The lesson plan is a document prepared by the teacher to define the theme of the lesson, its objective, what exactly it will be taught, the methodology to be used and the assessment to be used to analyze the assimilation of what was taught, among other things.
Check out a step by step on how to prepare a lesson plan, see a model and see examples of ready documents.
How to make a lesson plan
Through the lesson plan, the teacher must make a detailed reflection on the topic, and can identify, for example, points where students may have difficulties and how to solve any problems.
See a step-by-step guide to putting together a lesson plan.
1. Reflect on the target audience
Before starting to write the lesson plan, the teacher should reflect on his target audience: the students.
Any strategy adopted to approach a topic will be much more effective if directed to the reality of this audience; what works for one class may not work for another.
During this reflection, the teacher must consider a contextualization that includes, for example, cultural, economic, physical, social issues, etc.
2. Choose the topic of the lesson
Based on the teaching plan, planning that involves teaching tasks and objectives for a full academic year, the teacher must choose a topic.
The theme is the definition of what will be covered in the class; something very specific within a discipline, and which will be broken down into content in detail.
In a Portuguese class, for example, "verbal voices" can be a class topic.
3. Define the goal to be achieved
The goal is what the teacher wants students to learn from the lesson. In a Portuguese class whose theme is "verbal voices", for example, the teacher can define as objectives:
- Students must know how to differentiate the three verbal voices: passive voice, active voice and reflective voice.
- Students must be able to convert between voices. Example: passing a phrase from active to passive voice.
It is important to note that there is no limit on objectives per lesson plan.
4. Define the content to be covered
Content is an item in the lesson plan that is directly related to the topic, as it is subordinate to it, and to the purpose of the lesson.
Through the exposure and exploration of contents, the teacher conducts the students' learning in order to achieve the goals that they predefined in their lesson planning.
For the topic "verbal voices", for example, the teacher can define as content the concepts of active voice, passive voice and reflective voice.
5. Decide the duration of the class
The duration of the exploration of a given topic is at the discretion of the teacher, taking into account the syllabus that he must follow.
It is not mandatory that each topic be explored in a single class. If so, the teacher can, for example, allocate two or more classes for the exploration of certain content.
This decision is related to factors such as the annual school planning and the fixation on what was taught. In case the teacher concludes that a single class will not be enough for the class to be enlightened, he can allocate two or three classes to explore a certain subject.
6. Select teaching resources
Didactic resources are support materials that help the teacher in a pedagogical way, facilitating the development of the class.
Such resources are also used to motivate students and encourage their interest in the topic discussed.
Some examples of teaching resources:
- Eraser.
- DVD player.
- Poster.
- Computer.
- Film.
- Game.
- Map.
- Song.
- Projector.
- Black or white board.
- Reporting.
- Television.
Depending on the discipline, the teacher may feel the need to select more specific resources. A chemistry teacher, for example, may need a microscope or a test tube.
7. Define the methodology to be used
The methodology consists of the methods chosen by the teacher to guide the student's learning, that is, the paths he will choose to conduct the class.
This part of the class is of fundamental importance, as the strategy used by the teacher can either work as a great motivating agent or totally discourage the student.
In certain subjects, an expository class, for example, may work better than a class conducted through exercises, and vice versa.
Some examples of methodology:
- Applying exercises.
- Expository class.
- Dramatization.
- Case study.
- Directed Study.
- Text Study.
- Conceitual map.
- Panel.
- Field research.
- Seminar.
- Problems solution.
8. Choose how to assess student learning
The conclusion of a class takes place with the evaluation stage, when the teacher will consider the actual assimilation of the content by the student.
This step is also intended to assess whether the objectives predefined by the teacher were achieved.
Contrary to what many people think, applying a test with a grade given to the student is not the only way to do this validation. In fact, there are several ways to perform such an analysis.
Some evaluation examples:
- Student participation in the classroom.
- Written test.
- Oral test.
- Fixation exercises.
- Work done in the classroom.
- Homework.
9. Inform the references used
Finally, the teacher must indicate the references used as a source for the preparation of their lesson plan.
It is important to note that the term "references" does not only cover books and other printed materials.
In an era where technology and digital resources are increasingly present in education, it is natural that educators consult online content as an asset in preparing their classes.
Therefore, websites, documents and other online content used as a source can also be indicated as references.
Lesson Plan Template
Now that you've gone through the step-by-step instructions for creating a lesson plan, see below for a template that can be applied to different school levels.
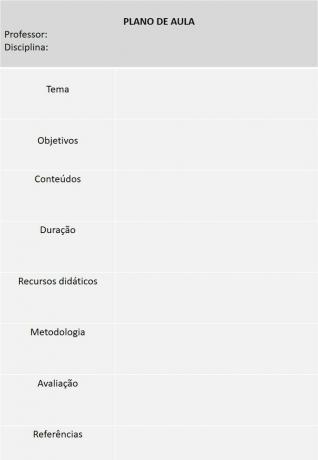
Examples of ready-made lesson plans
See examples of ready-made lesson plans, aimed at different school segments.
Early Childhood Lesson Plan
Oral and written language lesson plan
Lesson Plan for Elementary School
Portuguese lesson plan
High School Lesson Plan
math lesson plan
Also check out the contents below:
- remote lesson plan
- education in Brazil
- LDB (updated in 2019)
- Activities about verbs
- Portuguese activities
- literacy activities
- Activities for children's education
- Math Activities for Early Childhood Education
- 4th year math activities
- Physical Education Activities
- Dynamics for the first day of class
- Cooperative Games: what they are and examples


