
At maturation stage the first meiosis occurs and the I spermatocytes give rise to two haploid cells (n), that is, with half the number of chromosomes. The second meiosis that occurs at this stage produces four haploid (n) cells, called spermatids.
THE spermiogenesis, also called the differentiation period, is the final stage of spermatogenesis and is where the transformation of spermatids into sperm.
know more about gametes and gametogenesis.
Gametogenesis Exercises
question 1
(Fuvest) In human gametogenesis,
a) spermatocytes and secondary oocytes, formed at the end of the first meiotic division, have an amount of DNA equal to that of spermatogonia and oogonia, respectively.
b) haploid spermatids, formed at the end of the second meiotic division, undergo mitotic division in the ripening process to originate sperm.
c) spermatogonia and oogonia divide by mitosis and originate, respectively, spermatocytes and primary oocytes, which enter meiotic division from puberty onwards.
d) oogonia divide by mitosis and give rise to primary oocytes, which enter meiosis soon after birth.
e) spermatocytes and primary oocytes give rise to the same number of gametes at the end of the second meiotic division.
Correct alternative: a) spermatocytes and secondary oocytes, formed at the end of the first meiotic division, have an amount of DNA equal to that of spermatogonia and oogonia, respectively.
Meiosis gives rise to spermatocytes and oocytes. This type of cell division gives rise to cells with half the chromosomes of the mother cell, but as they are duplicated, then they have the same amount of DNA as spermatogonia and oogonia.
Therefore, if in spermatogonia and oogonia there are “2n” in spermatocytes and oocytes, there will be “n” and “n”.
question 2
(Unir-RO) Comparing ovulogenesis (I) with spermatogenesis (II), all of the alternatives below are correct, except:
a) In both processes, meiosis occurs.
b) Both are important to keep the number of chromosomes typical of each species constant.
c) I occurs in the ovaries and II in the testes.
d) There is greater production of gametes in II than in I.
e) In I and II, the cells formed are diploid.
Correct alternative: e) In I and II, the cells formed are diploid.
Spermatogenesis ends with the formation of four haploid cells (n), which will develop into sperm (n). Likewise, upon completion of meiosis in ovulogenesis, haploid cells, eggs (n) and polar cells (n), are formed.
Fertilization is then the result of the union of the female (n) and male (n) gametes.
question 3
(UFMA) Regarding human gametogenesis, it is correct to state that:
a) Each oocyte I produces 4 oocytes II.
b) Ovogonias and primary oocytes are formed throughout a woman's life.
c) Spermatogonia are formed only during intrauterine life.
d) Each I spermatocyte produces one sperm.
e) Ovulogenesis is only completed if oocyte II is fertilized.
Correct alternative: e) Ovulogenesis is only completed if oocyte II is fertilized.
The first meiotic division in ovulogenesis gives rise to oocyte II and the primary polar globule. The second meiotic division occurs with oocyte II, until metaphase II stage, when it is released through fertilization.
Fertilization, union of the female (n) and male (n) gametes through sperm penetration will cause an egg to be formed, concluding ovulogenesis.
Get more knowledge with the contents:
- Asexual and sexual reproduction
- male reproductive system
- female reproductive system
- Exercises on the female and male reproductive system